SN54ACT3632
512 × 36 × 2
CLOCKED BIDIRECTIONAL FIRST-IN, FIRST-OUT MEMORY
SGBS310A – SEPTEMBER 1996 – REVISED APRIL 1998
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME
I/O DESCRIPTION
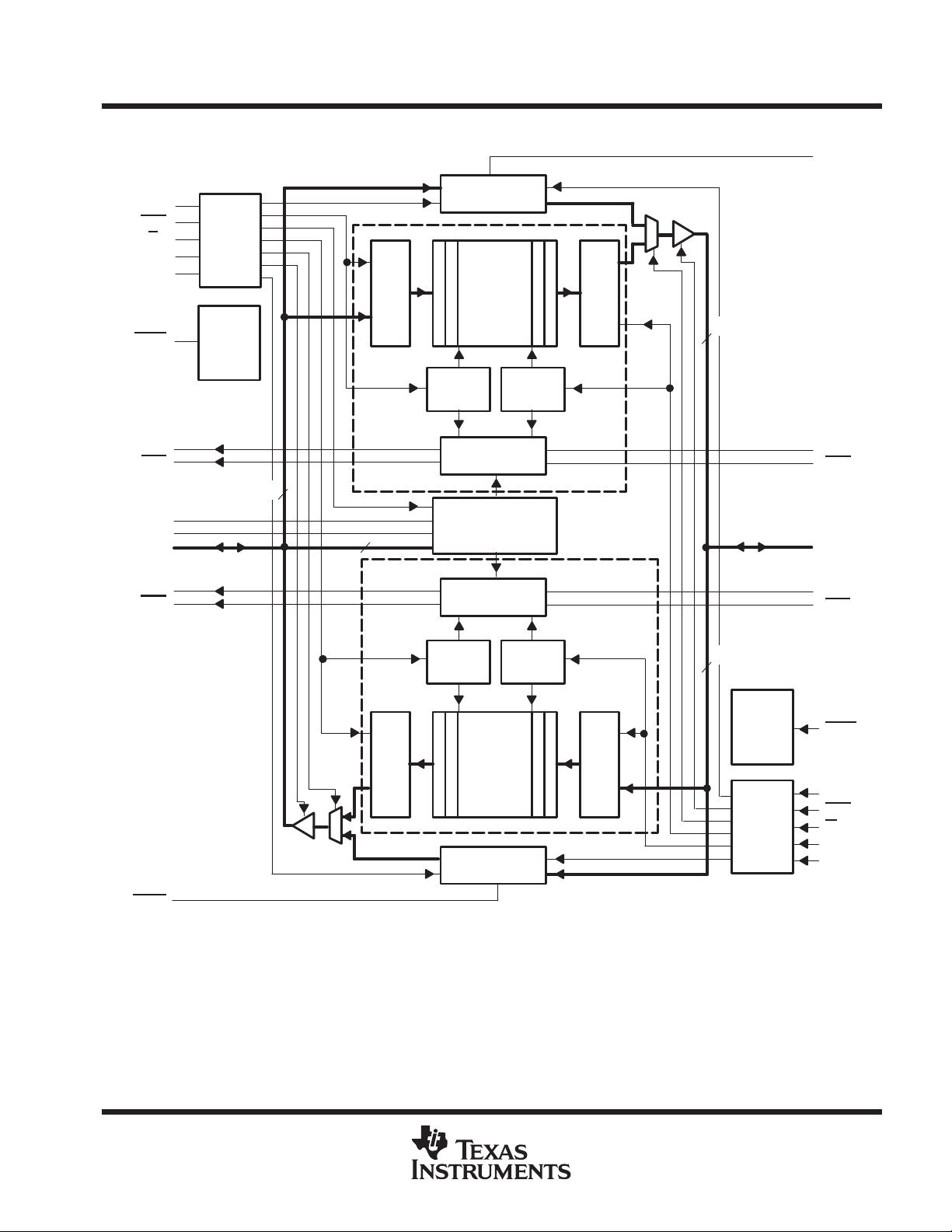
A0–A35 I/O Port-A data. The 36-bit bidirectional data port for side A.
AEA
O
(port A)
Port-A almost-empty flag. Programmable flag synchronized to CLKA. AEA is low when the number of words in FIFO2
is less than or equal to the value in the almost-empty A offset register, X2.
AEB
O
(port B)
Port-B almost-empty flag. Programmable flag synchronized to CLKB. AEB is low when the number of words in FIFO1
is less than or equal to the value in the almost-empty B offset register, X1.
AFA
O
(port A)
Port-A almost-full flag. Programmable flag synchronized to CLKA. AFA is low when the number of empty locations
in FIFO1 is less than or equal to the value in the almost-full A offset register, Y1.
AFB
O
(port B)
Port-B almost-full flag. Programmable flag synchronized to CLKB. AFB is low when the number of empty locations
in FIFO2 is less than or equal to the value in the almost-full B offset register, Y2.
B0–B35 I/O Port-B data. The 36-bit bidirectional data port for side B.
CLKA I
Port-A clock. CLKA is a continuous clock that synchronizes all data transfers through port A and can be
asynchronous or coincident to CLKB. IRA, ORA, AFA
, and AEA are all synchronized to the low-to-high transition of
CLKA.
CLKB I
Port-B clock. CLKB is a continuous clock that synchronizes all data transfers through port B and can be
asynchronous or coincident to CLKA. IRB, ORB, AFB
, and AEB are synchronized to the low-to-high transition of
CLKB.
CSA
I
Port-A chip select. CSA must be low to enable a low-to-high transition of CLKA to read or write data on port A. The
A0–A35 outputs are in the high-impedance state when CSA
is high.
CSB
I
Port-B chip select. CSB must be low to enable a low-to-high transition of CLKB to read or write data on port B. The
B0–B35 outputs are in the high-impedance state when CSB
is high.
ENA I Port-A enable. ENA must be high to enable a low-to-high transition of CLKA to read or write data on port A.
ENB I Port-B enable. ENB must be high to enable a low-to-high transition of CLKB to read or write data on port B.
FS1, FS0 I
Flag-offset selects. The low-to-high transition of a FIFO reset input latches the values of FS0 and FS1. If either FS0
or FS1 is high when a reset input goes high, one of three preset values is selected as the offset for the FIFO almost-full
and almost-empty flags. If both FIFOs are reset simultaneously and both FS0 and FS1 are low when RST1
and RST2
go high, the first four writes to FIFO1 program the almost-full and almost-empty offsets for both FIFOs.
IRA
O
(port A)
Input-ready flag. IRA is synchronized to the low-to-high transition of CLKA. When IRA is low, FIFO1 is full and writes
to its array are disabled. IRA is set low when FIFO1 is reset and is set high on the second low-to-high transition of
CLKA after reset.
IRB
O
(port B)
Input-ready flag. IRB is synchronized to the low-to-high transition of CLKB. When IRB is low, FIFO2 is full and writes
to its array are disabled. IRB is set low when FIFO2 is reset and is set high on the second low-to-high transition of
CLKB after reset.
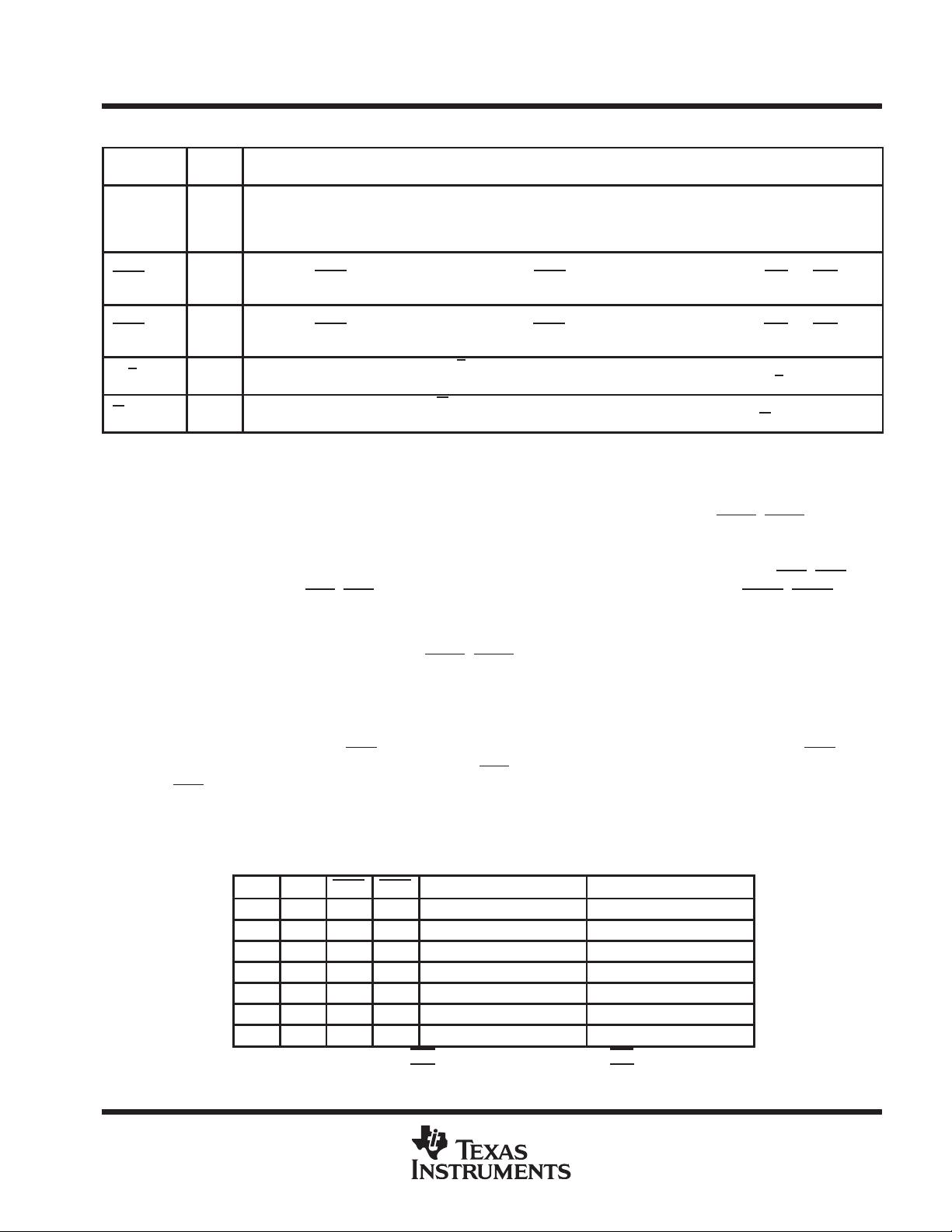
MBA I
Port-A mailbox select. A high level on MBA chooses a mailbox register for a port-A read or write operation. When
the A0–A35 outputs are active, a high level on MBA selects data from the mail2 register for output and a low level
selects FIFO2 output-register data for output.
MBB I
Port-B mailbox select. A high level on MBB chooses a mailbox register for a port-B read or write operation. When
the B0–B35 outputs are active, a high level on MBB selects data from the mail1 register for output and a low level
selects FIFO1 output-register data for output.
MBF1
O
Mail1 register flag. MBF1 is set low by the low-to-high transition of CLKA that writes data to the mail1 register. Writes
to the mail1 register are inhibited while MBF1
is low. MBF1 is set high by a low-to-high transition of CLKB when a
port-B read is selected and MBB is high. MBF1
is set high when FIFO1 is reset.
MBF2
O
Mail2 register flag. MBF2 is set low by the low-to-high transition of CLKB that writes data to the mail2 register. Writes
to the mail2 register are inhibited while MBF2
is low. MBF2 is set high by a low-to-high transition of CLKA when a
port-A read is selected and MBA is high. MBF2
also is set high when FIFO2 is reset.
ORA
O
(port A)
Output-ready flag. ORA is synchronized to the low-to-high transition of CLKA. When ORA is low, FIFO2 is empty
and reads from its memory are disabled. Ready data is present on the output register of FIFO2 when ORA is high.
ORA is forced low when FIFO2 is reset and goes high on the third low-to-high transition of CLKA after a word is loaded
to empty memory.



 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功