POWER DRIVER FOR STEPPER MOTORS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Hamburg, Germany
TMC5160 / TMC5160A DATASHEET
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
2-phase stepper motors from 1 to several 10A coil current
Motion Controller with SixPoint™
ramp
Step/Dir Interface with microstep interpolation MicroPlyer™
Voltage Range 8 … 60V DC
SPI & Single Wire UART
Encoder Interface and 2x Ref.-Switch Input
Highest Resolution 256 microsteps per full step
StealthChop2™ for quiet operation and smooth motion
Resonance Dampening for mid-range resonances
SpreadCycle™ highly dynamic motor control chopper
DcStep™ load dependent speed control
StallGuard2™ high precision sensorless motor load detection
CoolStep™ current control for energy savings up to 75%
Passive Braking and freewheeling mode
Full Protection & Diagnostics
Compact Size 7x7mm
2
(body) TQFP48 package / 8x8mm² QFN
APPLICATIONS
Robotics & Industrial Drives
Textile, Sewing Machines
Packing Machines
Factory & Lab Automation
High-speed 3D Printers
Liquid Handling
Medical
Office Automation
CCTV
ATM, Cash Recycler
Pumps and Valves
DESCRIPTION
The TMC5160 / TMC5160A is a high-power
stepper motor controller and driver IC
with serial communication interfaces. It
combines a flexible ramp generator for
automatic target positioning with indus-
tries’ most advanced stepper motor
driver. Using external transistors, highly
dynamic, high torque drives can be
realized. Based on TRINAMICs sophisti-
cated SpreadCycle and StealthChop
choppers, the driver ensures absolutely
noiseless operation combined with maxi-
mum efficiency and best motor torque.
High integration, high energy efficiency
and a small form factor enable miniatu-
rized and scalable systems for cost
effective solutions. The complete solution
reduces learning curve to a minimum
while giving best performance in class.
Universal high voltage controller/driver for two-phase bipolar stepper motor. StealthChop™ for quiet
movement. External MOSFETs for 1A to several 10A coil current. With Step/Dir Interface and SPI.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TMC5160/TMC5160A DATASHEET (Rev. 1.17 / 2022-MAY-25) 2
www.trinamic.com
APPLICATION EXAMPLES: HIGH VOLTAGE – MULTIPURPOSE USE
The TMC5160 scores with complete motion controlling features, powerful external MOSFET driver stages,
and high-quality current regulation. It offers a versatility that covers a wide spectrum of applications from
battery powered high efficiency systems up to embedded applications with 10A or more motor current per
coil. The TMC5160 contains the complete intelligence which is required to drive a motor. Receiving target
positions, the TMC5160 manages motor movement. Based on TRINAMICs unique features StallGuard2,
CoolStep, DcStep, SpreadCycle, and StealthChop, it optimizes drive performance. It trades off velocity vs.
motor torque, optimizes energy efficiency, smoothness of the drive, and noiselessness. The small form
factor of the TMC5160 keeps costs down and allows for miniaturized layouts. Extensive support at the chip,
board, and software levels enables rapid design cycles and fast time-to-market with competitive products.
High energy efficiency and reliability deliver cost savings in related systems such as power supplies and
cooling. For smaller designs, the software compatible integrated TMC5130 driver provides up to 1.4A of
motor current. The TMC5041 and TMC5072 family offer dual motor driving up to 1A, or single 2A.
CPU
TMC5160
High-Level
Interface
SPI
CPU
High-Level
Interface
TMC5160
TMC5160
More TMC5160 or TMC5130 or TMC5072
SPI or
UART
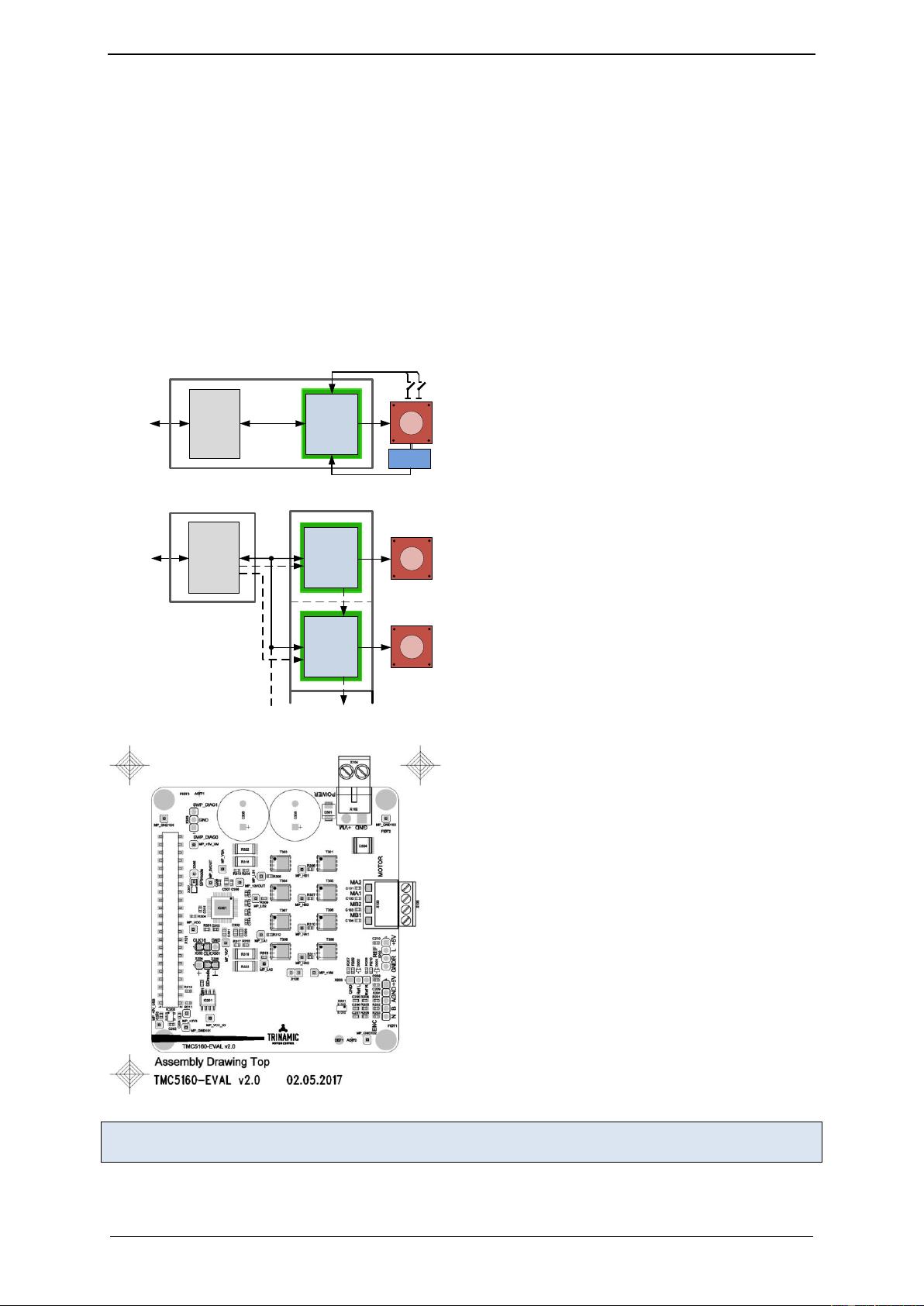
MINIATURIZED DESIGN FOR ONE STEPPER MOTOR
COMPACT DESIGN FOR MULTIPLE STEPPER MOTORS
M
Encoder
Ref.
Switches
M
M
Addr.
Addr.
NCS signal for SPI
Chaining
with UART
Hint: TMC5160 in this manual always refers to both, the TMC5160A and TMC5160, unless explicitly noted
with “non-A-version” or “A-version”. The A-version compatibly replaces the non-A-version.
An optional ABN encoder interface with
scaler unit and two reference switch inputs
are used to ensure correct motor movement.
Automatic interrupt upon deviation is
available.
An application with 2 stepper motors is
shown. Additionally, the ABN Encoder
interface and two reference switches can be
used for each motor. A single CPU controls
the whole system, as there are no real time
tasks required to move a motor. The CPU-
board and the controller / driver boards are
highly economical and space saving.
The TMC5160-EVAL is part of TRINAMICs
universal evaluation board system which
provides a convenient handling of the
hardware as well as a user-friendly
software tool for evaluation. The
TMC5160 evaluation board system
consists of three parts:
LANDUNGSBRÜCKE (base board),
ESELSBRÜCKE (connector board including
several test points), and TMC5160-EVAL.
TMC5160/TMC5160A DATASHEET (Rev. 1.17 / 2022-MAY-25) 3
www.trinamic.com
ORDER CODES
Order code
Description
Size [mm
2
]
TMC5160A-TA
Stepper Motor Controller/Driver IC, SPI, Step/Dir, UART, 8-60V,
eTQFP48, Tray
7 x 7 (body)
TMC5160A-TA-T
Stepper Motor Controller/Driver IC, SPI, Step/Dir, UART, 8-60V,
eTQFP48, Tape & Reel
7 x 7 (body)
TMC5160A-WA
Stepper Motor Controller/Driver IC, SPI, Step/Dir, UART, 8-60V, QFN56
Wettable Flanks, Tray
8 x 8
TMC5160A-WA-T
Stepper Motor Controller/Driver IC, SPI, Step/Dir, UART, 8-60V, QFN56
Wettable Flanks, Tape & Reel
8 x 8
TMC5160-EVAL-KIT
Full Evaluation Kit for TMC5160
126 x 85
TMC5160-EVAL
Evaluation Board for TMC5160 (excl. Landungsbrücke and Eselsbrücke)
85 x 55
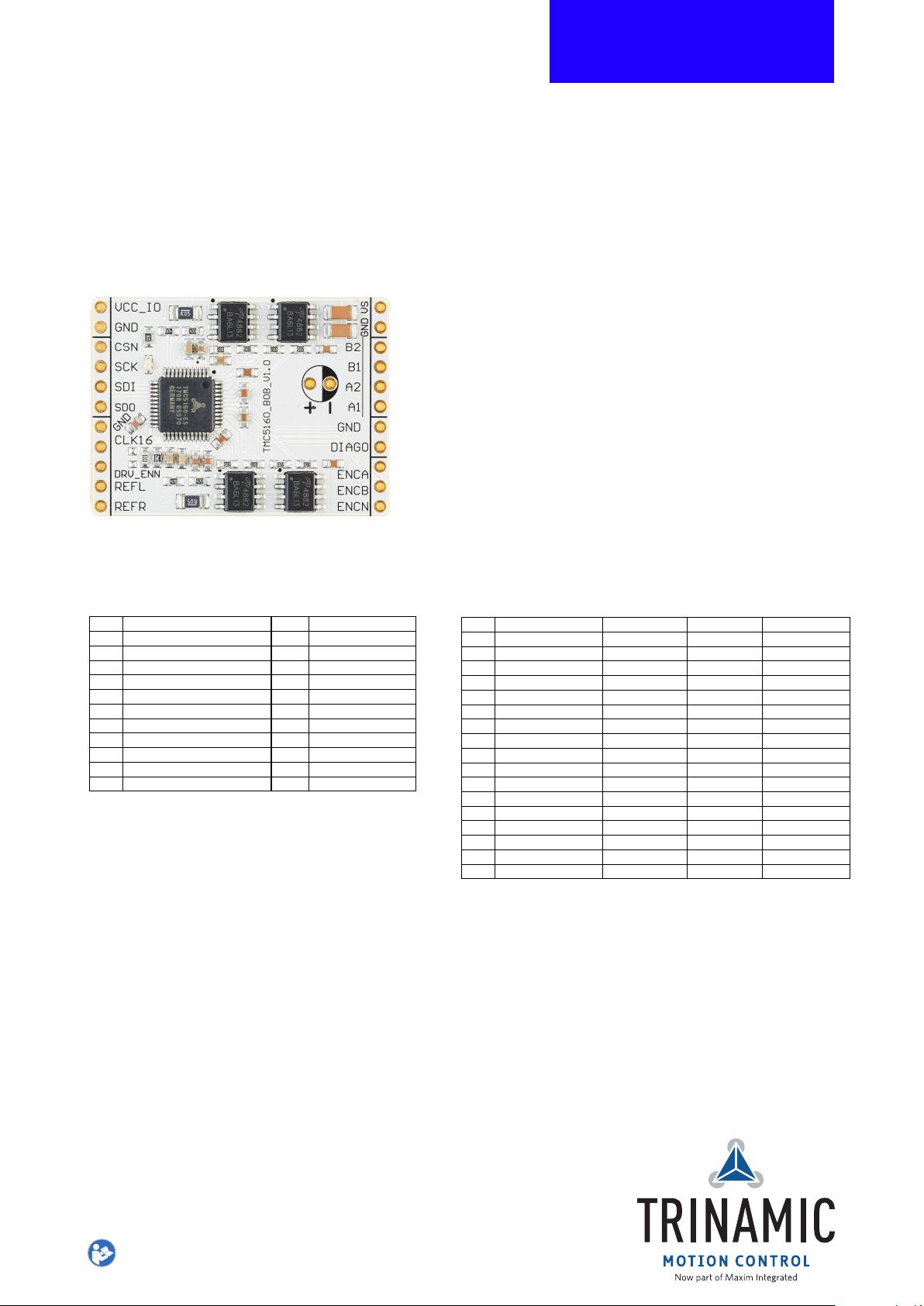
TMC5160-BOB
Breakout Board with TMC5160
38 x 28
TMC5160Silent
StepStick
Step Direction Driver Board with TMC5160
20 x 15
Table of Contents
1 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION ......................... 5
1.1 KEY CONCEPTS ................................................ 6
1.2 CONTROL INTERFACES ..................................... 7
1.3 SOFTWARE ...................................................... 7
1.4 MOVING AND CONTROLLING THE MOTOR ........ 8
1.5 AUTOMATIC STANDSTILL POWER DOWN......... 8
1.6 STEALTHCHOP2 & SPREADCYCLE DRIVER ....... 8
1.7 STALLGUARD2 – MECHANICAL LOAD SENSING .
....................................................................... 9
1.8 COOLSTEP – LOAD ADAPTIVE CURRENT .......... 9
1.9 DCSTEP – LOAD DEPENDENT SPEED ............. 10
1.10 ENCODER INTERFACE ..................................... 10
2 PIN ASSIGNMENTS ......................................... 11
2.1 PACKAGE OUTLINE ........................................ 11
2.2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS ................................. 12
3 SAMPLE CIRCUITS .......................................... 15
3.1 STANDARD APPLICATION CIRCUIT ................ 15
3.2 EXTERNAL GATE VOLTAGE REGULATOR .......... 16
3.3 CHOOSING MOSFETS AND SLOPE ................ 17
3.4 TUNING THE MOSFET BRIDGE ..................... 19
3.5 HIGHER VOLTAGE APPLICATIONS .................. 22
4 SPI INTERFACE ................................................ 23
4.1 SPI DATAGRAM STRUCTURE ......................... 23
4.2 SPI SIGNALS ................................................ 24
4.3 TIMING ......................................................... 25
5 UART SINGLE WIRE INTERFACE ................ 26
5.1 DATAGRAM STRUCTURE ................................. 26
5.2 CRC CALCULATION ....................................... 28
5.3 UART SIGNALS ............................................ 28
5.4 ADDRESSING MULTIPLE SLAVES .................... 29
6 REGISTER MAPPING ....................................... 31
6.1 GENERAL CONFIGURATION REGISTERS .......... 32
6.2 VELOCITY DEPENDENT DRIVER FEATURE
CONTROL REGISTER SET ............................................. 38
6.3 RAMP GENERATOR REGISTERS ...................... 40
6.4 ENCODER REGISTERS .................................... 45
6.5 MOTOR DRIVER REGISTERS ........................... 47
7 STEALTHCHOP™ .............................................. 57
7.1 AUTOMATIC TUNING ..................................... 57
7.2 STEALTHCHOP OPTIONS ............................... 60
7.3 STEALTHCHOP CURRENT REGULATOR ............ 60
7.4 VELOCITY BASED SCALING ........................... 63
7.5 COMBINE STEALTHCHOP AND SPREADCYCLE 64
7.6 FLAGS IN STEALTHCHOP ............................... 66
7.7 FREEWHEELING AND PASSIVE BRAKING ........ 66
8 SPREADCYCLE AND CLASSIC CHOPPER ... 68
8.1 SPREADCYCLE CHOPPER ................................ 69
8.2 CLASSIC CONSTANT OFF TIME CHOPPER ...... 72
9 SELECTING SENSE RESISTORS .................... 74
10 VELOCITY BASED MODE CONTROL ....... 76
11 DIAGNOSTICS AND PROTECTION......... 78
11.1 TEMPERATURE SENSORS ................................ 78
11.2 SHORT PROTECTION ...................................... 78
11.3 OPEN LOAD DIAGNOSTICS ........................... 80
12 RAMP GENERATOR ..................................... 81
12.1 REAL WORLD UNIT CONVERSION ................. 81
12.2 MOTION PROFILES ........................................ 82
12.3 VELOCITY THRESHOLDS ................................. 84
12.4 REFERENCE SWITCHES .................................. 85
12.5 RAMP GENERATOR RESPONSE TIME .............. 86
13 STALLGUARD2 LOAD MEASUREMENT ... 87
13.1 TUNING STALLGUARD2 THRESHOLD SGT ..... 88
13.2 STALLGUARD2 UPDATE RATE AND FILTER .... 90
13.3 DETECTING A MOTOR STALL ......................... 90

TMC5160/TMC5160A DATASHEET (Rev. 1.17 / 2022-MAY-25) 4
www.trinamic.com
13.4 HOMING WITH STALLGUARD ......................... 90
13.5 LIMITS OF STALLGUARD2 OPERATION .......... 90
14 COOLSTEP OPERATION ............................. 91
14.1 USER BENEFITS ............................................. 91
14.2 SETTING UP FOR COOLSTEP .......................... 91
14.3 TUNING COOLSTEP ....................................... 93
15 STEP/DIR INTERFACE ................................ 94
15.1 TIMING ......................................................... 94
15.2 CHANGING RESOLUTION ................................ 95
15.3 MICROPLYER AND STAND STILL DETECTION . 96
16 DIAG OUTPUTS ........................................... 97
16.1 STEP/DIR MODE ......................................... 97
16.2 MOTION CONTROLLER MODE ........................ 97
17 DCSTEP........................................................... 99
17.1 USER BENEFITS ............................................. 99
17.2 DESIGNING-IN DCSTEP ................................. 99
17.3 DCSTEP INTEGRATION WITH THE MOTION
CONTROLLER............................................................ 100
17.4 STALL DETECTION IN DCSTEP MODE ......... 100
17.5 MEASURING ACTUAL MOTOR VELOCITY IN
DCSTEP OPERATION ................................................ 101
17.6 DCSTEP WITH STEP/DIR INTERFACE ........ 102
18 SINE-WAVE LOOK-UP TABLE ................ 105
18.1 USER BENEFITS .......................................... 105
18.2 MICROSTEP TABLE ..................................... 105
19 EMERGENCY STOP .................................... 106
20 ABN INCREMENTAL ENCODER
INTERFACE .............................................................. 107
20.1 ENCODER TIMING ....................................... 108
20.2 SETTING THE ENCODER TO MATCH MOTOR
RESOLUTION ............................................................ 108
20.3 CLOSING THE LOOP .................................... 109
21 DC MOTOR OR SOLENOID .................... 110
21.1 SOLENOID OPERATION ............................... 110
22 QUICK CONFIGURATION GUIDE .......... 111
23 GETTING STARTED ................................... 116
23.1 INITIALIZATION EXAMPLES ......................... 116
24 STANDALONE OPERATION .................... 117
25 POWER-UP RESET ..................................... 119
26 CLOCK OSCILLATOR AND INPUT ......... 119
26.1 USING THE INTERNAL CLOCK ...................... 119
26.2 USING AN EXTERNAL CLOCK ....................... 119
27 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .......... 120
28 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .......... 120
28.1 OPERATIONAL RANGE ................................. 120
28.2 DC AND TIMING CHARACTERISTICS ............ 121
28.3 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS........................ 123
29 LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS................... 125
29.1 EXPOSED DIE PAD ...................................... 125
29.2 WIRING GND ............................................ 125
29.3 WIRING BRIDGE SUPPLY ............................ 125
29.4 SUPPLY FILTERING ...................................... 125
29.5 LAYOUT EXAMPLE ....................................... 126
30 PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA .............. 128
30.1 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS TQFP48-EP ..... 128
30.2 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS QFN-WA ......... 130
30.3 PACKAGE CODES ......................................... 131
31 DESIGN PHILOSOPHY ............................. 132
32 DISCLAIMER ............................................... 132
33 ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE.......................... 132
34 DESIGNED FOR SUSTAINABILITY ....... 132
35 TABLE OF FIGURES .................................. 133
36 REVISION HISTORY ................................. 134
37 REFERENCES ............................................... 134
TMC5160/TMC5160A DATASHEET (Rev. 1.17 / 2022-MAY-25) 5
www.trinamic.com
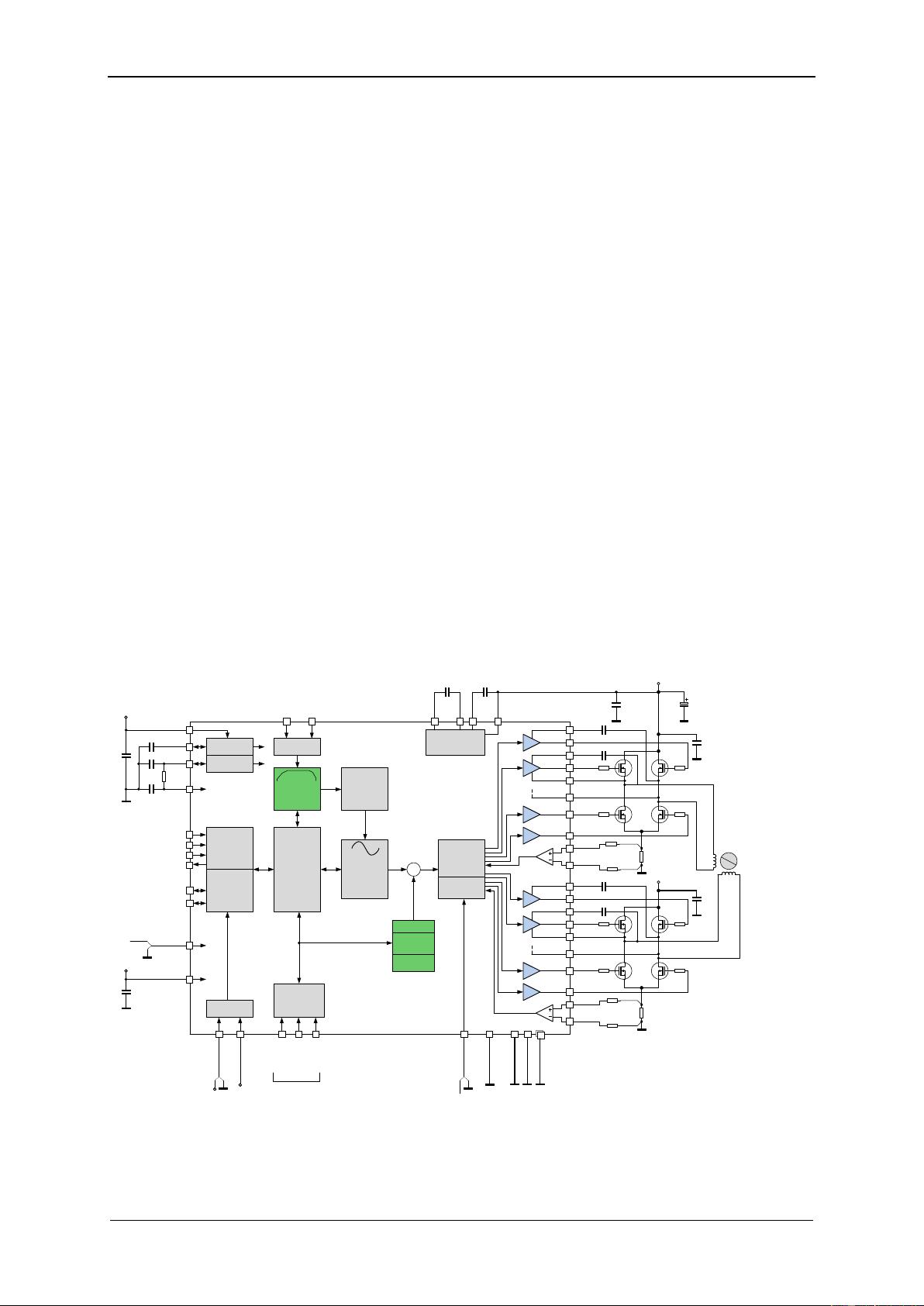
1 Principles of Operation
The TMC5160 motion controller and driver chip is an intelligent power component interfacing between
CPU and a high-power stepper motor. All stepper motor logic is completely within the TMC5160. No
software is required to control the motor – just provide target positions. The TMC5160 offers several
unique enhancements which are enabled by the system-on-chip integration of driver and controller.
The SixPoint ramp generator of the TMC5160 uses StealthChop, DcStep, CoolStep, and StallGuard2
automatically to optimize every motor movement. The TMC5160 ideally extends the TMC2100, TMC2130
and TMC5130 family to higher voltages and higher motor currents.
THE TMC5160 OFFERS THREE BASIC MODES OF OPERATION:
MODE 1: Full Featured Motion Controller & Driver
All stepper motor logic is completely within the TMC5160. No software is required to control the
motor – just provide target positions. Enable this mode by tying low pin SD_MODE.
MODE 2: Step & Direction Driver
An external high-performance S-ramp motion controller like the TMC4361 or a central CPU generates
step & direction signals synchronized to other components like additional motors within the system.
The TMC5160 takes care of intelligent current and mode control and delivers feedback on the state of
the motor. The MicroPlyer automatically smoothens motion. Tie SD_MODE high.
MODE 3: Simple Step & Direction Driver
The TMC5160 positions the motor based on step & direction signals. The MicroPlyer automatically
smoothens motion. No CPU interaction is required; configuration is done by hardware pins. Basic
standby current control can be done by the TMC5160. Optional feedback signals allow error detection
and synchronization. Enable this mode by tying pin SPI_MODE low and SD_MODE high.
47R
47R
LS
VCC_IO
TMC5160
SPI interface
CSN
SCK
SDO
SDI
Ref. switch
processing
REFL/STEP
REFR/DIR
DIAG / INT out
and
Single wire
interface
5V Voltage
regulator
charge pump
22n
100V
100n
16V
DIAG0/SWN
CLK_IN
DIAG1/SWP
+V
M
5VOUT
VSA
2.2µ
+V
IO
DRV_ENN
GNDD
GNDA
TST_MODE
DIE PAD
VCC
opt. ext. clock
12-16MHz
3.3V or 5V
I/O voltage
100n
100n
LS
stepper
motor
N
S
BMA2
100n
SRAH
C
E
2R2
470n
Encoder
unit
A B N
ENCB_DCEN
ENCA_DCIN
ENCN_DCO
Encoder input /
dcStep control in S/D
mode
SD_MODE
SPI_MODE
opt. driver enable
B.Dwersteg, ©
TRINAMIC 2014
R
S
SRAL
LA1
LA2
HA1
HA2
BMA1
HS
HS
CA1
C
B
CA2
C
B
+V
M
LS
LS
BMB2
SRBH
R
S
SRBL
LB1
LB2
HB1
HB2
BMB1
HS
HS
CB1
C
B
CB2
C
B
+V
M
Both GND: UART mode
CPI
CPO
VCP
VS
11.5V Voltage
regulator
12VOUT
2.2µ
mode selection
470n
470n
R
G
R
G
R
G
R
G
R
G
R
G
R
G
R
G
47R
47R
+V
IO
pd pd pd
+V
IO
Stepper driver
Protection
& diagnostics
spreadCycle &
stealthChop
Chopper
programmable
sine table
4*256 entry
stallGuard2™
coolStep™
x
linear 6 point
RAMP generator
Step &
Direction pulse
generation
Control register
set
Interface
dcStep™
coolStep
&
stealthChop
motor driver
B.Dwersteg, ©
TRINAMIC 2014
Motion control
Figure 1.1 TMC5160 basic application block diagram (motion controller)

















