第 35 卷 第 14 期 中 国 电 机 工 程 学 报 Vol.35 No.14 Jul. 20, 2015
2015 年 7 月 20 日 Proceedings of the CSEE ©2015 Chin.Soc.for Elec.Eng. 3569
DOI:
10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.14.011
文章编号:
0258-8013 (2015) 14-3569-08
中图分类号:
TM 73
含电热联合系统的微电网运行优化
贠
李正茂,张峰,梁军, 志皓,张俊
(电网智能化调度与控制教育部重点实验室(山东大学),山东省 济南市 250061)
Optimization on Microgrid With Combined Heat and Power System
LI Zhengmao, ZHANG Feng, LIANG Jun, YUN Zhihao, ZHANG Jun
(Key Laboratory of Power System Intelligent Dispatch and Control (Shandong University), Ministry of Education, Jinan 250061,
Shandong Province, China)
ABSTRACT: Along with the rapid development of energy
internet and the closer relationship between power and heat,
this paper proposed the combined heat and power dispatch
model for regional grid-connected microgrid. Taking into
consideration energy storage, time-of-use (TOU)
electricity
price and timing sequence characteristics of different types of
load and distributed generators, a microgrid consisting of a
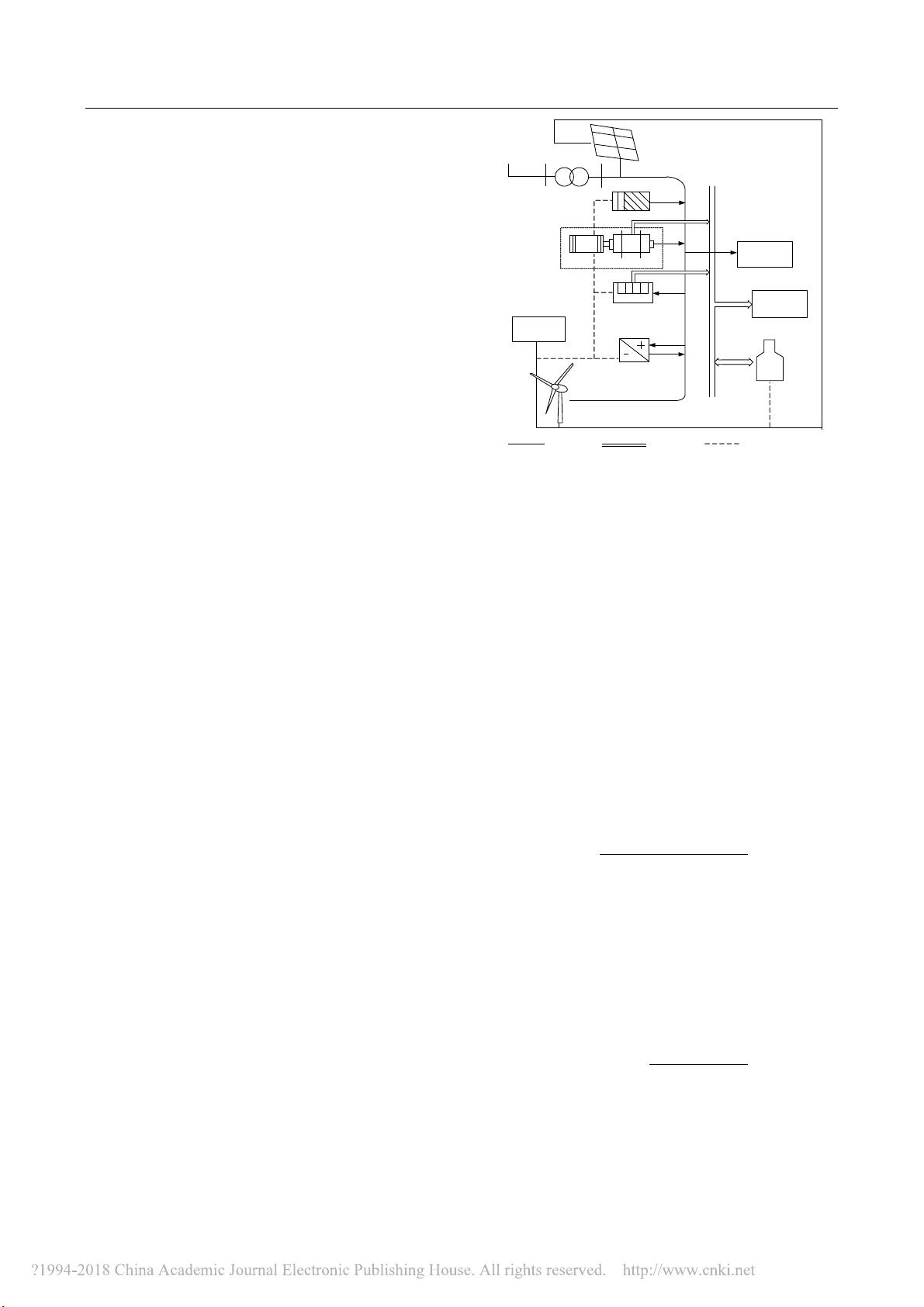
wind turbine, a photovoltaic, a combined heat and power
system, an electric boiler, a fuel cell and an energy
storage system was selected. The optimization method based
on the Cplex software was employed to obtain the optimal
costs and operation modes of the microsources in the
scheduling period, and then compared the model with two
traditional methods of scheduling. The simulation results
indicat that the proposed model could balance the power and
heat output and decrease the operation costs. This model can
serve as references for the development of energy internet and
power and heat scheduling.
KEY WORDS: energy internet; combined heat and power;
microgrid; economic dispatch ; energy storage system
摘要:在当前能源互联网迅速发展及电热联系日渐紧密的环
境下,提出基于电热联合调度的区域并网型微电网运行优化
模型。综合网内储能特性、分时电价、电热负荷与分布式电
源的时序特征,以包含风机、光伏电池、热电联产系统、电
锅炉、燃料电池和储能系统的并网型微电网为例,采用 Cplex
优化软件求得调度周期内各微电源最佳出力及总运行成本,
并与两种常见电热调度方式进行比较。仿真算例表明:联合
调度模型能实现电热统一协调调度并降低微电网运行成本。
该模型可为电热之间能源互联及规划运营提供参考。
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(51307101,51177091);山东省
优秀中青年科学家科研奖励基金(BS2013NJ011)。
Project Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China
(51307101, 51177091); Science and Technology Foundation for
Middle-aged and Young Scientist of Shandong Province (BS2013NJ011).
关键词:能源互联网;电热联合;微电网;经济调度;储能
系统
0 引言
随着社会能源结构的调整、电力系统的发展及
储能技术的日益成熟,蓄电池及超级电容等电储能
设备被大量应用到电力系统中以提高新能源渗透
率并实现对电能的削峰填谷
[1]
。本质上,一切能量
(如电能、热能和机械能等)的存储均可被称为储能,
但目前储能在电力系统中的应用实际上仅限于电
能的存储,即电能转换为其他形式的能量并在需要
时转换为电能回馈到电力系统中去。因此,电力系
统中的储能应用大大局限了储能技术的使用范畴。
而包括电力系统、热力系统和燃气系统等在内的供
能系统,目前均为各自规划、单独设计、独立运行,
出现问题时也都在各系统内单独解决,系统间缺乏
协调,不利于从全社会总能源供应的层面实现清
洁、高效、可靠的目标
[2]
。
2013 年 8 月,国家电网积极倡导“以电代煤、
以电代油、电从远方来”的能源消费新模式,同时,
随着能源互联网发展及电气化水平的提高,电能转
化为热能消耗的比例将越来越大
[2-3]
,电、热系统的
联系也将日渐紧密。综合考虑电能“易传输、难存
储”而热能“易存储、难传输”的互补性特征,在
区域型微电网的电、热力系统间加入储能及电热转
换单元从而对电热联合调度,可更好地匹配可再生
能源出力及电热负荷的峰谷特性,从而总体提高能
源系统可控性
[4]
。
针对微电网电热调度的研究,多以优化微电网
经济运行、提高一次能源利用率为主。文献[5-7]均
以一个包含可再生能源、电储能、热电联产系统等