没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
实施需求管理:专业软件工具或 PDM 系统的任务?
需积分: 17 0 下载量 68 浏览量
2021-06-29
19:14:14
上传
评论
收藏 401KB PDF 举报
温馨提示
Implementing requirements management: A task for specialized software tools or PDM systems? Implementing Requirements Management: A Task for Specialized Software Tools or PDM Systems? Johan Malmqvist Chalmers University of Technology, Machine and Vehicle Design, SE-412 96 Göteborg, Sweden IMPLEMENTING REQUIREMENTS MANAGEMENT Received May 25, 2000; Accepted September 15, 2000 ABSTRACT This article argues that product models that include the requirements posed on the product have many poten
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

Implementing
Requirements
Management: A Task for
Specialized Software Tools
or PDM Systems?
Johan Malmqvist
Chalmers University of Technology, Machine and Vehicle Design, SE-412 96 Göteborg, Sweden
IMPLEMENTING REQUIREMENTS MANAGEMENT
Received May 25, 2000; Accepted September 15, 2000
ABSTRACT
This article argues that product models that include the requirements posed on the product
have many potential benefits. For example, they facilitate managing the design process so
that its goals are met by enabling a continuous follow-up of the requirements satisfaction
status and by supporting the analysis of the consequences of design changes. The paper first
introduces a concept for a requirements-driven integrated product and process model. The
conditions for support for requirements management are discussed based on this model.
Finally, two different ways of implementing the concept: by using specialized Systems
Engineering/Requirements Management tools or by using PDM (Product Data Management)
systems are analyzed. © 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Syst Eng 4:49-57, 2001
1. INTRODUCTION
Many firms have today formulated a vision where they
aim to develop products based on virtual product and
manufacturing process models that enable a “total”
digital representation of the future product and its
manufacturing process. This means that the model must
be able to manage requirement information, function
structures, CAD models, drawings, NC programs,
analysis models, assembly instructions, and other data.
It is, however, well known that one of the most severe
limitations of current CAD/CAM/CAE/PDM systems
towards realizing such visions is the lack of functional-
ity for requirements management (RM). This results in
limited support for the early phases of the design proc-
ess where requirements are identified and conceptual
solutions are evaluated against the requirements, as well
as for later phases where requirement changes may
necessitate redesign.
Regular Paper
Contract grant sponsor: Swedish National Board of Technical De-
velopment (NUTEK)
Systems Engineering, Vol. 4, No. 1, 2001
© 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
49
In this paper, different technical solutions for imple-
menting support for requirements management in
CAD/CAM/CAE/PDM systems are analyzed. The
starting point of the analysis is a classification of prod-
uct models as requirement models, product and life-cy-
cle system definition models, and property models.
Further, a number of aspects in which the RM support
can vary are discussed: requirements capture, content
and granularity of product model, system and organiza-
tional integration, and data management. The granular-
ity of the information in the product model is given
special consideration since it determines what level of
traceability can be supported. Three variants of granu-
larity and their traceability support are analyzed. This
is followed by an analysis of two classes of technical
solutions for the implementation. These are specialized
Systems Engineering/Requirements Management
(SE/RM) tools and PDM (Product Data Management)
systems. Here a PDM system solution is to be seen as
a “simple” solution based on software that most firms
already have (or are currently implementing).
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 describes a concept for an integrated require-
ments-driven product and process model. Section 3
discusses various conditions for computer support for
requirements management. Section 4 analyses how dif-
ferent technical solutions meet these objectives. Sec-
tions 5 and 6 end the paper by discussion and conclu-
sions.
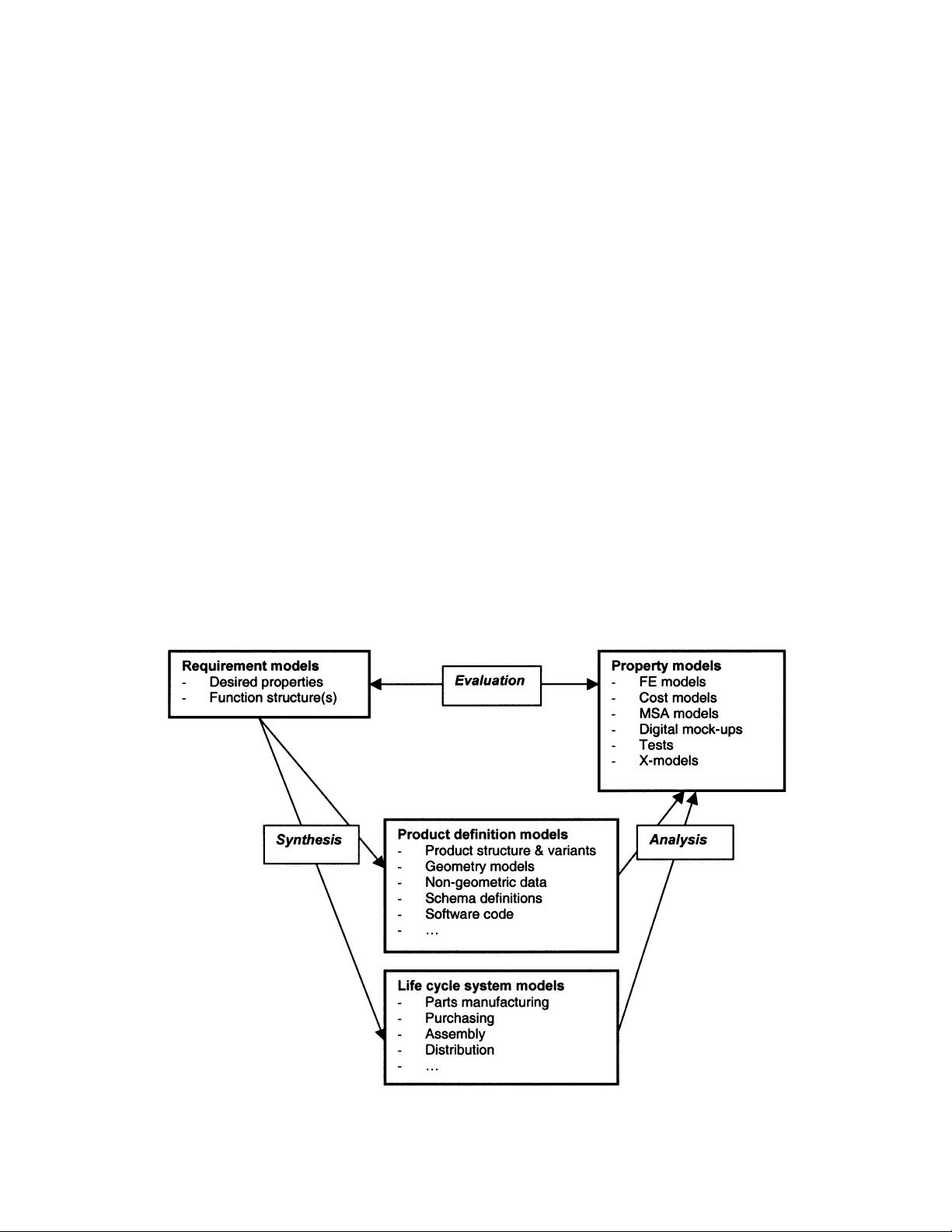
2. REQUIREMENTS-DRIVEN INTEGRATED
PRODUCT AND PROCESS MODEL
This section introduces the concept of a requirements-
driven integrated product and process model. The con-
cept is shown in Figure 1. In the next section, we will
discuss the functions of a requirements management
system with regard to this integrated product model.
The integrated model consists of four basic model
types: requirement models, product definition models,
life-cycle system models, and property models. The
model is based on the Chromosome model [Andreasen,
1992], although slightly simplified and rearranged to
suit the purpose of this paper. According to the Chro-
mosome model, which is based on Hubka’s technical
systems theory [Hubka and Eder, 1988], requirement
models are those that state the desired properties of the
product, thus including demands, wishes, and func-
tions. Product definition models define the product, i.e.,
its structure, form, material, surface quality, software
code, etc. Life-cycle system models define the various
systems with which the product interacts during its life
Figure 1. Requirements-driven integrated product and process model.
50 MALMQVIST
剩余8页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

weixin_38698943
- 粉丝: 2
- 资源: 900
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功