没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

S32K1XX
S32K1xx Data Sheet
Notes
• The following two attachments are available with the
Datasheet:
– S32K1xx_Orderable_Part_Number_ List.xlsx
– S32K1xx_Power_Modes_Configuration.xlsx
Key Features
• Operating characteristics
– Voltage range: 2.7 V to 5.5 V
– Ambient temperature range: -40 °C to 105 °C for
HSRUN mode, -40 °C to 125 °C for RUN mode
• Arm™ Cortex-M4F/M0+ core, 32-bit CPU
– Supports up to 112 MHz frequency (HSRUN mode)
with 1.25 Dhrystone MIPS per MHz
– Arm Core based on the Armv7 Architecture and
Thumb®-2 ISA
– Integrated Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
– Configurable Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller
(NVIC)
– Single Precision Floating Point Unit (FPU)
• Clock interfaces
– 4 - 40 MHz fast external oscillator (SOSC) with up
to 50 MHz DC external square input clock in
external clock mode
– 48 MHz Fast Internal RC oscillator (FIRC)
– 8 MHz Slow Internal RC oscillator (SIRC)
– 128 kHz Low Power Oscillator (LPO)
– Up to 112 MHz (HSRUN) System Phased Lock
Loop (SPLL)
– Up to 20 MHz TCLK and 25 MHz SWD_CLK
– 32 kHz Real Time Counter external clock
(RTC_CLKIN)
• Power management
– Low-power Arm Cortex-M4F/M0+ core with
excellent energy efficiency
– Power Management Controller (PMC) with multiple
power modes: HSRUN, RUN, STOP, VLPR, and
VLPS. Note: CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/
erase will trigger error flags in HSRUN mode (112
MHz) because this use case is not allowed to
execute simultaneously. The device will need to
switch to RUN mode (80 Mhz) to execute CSEc
(Security) or EEPROM writes/erase.
– Clock gating and low power operation supported on
specific peripherals.
• Memory and memory interfaces
– Up to 2 MB program flash memory with ECC
– 64 KB FlexNVM for data flash memory with ECC
and EEPROM emulation. Note: CSEc (Security) or
EEPROM writes/erase will trigger error flags in
HSRUN mode (112 MHz) because this use case is
not allowed to execute simultaneously. The device
will need to switch to RUN mode (80 MHz) to
execute CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/erase.
– Up to 256 KB SRAM with ECC
– Up to 4 KB of FlexRAM for use as SRAM or
EEPROM emulation
– Up to 4 KB Code cache to minimize performance
impact of memory access latencies
– QuadSPI with HyperBus™ support
• Mixed-signal analog
– Up to two 12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter
(ADC) with up to 32 channel analog inputs per
module
– One Analog Comparator (CMP) with internal 8-bit
Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)
• Debug functionality
– Serial Wire JTAG Debug Port (SWJ-DP) combines
– Debug Watchpoint and Trace (DWT)
– Instrumentation Trace Macrocell (ITM)
– Test Port Interface Unit (TPIU)
– Flash Patch and Breakpoint (FPB) Unit
• Human-machine interface (HMI)
– Up to 156 GPIO pins with interrupt functionality
– Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI)
NXP Semiconductors
Document Number S32K1XX
Data Sheet: Technical Data
Rev. 9, 09/2018
NXP reserves the right to change the production detail specifications as may be
required to permit improvements in the design of its products.

• Communications interfaces
– Up to three Low Power Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (LPUART/LIN) modules with DMA support
and low power availability
– Up to three Low Power Serial Peripheral Interface (LPSPI) modules with DMA support and low power availability
– Up to two Low Power Inter-Integrated Circuit (LPI2C) modules with DMA support and low power availability
– Up to three FlexCAN modules (with optional CAN-FD support)
– FlexIO module for emulation of communication protocols and peripherals (UART, I2C, SPI, I2S, LIN, PWM, etc).
– Up to one 10/100Mbps Ethernet with IEEE1588 support and two Synchronous Audio Interface (SAI) modules.
• Safety and Security
– Cryptographic Services Engine (CSEc) implements a comprehensive set of cryptographic functions as described in the
SHE (Secure Hardware Extension) Functional Specification. Note: CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/erase will
trigger error flags in HSRUN mode (112 MHz) because this use case is not allowed to execute simultaneously. The
device will need to switch to RUN mode (80 MHz) to execute CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/erase.
– 128-bit Unique Identification (ID) number
– Error-Correcting Code (ECC) on flash and SRAM memories
– System Memory Protection Unit (System MPU)
– Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) module
– Internal watchdog (WDOG)
– External Watchdog monitor (EWM) module
• Timing and control
– Up to eight independent 16-bit FlexTimers (FTM) modules, offering up to 64 standard channels (IC/OC/PWM)
– One 16-bit Low Power Timer (LPTMR) with flexible wake up control
– Two Programmable Delay Blocks (PDB) with flexible trigger system
– One 32-bit Low Power Interrupt Timer (LPIT) with 4 channels
– 32-bit Real Time Counter (RTC)
• Package
– 32-pin QFN, 48-pin LQFP, 64-pin LQFP, 100-pin LQFP, 100-pin MAPBGA, 144-pin LQFP, 176-pin LQFP package
options
• 16 channel DMA with up to 63 request sources using DMAMUX
S32K1xx Data Sheet, Rev. 9, 09/2018
2 NXP Semiconductors

Table of Contents
1 Block diagram.................................................................................... 4
2 Feature comparison............................................................................ 5
3 Ordering information......................................................................... 7
3.1 Selecting orderable part number ...............................................7
3.2 Ordering information ................................................................8
4 General............................................................................................... 9
4.1 Absolute maximum ratings........................................................9
4.2 Voltage and current operating requirements..............................10
4.3 Thermal operating characteristics..............................................11
4.4 Power and ground pins.............................................................. 12
4.5 LVR, LVD and POR operating requirements............................14
4.6 Power mode transition operating behaviors.............................. 15
4.7 Power consumption................................................................... 16
4.8 ESD handling ratings.................................................................22
4.9 EMC radiated emissions operating behaviors........................... 22
5 I/O parameters....................................................................................23
5.1 AC electrical characteristics...................................................... 23
5.2 General AC specifications......................................................... 23
5.3 DC electrical specifications at 3.3 V Range.............................. 24
5.4 DC electrical specifications at 5.0 V Range.............................. 25
5.5 AC electrical specifications at 3.3 V range .............................. 26
5.6 AC electrical specifications at 5 V range ................................. 26
5.7 Standard input pin capacitance.................................................. 27
5.8 Device clock specifications....................................................... 27
6 Peripheral operating requirements and behaviors..............................28
6.1 System modules.........................................................................28
6.2 Clock interface modules............................................................ 28
6.2.1 External System Oscillator electrical specifications....28
6.2.2 External System Oscillator frequency specifications . 30
6.2.3 System Clock Generation (SCG) specifications..........32
6.2.3.1 Fast internal RC Oscillator (FIRC)
electrical specifications............................ 32
6.2.3.2 Slow internal RC oscillator (SIRC)
electrical specifications ........................... 32
6.2.4 Low Power Oscillator (LPO) electrical specifications
......................................................................................33
6.2.5 SPLL electrical specifications .....................................33
6.3 Memory and memory interfaces................................................33
6.3.1 Flash memory module (FTFC) electrical
specifications................................................................33
6.3.1.1 Flash timing specifications —
commands................................................ 33
6.3.1.2 Reliability specifications..........................38
6.3.2 QuadSPI AC specifications..........................................39
6.4 Analog modules.........................................................................43
6.4.1 ADC electrical specifications...................................... 43
6.4.1.1 12-bit ADC operating conditions.............43
6.4.1.2 12-bit ADC electrical characteristics....... 45
6.4.2 CMP with 8-bit DAC electrical specifications............ 47
6.5 Communication modules...........................................................51
6.5.1 LPUART electrical specifications............................... 51
6.5.2 LPSPI electrical specifications.................................... 51
6.5.3 LPI2C electrical specifications.................................... 57
6.5.4 FlexCAN electical specifications.................................58
6.5.5 SAI electrical specifications........................................ 58
6.5.6 Ethernet AC specifications.......................................... 60
6.5.7 Clockout frequency......................................................63
6.6 Debug modules.......................................................................... 63
6.6.1 SWD electrical specofications .................................... 63
6.6.2 Trace electrical specifications......................................65
6.6.3 JTAG electrical specifications..................................... 66
7 Thermal attributes.............................................................................. 69
7.1 Description.................................................................................69
7.2 Thermal characteristics..............................................................69
7.3 General notes for specifications at maximum junction
temperature................................................................................ 74
8 Dimensions.........................................................................................75
8.1 Obtaining package dimensions .................................................75
9 Pinouts................................................................................................76
9.1 Package pinouts and signal descriptions....................................76
10 Revision History.................................................................................76
S32K1xx Data Sheet, Rev. 9, 09/2018
NXP Semiconductors 3

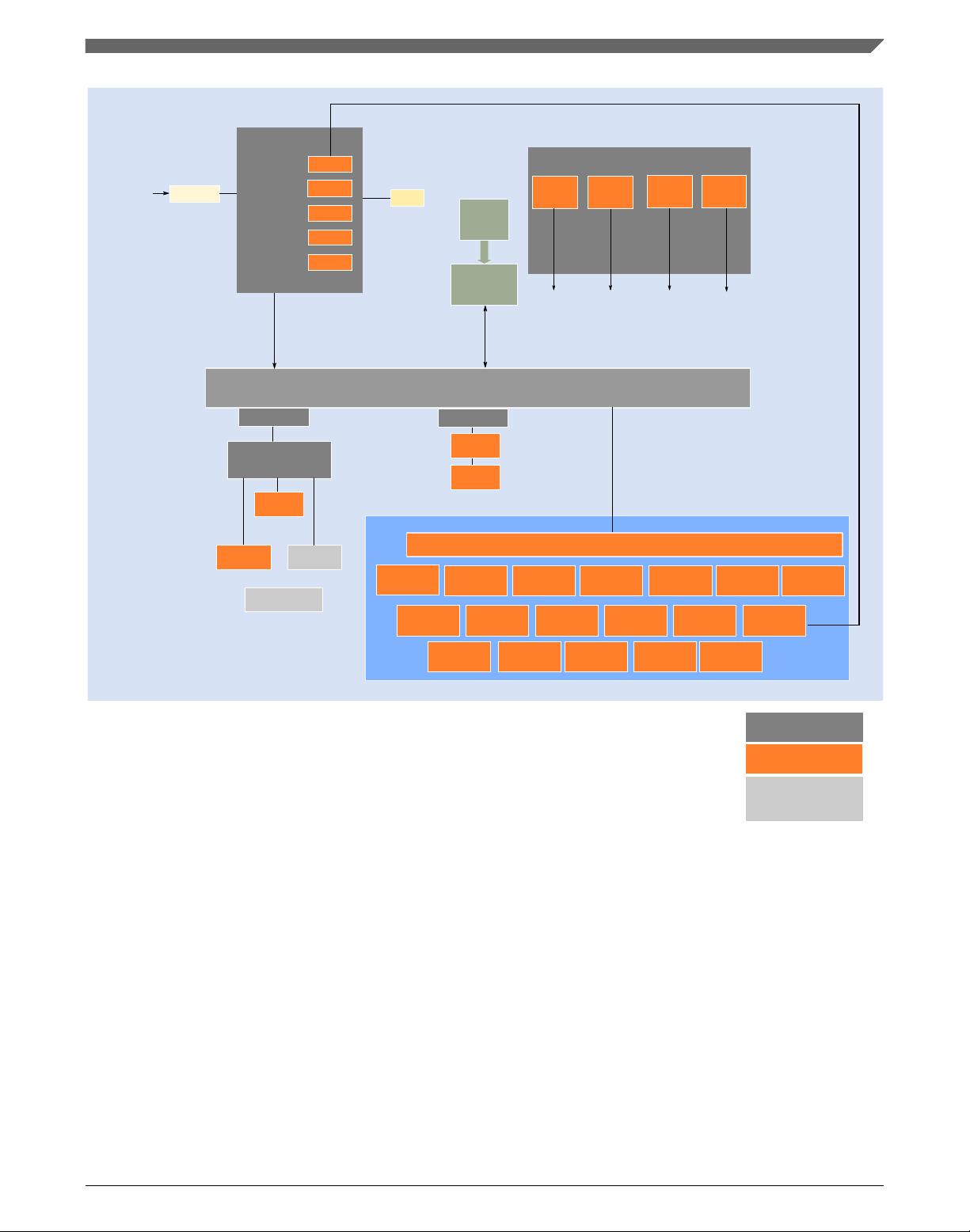
1 Block diagram
Following figures show superset high level architecture block diagrams of S32K14x
series and S32K11x series respectively. Other devices within the family have a subset of
the features. See Feature comparison for chip specific values.
Mux
Trace
port
Crossbar switch (AXBS-Lite)
eDMA
DMA
MUX
Core
Peripheral bus controller
CRC
WDOG
S1
M0
M1
DSP
NVIC
ITM
FPB
DWT
AWIC
SWJ-DP
TPIU
JTAG &
Serial Wire
Arm Cortex M4F
ICODE
DCODE
AHB-AP
PPB
System
M2
S2
GPIO
Mux
FPU
Clock
SPLL
LPO
128 kHz
Async
512B
TCD
LPIT
LPI2C
FlexIO
Flash memory
controller
Code flash
S0
Data flash
Low Power
Timer
12-bit ADC
TRGMUX
LPUART
LPSPI
FlexCAN
FlexTimer
PDB
generation
LPIT
Peripherals present
on all S32K devices
Peripherals present
on selected S32K devices
Key:
Device architectural IP
on all S32K devices
S3
FIRC
48 MHz
M3
ENET
SAI
SOSC
8-40 MHz
(see the "Feature Comparison"
memory
memory
4-40 MHz
QuadSPI
RTC
CMP
8-bit DAC
SIRC
8 MHz
FlexRAM/
SRAM
1: On this device, NXP’s system MPU implements the safety mechanisms to prevent masters from
accessing restricted memory regions. This system MPU provides memory protection at the
level of the Crossbar Switch. Each Crossbar master (Core, DMA, Ethernet) can be assigned
different access rights to each protected memory region. The Arm M4 core version in this family
does not integrate the Arm Core MPU, which would concurrently monitor only core-initiated memory
accesses. In this document, the term MPU refers to NXP’s system MPU.
2: For the device-specific sizes, see the "On-chip SRAM sizes" table in the "Memories and Memory Interfaces"
chapter of the S32K1xx Series Reference Manual.
section)
ERM
EWM
MCM
Lower region
Upper region
Main SRAM
2
Code Cache
System MPU
1
EIM
LMEM
controller
LMEM
QSPI
CSEc
3
System MPU
1
System MPU
1
System MPU
1
3: CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/erase will trigger error flags in HSRUN mode (112 MHz) because this
use case is not allowed to execute simultaneously. The device need to switch to RUN mode (80 MHz) to
execute CSEc (Security) or EEPROM writes/erase.
Figure 1. High-level architecture diagram for the S32K14x family
Block diagram
S32K1xx Data Sheet, Rev. 9, 09/2018
4 NXP Semiconductors
Crossbar switch (AXBS-Lite)
eDMA
DMA
MUX
SW-DP
Unified Bus
Serial Wire
AHBLite
AHBLite
AWIC
S0
S1
Clock
LPO
128 kHz
generation
Peripheral bus controller
CRC
WDOG
LPIT
LPI2C
FlexIO
Low Power
Timer
12-bit ADC
TRGMUX
LPUART
LPSPI
FlexCAN
FlexTimer
PDB
LPIT
RTC
CMP
8-bit DAC
ERM
CMU
GPIO
M0
M2
Flash memory
controller
Data flash
memory
FlexRAM/
SRAM
2
Code flash
memory
IO PORT
NVIC
PPB
MTB+DWT
BPU
AHB-AP
Arm Cortex M0+
Peripherals present
on all S32K devices
Peripherals present
on selected S32K devices
Key:
Device architectural IP
on all S32K devices
(see the "Feature Comparison"
1: On this device, NXP’s system MPU implements the safety mechanisms to prevent masters from
accessing restricted memory regions. This system MPU provides memory protection at the
level of the Crossbar Switch. Crossbar master (Core, DMA) can be assigned
different access rights to each protected memory region. The Arm M0+ core version in this family
does not integrate the Arm Core MPU, which would concurrently monitor only core-initiated memory
accesses. In this document, the term MPU refers to NXP’s system MPU.
2: For the device-specific sizes, see the "On-chip SRAM sizes" table in the "Memories and Memory Interfaces"
chapter of the S32K1xx Series Reference Manual.
section)
S2
IO PORT
CSEc
System MPU
1
System MPU
1
SOSC
4-40 MHz
SIRC
8 MHz
FIRC
48 MHz
EIM
SRAM
2
Figure 2. High-level architecture diagram for the S32K11x family
2
Feature comparison
The following figure summarizes the memory, peripherals and packaging options for the
S32K1xx devices. All devices which share a common package are pin-to-pin compatible.
NOTE
Availability of peripherals depends on the pin availability in a
particular package. For more information see IO Signal
Feature comparison
S32K1xx Data Sheet, Rev. 9, 09/2018
NXP Semiconductors 5
剩余83页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

愛德華117
- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 3
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 铜铆钉送料铆接设备(sw09+工程图+BOM)全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- SLM 增材制造 ansys fluent模拟 选区激光熔化,电子束选区熔化的模拟过程 高功率激光选区融化熔池流动与小孔动态特征 扫描速度、小孔深度,激光功率,热源深度等都可随意设置 有视频教程,上
- 基于新型滑模观测器无位置速度传感器的永磁同步电机(PMSM)控制,采用S型函数替代开关函数,无需LPF(低通滤波器),转子位置额外补偿器 且使用可变观测增益,提高系统鲁棒性 提供参考lunwen
- Nature Communications电热力介电击穿lunwen仿制 comsol 描述:击穿驱动力主要包括静电能,弹性能和焦耳热能,并且通过热扩散方程模拟击穿过程中温度分布,显示击穿过程中电树
- Vue低代码可视化表单-源码
- queue-race-hack仓库入口
- 半光滑牛顿法非线性优化带35个测试函数 半光滑牛顿法求解非线性目标函数约束优化问题的MATLAB自编源代码,不调用MATLAB优化库函数,每个函数开头有简单英语注释,求解速度比MATLAB自带优化库函
- livewallpaper-源码
- vue3-element-admin-源码
- xdoj-frontend-xdoj
- 光储并网直流微电网仿真模型(matlab simulink,2018),包含: 1.MPPT模块,实现光伏输入最大功率跟踪; 2.储能电池模块; 3.超级电容模块; 控制策略简介: 糸统使用二阶低通滤
- 重型高速电梯安全钳sw19可编辑全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- SLM 增材制造 ansys fluent模拟 选区激光熔化,电子束选区熔化的模拟过程 模拟小孔过程,锥形高斯热源
- 重载高速梯主机及主机架sw19全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- 小程序 商城 -Java 商城-源码
- offer-hack仓库入口
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功