PowerConnect Application Note #18 February 2004
www.dell.com/networking 1
Understanding IGMP Snooping
This Application Note relates to the following Dell PowerConnect™ product(s):
• PowerConnect 33xx switches
Abstract
This Application Note explains how a feature called IGMP snooping can significantly reduce traffic from
streaming media and other bandwidth-intensive IP multicast applications. This document introduces the
IGMP protocol and provides step-by-step instructions for configuring Dell PowerConnect 33xx switches to
use IGMP snooping.
Applicable Network Scenarios
By default, layer 2 devices such as Dell PowerConnect 33xx switches treat IP multicast traffic in the same
manner as broadcast traffic – namely, by forwarding frames received on one interface to all other
interfaces. This may create excessive traffic on the network and degrade the performance of hosts
attached to the switches. Every frame received by each host generates an interrupt that the host must
process, robbing cycles that might instead be used by applications.
Layer 3 devices have less of a problem with rampant broadcast and multicast traffic because of their
ability to segment networks and forward traffic only to actual destination interfaces.
With Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping, Layer 2 devices also can make intelligent
multicast forwarding decisions by examining the contents of each frame’s Layer 3 IP header.
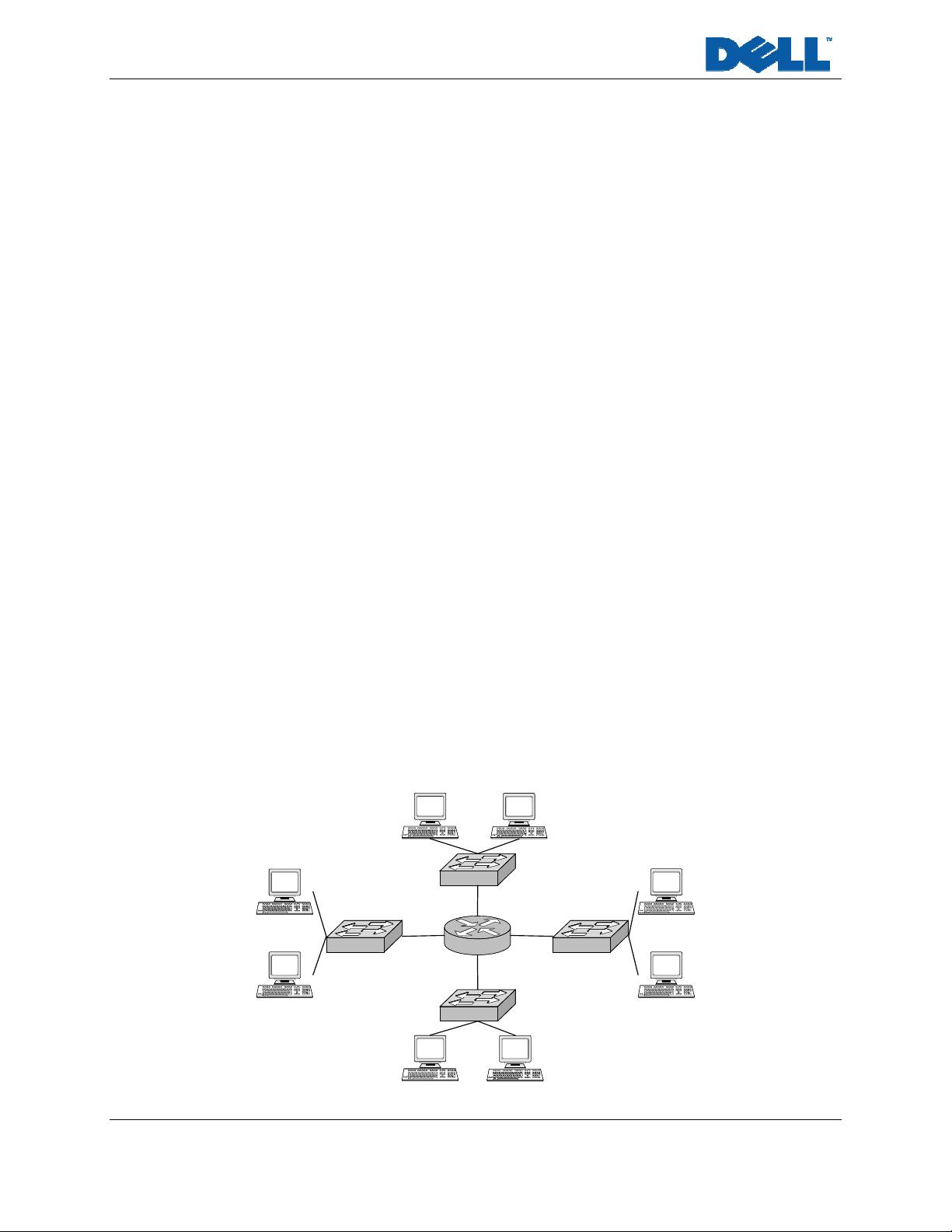
Consider the example of a heterogeneous Layer 2 and Layer 3 network that does not use IGMP snooping.
The figure below shows a simple network in which eight hosts connect to four Layer 2 switches. The
switches in turn connect to one router in the middle.
A
B
C
D















