
DS100BR210
SNLS348E –OCTOBER 2011 –REVISED JANUARY 2015
www.ti.com
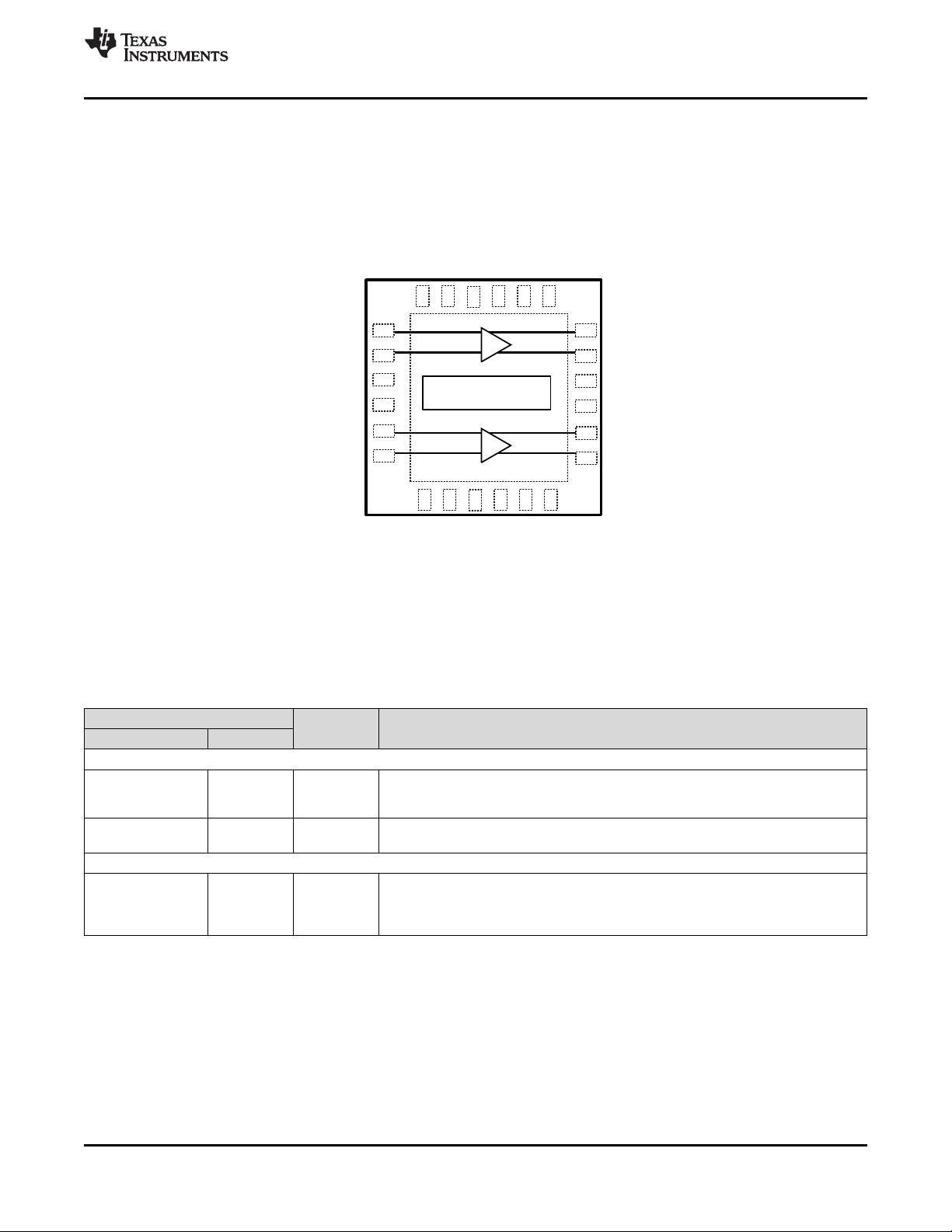
Pin Functions
(1)
(continued)
PIN
I/O, TYPE DESCRIPTION
NAME NUMBER
ENSMB = Float or 1 (SMBus MODES)
I, 2-LEVEL, Clock output when loading EEPROM configuration, reverting to SMBus clock input
LVCMOS, when EEPROM load is complete (ALL_DONE = 0).
SCL 5
O, Open External 2 kΩ to 5 kΩ pull-up resistor to VDD (2.5 V mode) or VIN (3.3 V mode)
Drain recommended as per SMBus interface standards
(2)
I, 2-LEVEL, In both SMBus Modes, this pin is the SMBus data I/O. Data input or open drain output.
LVCMOS, External 2 kΩ to 5 kΩ pull-up resistor to VDD (2.5 V mode) or VIN (3.3 V mode)
SDA 4
O, Open recommended as per SMBus interface standards
(2)
Drain
ENSMB Master or Slave mode
I, 4-LEVEL, SMBus Slave Address Inputs. In SMBus mode, these pins are the user set SMBus
AD0-AD3 10, 9, 2, 1
LVCMOS slave address inputs. There are 16 addresses supported by these pins.
Pins must be tied Low or High when used to define the device SMBus address.
(3)
ENSMB = Float: When using SMBus Master Mode, a logic low on this pin starts the
load from the external EEPROM.
I, 2-LEVEL,
READEN 17 ENSMB = 1: When using SMBus Slave Mode, the VOD_SEL/READEN pin must be
LVCMOS
tied Low for the AD[3:0] to be active. If this pin is tied High or left floating, an address
of 0xB0 will be used for the DS100BR210.
When using an External EEPROM (ENSMB = Float), Valid Register Load Status
O, 2-LEVEL, Output
DONE 18
LVCMOS High = External EEPROM load failed or incomplete
Low = External EEPROM load passed
ENSMB = 0 (PIN MODE)
EQA[1:0] and EQB[1:0] control the level of equalization on the input pins. EQA[1:0]
controls the A channel, and EQB[1:0] controls the B channel. The pins are only active
EQA0, EQA1 10, 9 I, 4-LEVEL, when ENSMB = 0.
EQB0, EQB1 1, 2 LVCMOS When ENSMB = 1, the SMBus registers provide independent control of each channel,
and the EQB0/B1 pins are converted to SMBus AD2/AD3 inputs.
See Table 3 for additional information.
DEMA and DEMB control the level of de-emphasis for the output driver when in 10G
mode. DEMA controls the A channel, and DEMB controls the B channel. The pins are
I, 4-LEVEL, only active when ENSMB = 0.
DEMA, DEMB 4, 5
LVCMOS When ENSMB = 1, the SMBus registers provide independent control of each channel,
and the DEM pins are converted to SMBus SCL and SDA pins.
See Table 4 for additional information.
VOD Select
High = 10G-KR Mode (VOD = 1.1 Vpp or 1.3 Vpp)
I, 4-LEVEL, Float = (VOD = 1.0 Vpp)
VOD_SEL 17
LVCMOS 20 kΩ to GND = (VOD = 1.2 Vpp)
1 kΩ to GND = (VOD = 700 mVpp)
See for additional notes. See Table 2 for additional information.
Controls Device Mode of Operation
High= 10GbE Mode, Continuous Talk (Output Always On)
I, 4-LEVEL, Float = 10G-KR Mode, Slow OOB
MODE 18
LVCMOS 20 kΩ to GND = eSATA Mode, Fast OOB, Auto Low Power on 100 µs of inactivity. SD
stays active.
1 kΩ to GND = SAS Mode, Fast OOB
CONTROL PINS — BOTH PIN AND SMBus MODES (LVCMOS)
I, 2-LEVEL, High = OUTA Disabled, OUTB Disabled
TX_DIS 6
LVCMOS Low = OUTA and OUTB Enabled
O, Open Indicates Loss of Signal (Default is LOS on INA). Can be modified via SMBus
LOS 13
Drain registers.
The SD_TH pin controls LOS threshold setting
Assert (mVpp), Deassert (mVpp)
I, 4-LEVEL, High = 190 mVpp, 130 mVpp
SD_TH 14
LVCMOS Float = 180 mVpp, 110 mVpp (Default)
20 kΩ to GND = 160 mVpp, 100 mVpp
1 kΩ to GND = 210 mVpp, 150 mVpp
(4)
(2) SCL and SDA pins can be tied either to 3.3 V or 2.5 V, regardless of whether the device is operating in 2.5 V mode or 3.3 V mode.
(3) Setting VOD_SEL = High in SMBus Mode will force the SMBus Address = 0xB0
(4) Using values less than the default level can extend the time required to detect LOS and are not recommended.
4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2011–2015, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: DS100BR210


 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功