没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
内容概要:本文构建了一个数学框架来定量评估国家的脆弱性,通过综合经济、政治、人口和社会环境等因素的数据集,建立动态系统模拟市场波动。同时引入分支图描绘国家稳定状态、易感状态和脆弱状态之间的转折点。通过对叙利亚、古巴和新西兰三个实际案例的研究,模型揭示了气候变化对国家稳定的影响,如叙利亚水资源不足和古巴自然灾害造成的经济损失。最后讨论人类干预措施及其成本对脆弱性改善的效果。 适用人群:适用于政策制定者、研究人员以及关注国际关系和发展经济学的专业人士。 使用场景及目标:可用于预测不同参数变化时国家稳定的趋势,为政策决策提供科学依据;也可用于城市级别的稳定性和韧性分析,拓展研究范围。 其他说明:本文提出了一个灵活且具有普适性的模型,但存在参数权重设定等问题需要进一步改进和完善。未来可能应用于更大区域(如洲际)层面的脆弱性评估研究中。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

Team # 93840 Page 1 of 19
Motivated to measure a country's stability quantitatively and more accurately, our team
builds a mathematical framework to identify the current status of a country. In the paper, we
introduce a composite index processing comprehensive datasets that consist of di erent factors
including economy, politics, demographics and climate change.
With the composite measure, we build a dynamic system simulating the uctuation of the
market as a result of the variations in di erent sectors. This system not only describes the current
fragility of a country facing potential alternation in social and environmental factors, but also it
predicts the equilibrium states that the country would approach overtime.
Moreover, we propose a bifurcation plot that depicts the tipping points between three states
of a country in terms of its fragility: stable state, vulnerable state, and fragile state. We then
further apply our model and bifurcation plot in real-life case analyses with three selected
countries, Syria, Cuba and New Zealand.
After calibrating parameters and comparing di erent factors in each country, we nd out that
climate conditions play a signi cant role in Syria's fragile state due to factors such as limited
water resources and food supply. We also nd that factors of droughts and occurrence of natural
disasters in Cuba caused huge market losses and Cuba would reach the tipping point under
appropriate human intervention.
精品数模资料,各类比赛优秀论文、学习教程、写作模板与经验技巧、matlab程序代码资料等,尽在淘宝店铺:闵大荒工科男的杂货铺!

Team # 93840 Page 2 of 19
1 Introduction
Climate change includes increased droughts, shrinking glaciers, temperature rise and sea
level rise. Despite a scienti c consensus on global warming, climate change denial and doubts
still exist and the impacts of climate change and the extent to which it is caused by humans are
suspected. In our paper, we build a mathematical framework to determine a country's fragility
with a composite measure considering multiple factors including economic, political and
demographic indicators and climate change. In section 6, we select three countries, Syria, Cuba
and New Zealand to do case studies and further analyze the idea of tipping points in the speci c
contexts. In section 7, we examine the e ects of human intervention and estimate the total cost of
intervention based on our model and research. In section 8, we discuss our limitations and
strengths, consider the scenarios for smaller \states" and larger \states", and talk about potential
future research on this topic and our framework.
2 Assumptions
Our framework measures the market impacts of di erent factors such as climate change,
economic status, political stability and demographic pro les in the unit of US dollars
because we think it is more e cient to quantify and examine the extent of e ects.
We de ne the state as a country for consistency and data collection purpose.
We assume all data we obtain are trustworthy since all of sources are reliable. Thus, we are
con dent that our metrics can re ect the accurate condition.
3 Framework
3.1 De ning Fragility
Before devising our model, we rst de ne three possible states of a country: stable state,
vulnerable state, and fragile state.
Stable state A stable country should be less likely to be in uenced by the incidents such as
economic downturns, natural disasters, or political instability. Even if there is a crisis, a stable
country can quickly recover and return to its equilibrium state.
精品数模资料,各类比赛优秀论文、学习教程、写作模板与经验技巧、matlab程序代码资料等,尽在淘宝店铺:闵大荒工科男的杂货铺!

Team # 93840 Page 3 of 19
Vulnerable state A vulnerable country is more susceptible then a stable country to the
changes in the economy, politics, demographics and climate. A damaging event could cause the
country leave its current state and gradually become a fragile state; a favorable event could, on
the contrary, lead the country approach to the stable state.
Fragile state A fragile country is the currently experiencing uctuations in economy and
politics. It does not possess a strong economy or a well-regulated society. As a result, any small
turbulence could bring large impacts on all factors. Moreover, even if the country manages to
recover from these disturbances, it can only resume to its previous fragile state.
3.2 The Model
To quantify a country's fragility, we use a dynamic system, in terms of money (M), to
estimate the impacts of changes in di erent factors on a country. However, we believe that money
is not the sole predictor of the fragility of a country. Thus, in our model, we incorporate factors
including economy, politics, demographics and climate.
M = f(E; P; D; C)
(1)
Here, M is a function of E; P; D; and C, where M represents the market impact of those factors,
and E, P , D, C are the economic, political, demographical and climate change metrics
respectively. In this way, we could comprehensively analyze a country's capability to combat
unexpected events categorized under di erent sectors. We achieve this simulation by studying
how the variation in one parameter would in uence the overall fragility of the society.
Further developing our model, we realize that the derivative of M is an autonomous function,
that is growth rate of the market is not dependent on time. Yet, the growth rate of the market is
described as the positive impact minus the negative impact.
growth rate = positive($) negative($)
(2)
The positive impact considers the natural growth of the market itself accompanied with a limited
capacity which varies depending on the parameters. The negative impact is composed of human
intervention, disturbing climate change and other unfavorable variation in the
精品数模资料,各类比赛优秀论文、学习教程、写作模板与经验技巧、matlab程序代码资料等,尽在淘宝店铺:闵大荒工科男的杂货铺!
Team # 93840
Page 4 of 19
parameters that we have de ned.
M
BM
2
p
′
(M) = m
1
M(1
); g
′
(M) =
(3)
km
2
A
2
+ M
2
Inspired by the outbreak system by Ludwig et al. (1978), we obtain the functions above. p
′
(M)
represents the market growth with limited capacity, where m
1
describes the growth rate, m
2
represents the maximum of market capacity, and k is a scale factor that measures how economy,
politics, demographics and climate change would a ect the actual limit of the market. To come up
with the value of k, we use a composite index consisting of metrics in economy, politics,
demographics and climate change. g
′
(M) represents the negative impact that could potentially
slow down the market growth. In the early development stage, M is small and the negative
market impact would only show signs. However, when the market exceeds a critical level A, the
negative impact would turn on quickly. This happens when the harmful events have built up to
an extent that they cause a chain of reactions and the impact would nally reach to its limitation B.
Therefore, we have the whole model:
dM
= m
1
M(1
M
)
BM
2
(4)
dt
km
2
A
2
+ M
2
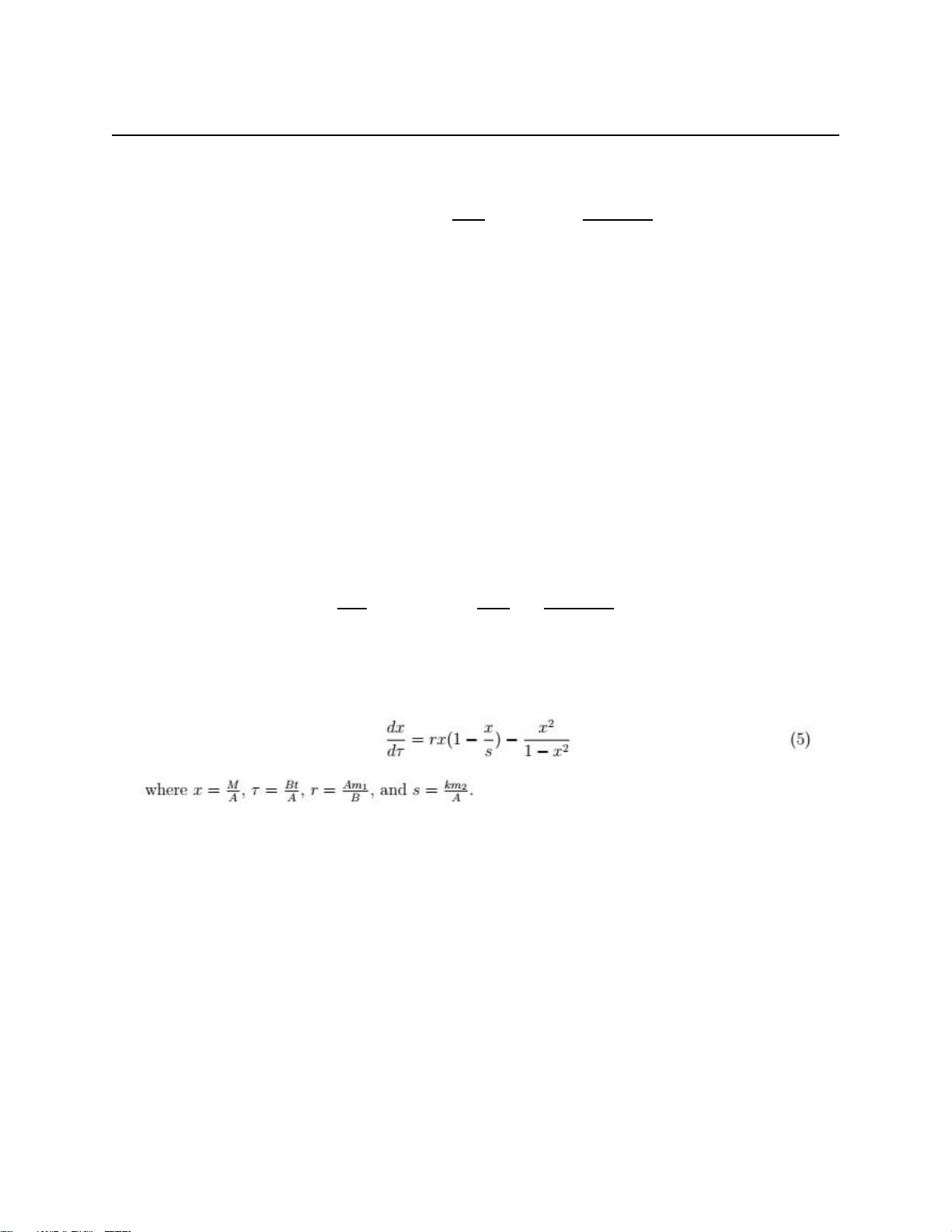
In order for us to examine the model more easily, we have converted the function into a
dimensionless form so that there are only two parameters, r and s.
Next step, we de ne all parameters and the techniques of processing relevant data.
4 Metrics for Assessing Fragility
Our metrics are similar to indicators used in the Fragile States Index. But, instead of rating
those factors, we target to collect both quantitative and qualitative data by coun-try and by year.
Besides, our metrics will be more concise because we nd that there are some overlapping
variables in FSI. For example, both Factionalized Elites of the Cohesion indicators and Uneven
Development in Economic indicators have considered the wealth dis-tribution and tries to assess
the equality of wealth (Marshall and Cole, 2017). In the end, using RStudio, we process all the
datasets and obtain a composite index.
精品数模资料,各类比赛优秀论文、学习教程、写作模板与经验技巧、matlab程序代码资料等,尽在淘宝店铺:闵大荒工科男的杂货铺!

Team # 93840 Page 5 of 19
4.1 Climate Change
Climate change is expected to have negative impacts on human societies and economies,
which may bring huge economic losses.
Occurrence of natural disasters
EM-DAT contains data on the occurrence and e ects of di erent types of natural disasters
worldwide from 1900 to present. However, the data is not publicly available. So we use
probabilistic risk results provided by UNISDR. The probabilistic risk results provide
results of an estimate of probable loss levels in a country based on historic events. This
data is useful because it considers damages caused by small, moderate and severe events
and obtains a robust metric for risking ranking and comparison.
Deforestation
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) contains comprehensive forestry datasets such
as forest coverage, reforestation, burned forest and economic value of the country's
forestry value. Among them, we select the annual Tree cover loss rate by country with unit
of hectare to re ect the deforestation rate as part of climate change.
Droughts/ oods
We use Precipitation Anomaly from World Bank to re ect occurrence of both droughts
and oods. This dataset includes historical monthly precipitation worldwide from 1900
to present.
Rising sea levels/shrinking glaciers
Although sea level rise is a major component of global climate change, it is not a typical
question for all countries. Since rising sea level and green house e ects are tightly related,
we only consider temperature rises instead of rising sea level.
Rising temperatures
We retrieve historical temperature data from World Bank. This data is called Global
Historical Climatology Network version 2 station monthly mean temperatures and station
metadata created by U.S. National Climatic Data Center. This dataset contains quality-
controlled, adjusted monthly mean temperature in unit of degree Celsius.
4.2 Economical Metrics
The economic meta-metrics considers factors related to economic decline within a country.
Except for the economic factors listed below, we have also considered unequal development
精品数模资料,各类比赛优秀论文、学习教程、写作模板与经验技巧、matlab程序代码资料等,尽在淘宝店铺:闵大荒工科男的杂货铺!
剩余23页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

pk_xz123456
- 粉丝: 2284
- 资源: 2353

下载权益

C知道特权

VIP文章

课程特权
开通VIP
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 一个用于 go 的 cron 库.zip
- 基于BJUI + Spring MVC + Spring + Mybatis框架的办公自动化系统设计源码
- 基于百度地图的Java+HTML+JavaScript+CSS高速公路设备管理系统设计源码
- 基于Django Web框架的母婴商城实践项目设计源码
- 一个使用 Go 编程语言和 WebAssembly 构建渐进式 Web 应用程序的包 .zip
- 基于Python桌面画笔的自动画图设计源码
- 基于Java语言的中医通病例问询子系统设计源码
- 基于Java语言的云南旅游主题设计源码
- 基于Java的ExamManageSystem软件详细设计课程设计源码
- 基于Java开发的简洁方便ORM工具BeetlSQL设计源码
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功