没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
内容概要:本文通过构建单层和多层通信网络模型,研究了信息在网络中的传播及其对公众意见的影响。首先定义了信息的三个属性(极端性、娱乐性和新颖性),并通过无异曲线确定了信息的内在价值。然后建立了一个动态信息流动模型,模拟了信息在网络中的传播过程,并通过BBC新闻的实际数据验证了模型的有效性和可靠性。最后引入阈值效应,建立了公众意见变化的机制,分析了四个主要参数对信息传播和公共意见的影响,得出了一些重要的结论。 适用人群:适用于从事社会网络研究的研究人员,以及关注信息传播和公众意见变化的学者和技术人员。 使用场景及目标:①了解信息在网络中的传播规律;②研究信息的属性对传播速度和范围的影响;③分析媒体和个体节点在信息传播中的不同角色;④预测未来社会信息网络的演化趋势。 其他说明:本文结合多个理论模型和实际案例,全面分析了信息在社会网络中的传播机制,为相关领域的研究提供了有力支持。同时,文中提出的多个假设和简化方法也为后续研究指明了方向。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

Team # 49436 Page 1 of 22
For office use only
T1
________________
T2
________________
T3
________________
T4
________________
Team Control Number
49436
Problem Chosen
D
For office use only
F1
________________
F2
________________
F3
________________
F4
________________
2016
MCM/ICM
Summary Sheet
Who Moved My Opinion?
As society’s networks evolve, information becomes a new kind of property because of its
great power to change public opinion. In our paper, we study the flow of information, the
evolution of communication networks and the information’s influence on publics.
At the beginning, we describe the topologies of two types of communications which are
Mass Communication and Interpersonal Communication. By combining these two types of
communications, we construct the single-layer communication network which represents a
certain communication technique. Then we study the six periods classified by the techniques
and construct the multi-layer information networks based on the single-layer network.
Then we define the three attributes of information which are extremeness, entertainment
and newness. By using the concept of Indifference Curve, we determine the inherent value of
information based on its attributes. And we find the news according to the Pareto Principle.
Combining the multi-layer information networks and the inherent value of information,
we construct the dynamic information flow model. This model is used to describe how
information flows within our society’s networks.
In order to validate our models, we find data of a piece of news of BBC Tech and simulate
the information flow in today’s society. We find that the real amount of received nodes are 44
and our model’s result is 43.85. Also, the standard error of received nodes’ amount is 4.63. So,
the predict capacity and the reliability of our model is great.
We define the capacity as the user percentage, and the relations as the relative strength of
networks. By introducing the Life-Cycle Theory, we build a prediction model to predict the
relations and capacities of networks in 2050. We find that there will be 7 communication
techniques at that time and the strongest network is a rising network whose capacity is 0.9611.
Later, we modify our information flow model by appending the opinion of people. Then
we use this model to describe the mechanism of the change of public opinion based on
Threshold Effect. Then we analyze the influence of four main parameters in our model and get
three main conclusions: (1) Stubborn minorities. (2) Powerful media. (3) More homogeneous
more efficient.
Finally, we give the strengths and weaknesses of our models.

Team # 49436 Page 2 of 22
Contents
1. Introduction .................................................................................................. 3
1.1 Problem Background ............................................................................... 3
1.2 Previous Research .................................................................................... 3
1.3 Our Work .................................................................................................. 3
2. Assumptions and Justification ...................................................................... 4
3. Topology of Information Networks .............................................................. 4
3.1 Two Types of Communications ............................................................... 4
3.2 A Slice of Toast: Construct Single-Layer Network .................................. 6
3.3 Slices of Toast: Construct Multi-Layer Networks ................................... 7
4. Model of Inherent Value of Information ...................................................... 8
4.1 Attributes of Information ......................................................................... 9
4.2 The Inherent Value of Information ........................................................... 9
4.3 Pick News out of Information ................................................................ 10
5. The Dynamic Information Flow Model ..................................................... 10
5.1 The Forwarding Rules of Media Nodes ................................................. 11
5.2 The Forwarding Rules of Person Nodes ................................................ 11
6. How a BBC’s News Disseminated: Validate Our Model ........................... 12
6.1 Find Data for Simulation ....................................................................... 12
6.2 Simulation .............................................................................................. 12
6.3 Results .................................................................................................... 13
7. The Evolution of Information Networks .................................................... 13
7.1 Definitions of capacities and relationships of networks ........................ 14
7.2 Emergence of a New Network ............................................................... 14
7.3 The Peak of Different Networks ............................................................ 14
7.4 Networks’ Evolution Based on Life-Cycle Theory ................................ 14
7.5 Prediction of Society’s Information Networks in 2050 ......................... 16
8. Change People’s Minds: An Opinion-Changing Model ............................. 16
8.1 The Opinion of Publics .......................................................................... 17
8.2 The Opinion-Changing Mechanism ....................................................... 17
9. Sensitivity analyses .................................................................................... 18
9.1 More people agree at first, more people agree at last ............................ 18
9.2 Want a bigger influence, go to find a media .......................................... 19
9.3 More Homogeneous, More Efficient ..................................................... 19
9.4 Media Nodes vs. Person Nodes ............................................................. 20
10. Strengths and Weaknesses .......................................................................... 21
10.1 Strengths .............................................................................................. 21
10.2 Weaknesses .......................................................................................... 21
11. References .................................................................................................. 22

Team # 49436 Page 3 of 22
1. Introduction
1.1 Problem Background
Under a certain network situation, the flow and the speed of information are
influenced by two main factors: (1) The inherent value of information. (2) Whether the
information is forwarded by big media. However, the evolution of the society’s
information network never stops, which allows us to study the evolution of the society’s
functions and structure by taking a historical perspective of flow of information.
In the paper, we have been asked to answer the following questions:
Establish models to describe the flow of information and find what makes
news.
Test our models’ reliability and prediction capability.
Predict the relationships and capacities of 2050’s society information network.
Define people’s opinion and use our models to find how publics’ interest and
opinion can be changed by information.
Test our model with the four aspects in the flow of information.
1.2 Previous Research
Scholars have been studying the society’s information networks for a long time.
At the beginning, they use the epidemic model to describe the flow of information. In
1998, D.J.Watts and S.H.Strogatz establish WS Small World Model to show the flow
of information and find that the speed of information is fastest in the Small World
Model[1]. In 2002, Staniford S, Paxson V and Weaver N use the Random Constant
Spread Model to study the information flow on the Internet [2]. D.J.Watts and
P.S.Dodds find that the flow of information is easily influenced by the people who are
easily influenced [3]. Also, there have been many experts studying the evolution of
society’s information networks. In these researches, Ellision.N.B’s and Castells M ‘s
work is impressive [4][5].
1.3 Our Work
We firstly build a single-layer information networks. Then we form a multi-layer
networks by combining single-layer networks with the same nodes. After that, we
define the information forward mechanism to allow information to flow in our networks.
Secondly, we use a real information flow’s example to validate our model. We find data
on the Facebook and use our model to simulate it. Thirdly, we explore the principle of
the information networks’ evolution. Then we make a prediction of capacities and
relationships in 2050.Fourthly, we model how people’s opinion be changed. According
to the threshold effect, we give a certain mechanism of people changing their mind.
Finally, we apply our models to analyze how information value, people’s initial opinion,
information source and topology influence spread range and public opinion.

Team # 49436 Page 4 of 22
2. Assumptions and Justification
The information does not change when it flows within the social information
networks. In the flow of information, the content of information may change
randomly and it is nearly impossible to consider the random changes in the contents
of information.
Information’s size is the same. In real world, the size of information will influence
the time. However, the size will only change the time and will not influence the
flow mode.
The population does not change. The population changes the nodes. But it will
not change the way in which information flows in the networks.
Information’s value satisfies the Pareto Principle. The Pareto principle states
the phenomenon that for many events, roughly 80% of the effects come from 20%
of the causes [8]. We assume that the value of information also accords with it.
Communication between people is directed. Although the relations of people are
undirected, the information flow has a direction. Directed communication can
describe the information flow better.
People will forward information that is valuable and consistent with their
opinion. In our daily life, people like the information of high inherent value and
consistent opinion with them. In addition, they are also willing to share it.
Once a new technique emerged, the network based on the former technique
will begin to decay. Usually, the new technique is better than the old one. Thus
people are more willing to use the new technique. The old technique will not decay
right away in real world. But the time difference is usually small, so the assumption
makes sense.
3. Topology of Information Networks
In this section, we will study the topology of information networks and construct
multi-layer networks of information flow. First, we introduce two types of
communications in information networks. Then we define the nodes and the edges in
our models. Furthermore, we use these two types of communications to build a single-
layer network which represents the network of a certain kind of communication
technique. Finally, we obtain the multi-layer networks with the consideration of several
communication techniques being used at the same time.
3.1 Two Types of Communications
In the information networks, there are mainly two types of communications: Mass
Communication and Interpersonal Communication. Mass Communications are the
communications between media and the publics. And Interpersonal Communications
are the communications between people. [6] We will discuss the two types of
communications because they have significantly different topologies.
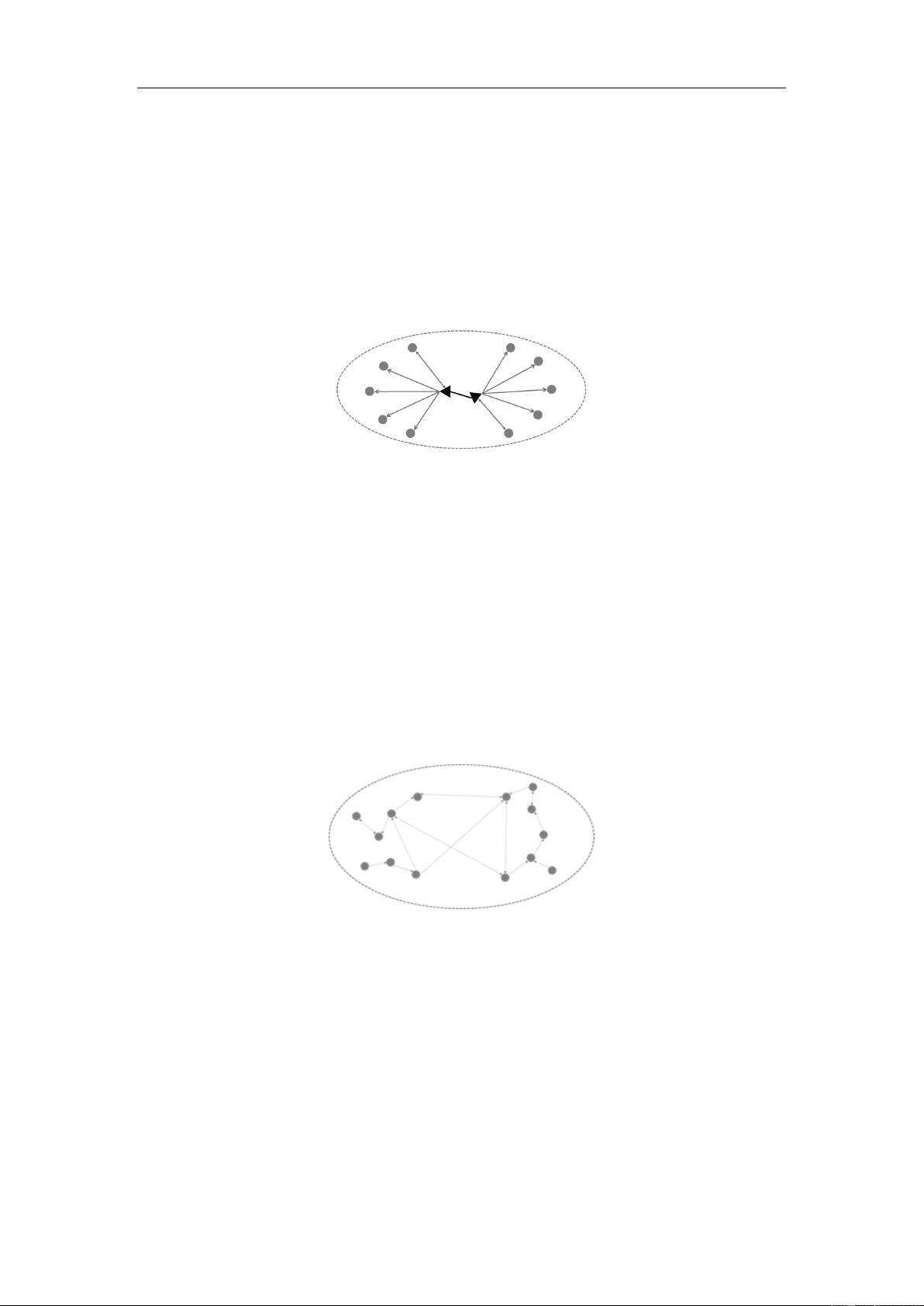
Team # 49436 Page 5 of 22
3.1.1 The Mass Communication
The Mass Communications developed quickly as technology improved. The first
medium come with the emergence of newspaper, which created a brand new way for
publics to gain information. With the inventions of the radio and television, media could
reach a wider range of publics. And as Internet went into more and more households,
media provided publics with varieties of information. One of the characters of Mass
Communications is that a medium can reach many people in a star topology, so this
kind of topology has a great ability of spreading information. Since media are connected,
the topology of the Mass Communication is as follow:
Figure 1. The topology of Mass Communication.
In this figure, dots represent publics and triangles represents media. Edges
represent the communications between publics and media. Nowadays, these media
include broadcasting companies such as ABC (American Broadcasting Corporation),
newspapers such as The Times and webs that have relatively great influence.
3.1.2 The Interpersonal Communication
The Interpersonal Communications always exist in our society. The very simple
example of Interpersonal Communications is speech. But as the techniques improved
quickly, the Interpersonal Communications became rich in forms from speech, mail,
telegraph, telephone to nowadays instant messages. Abundant techniques make
Interpersonal Communications much stronger and more complex. The topology of
Interpersonal Communications has random-like edges linking the person nodes. The
figure below shows a topology of Interpersonal Communications.
Figure 2. The topology of Interpersonal Communication.
3.1.3 Nodes
As we discussed above, we divide nodes into two types: one is media node, the
other is person node. Media nodes represent the media that are the centers of Mass
Communications. And person nodes represent publics. In our models, all of the nodes
have four attributes:
The type. The type of a node shows that this node is whether a media node or
person node.
The degree. The degree of a node is the number of nodes that connect to this
node.
The state. A node can be in one of three states which are
剩余21页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

pk_xz123456
- 粉丝: 2859
- 资源: 4045

下载权益

C知道特权

VIP文章

课程特权
开通VIP
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- NBA网上商城管理系统的设计与实现
- 精选毕设项目-爱靓女带后台.zip
- 精选毕设项目-城市地图带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-巴爷商城带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-集思笑话,含Vue.js后端,点赞.zip
- 精选毕设项目-简易记账带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-客家旅运带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-看书阅读带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-实时巴士带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-喵喵小说.zip
- 精选毕设项目-天气预报带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-式神猎手带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-外卖搭伴拼团php后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-图片预览带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-写笔记带后端.zip
- 精选毕设项目-游轮中心带后端.zip
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功