Analyzing Comprehensive QoS with Security Constraints for Servic...
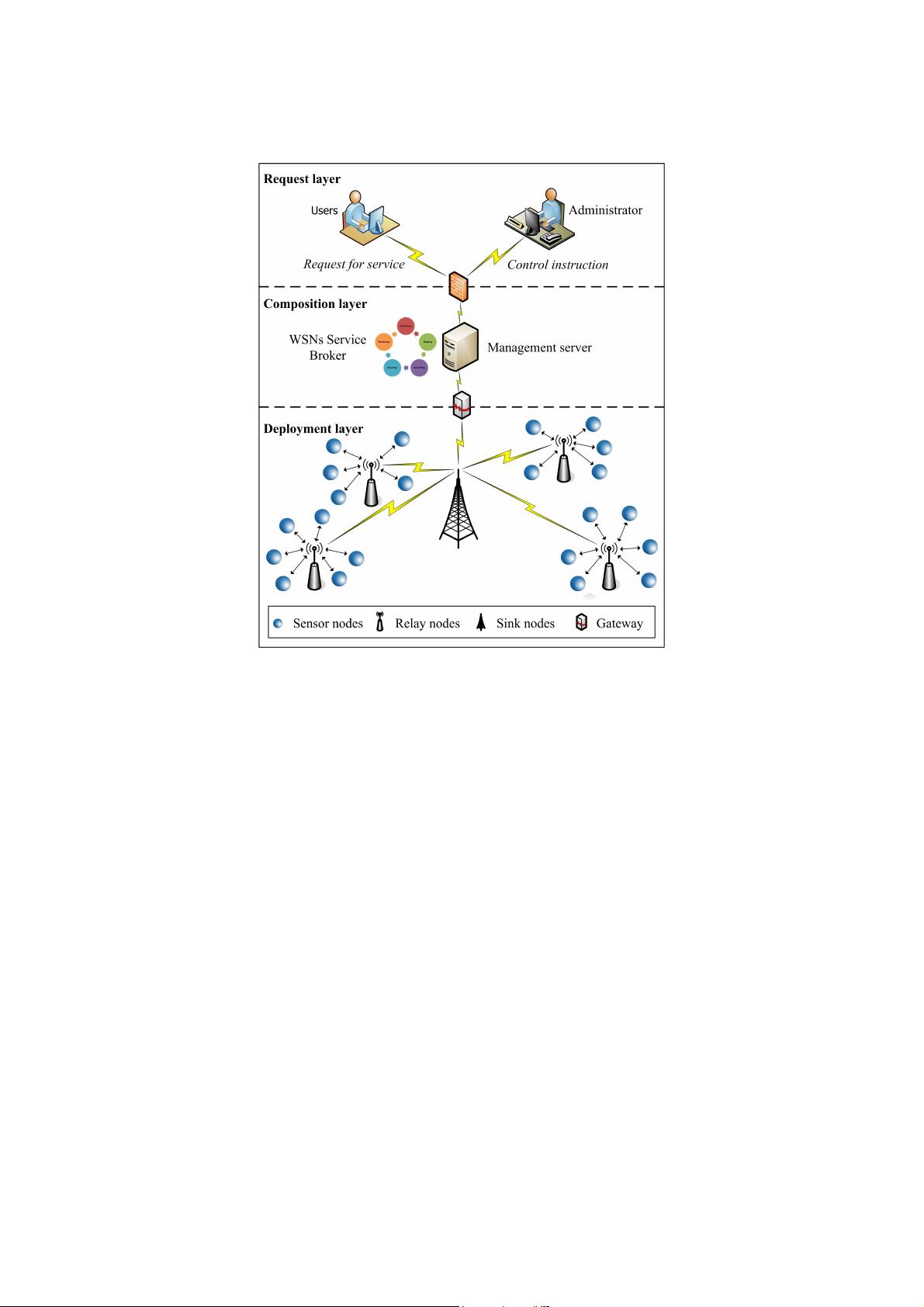
Analyzing Comprehensive QoS with Security Constraints for Services Composition Applications in Wireless Sensor Networks 本文的研究主题是“无线传感器网络中具有安全约束的服务组合应用的综合服务质量(QoS)分析”。在无线传感器网络(WSNs)环境下,服务质量(QoS)的管理是一项复杂而具有挑战性的工作。由于WSNs的开放性、动态性以及复杂性,服务组合应用(SCAs)的QoS面临严重挑战。服务质量不仅包括传统意义上的性能指标,如响应时间、吞吐量、系统可用性等,还包括安全性能。 在此研究中,作者提出了一种改进的方法——矢量通用生成函数(VUGF),它能够同时分析多个服务质量指标,包括安全性能,并在WSNs中对服务组合应用进行综合QoS分析。VUGF技术考虑了QoS指标之间的关系,相对于以往的方法具有显著的优势,因为它解决了单独分析时可能产生的片面和不准确的问题。为了确保多服务无线传感器网络的最优设计,本研究以一种新视角提出了一种新的服务质量分析工具。 文章首先指出了以往研究的局限性,即大多数研究因为计算复杂度的原因,将QoS的不同指数分开到不同的领域进行独立研究,从而忽略了这些指数之间的相互影响。结果往往导致服务质量分析结果既不全面也不准确。文章进一步指出,通用生成函数(UGF)在QoS分析上显示出速度和精确度的优势,但传统的UGF一次只能分析一个QoS指标,无法同时考虑多个指标之间的相互关系。 研究者们通过改进UGF技术,提出了矢量通用生成函数(VUGF),它可以同时分析多个服务质量指标,并且包括安全性在内的考量。这一方法通过数值示例表明,它可以用于评估在WSNs中受到安全约束的服务组合应用的综合QoS。因此,VUGF技术可以有效地应用于多服务WSNs的最优设计中。 文章在第一部分“引言”中,首先介绍了无线传感器网络的背景,并且强调了服务质量对软件开发在多服务无线传感器网络中的基础性作用。引言中强调了服务质量分析的重要性,并提出当前研究存在的主要问题。此外,文章还介绍了与本研究主题相关的关键词,包括无线传感器网络、服务质量、安全约束、服务组合以及通用生成函数。 在“引言”部分,作者对研究的动机和目的进行了详细的阐述。VUGF技术的提出旨在解决无线传感器网络环境下的多服务质量指标分析问题,特别是考虑了服务质量指标之间的相互关系,以及服务质量分析中的安全性能考量。这为无线传感器网络中多服务应用的设计和评估提供了一种新的工具和方法。 文章的“引言”部分为理解整个研究提供了重要的背景信息,明确指出了研究问题所在,并提出了解决方案。同时,引言部分也为读者提供了关于无线传感器网络服务质量分析当前状况的概述,并指出了本研究的创新点和预期的贡献。此外,作者还提到了研究的结构安排,让读者对接下来的内容有一个预期。 总体而言,这篇研究论文将重点放在了无线传感器网络的服务组合应用上,深入探讨了服务质量的复杂性,尤其是在考虑安全约束的情况下。VUGF技术的提出和应用展示了其在综合分析服务质量指标上的潜力,同时也展示了在无线传感器网络设计方面的应用前景。



剩余30页未读,继续阅读

- 粉丝: 5
- 资源: 882
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 化工行业:基于强化学习的DeepSeek实验方案生成微调策略.pdf
- 教育个性化学习:知识蒸馏构建学科能力评估模型.pdf
- 建筑工程:DeepSeek+BIM模型自动生成施工方案全流程.pdf
- 教育行业:零代码构建DeepSeek智能题库系统,日均成本仅5美元.pdf
- 金融合规检查:增量训练构建反洗钱模型快速迭代方案.pdf
- 教育行业落地:用提示词工程构建智能题库生成系统.pdf
- 教育行业突破:用DeepSeek-Coder实现编程教学智能批改.pdf
- 金融量化投资:DeepSeek微调实现多因子策略生成.pdf
- 金融领域适配技巧:量化训练实现信贷风控模型成本降低90%.pdf
- 金融行业:基于LoRA的DeepSeek信贷风险评估微调方案,成本直降80%.pdf
- 跨境电商:DeepSeek多语言客服模型训练数据增强技巧.pdf
- 跨境贸易:DeepSeek多语言合同风险扫描系统搭建指南.pdf
- 零代码适配术:用DeepSeek打造医疗问诊知识库,3天上线临床决策系统.pdf
- 零售库存管理:联邦学习实现多门店销量预测系统.pdf
- 零售门店数字化:DeepSeek摄像头数据实时分析+货架陈列优化模型训练指南.pdf
- 零售业实战:知识蒸馏技术赋能DeepSeek库存预测轻量化.pdf


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功