没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
内容概要:该论文提出了一种高效的HEVC(高效率视频编码)视频隐藏算法,主要创新点在于采用修改后的EMD(利用修改方向)编码方法对不同大小的预测单元(PU)分区模式进行调整,从而显著提升数据嵌入容量,保持良好的视觉质量。通过对现有的预测单元分配方式进行改进以及对不同的映射方式进行了实验评估,研究结果显示该方法不仅大幅提高了数据嵌入能力而且在视觉质量和比特率方面表现良好。文中还包括对比现有几种优秀的基于PU划分方式的数据隐匿方法,并对其抗隐蔽检测性能进行了评估,验证了该新算法的安全性和实用性。 适用人群:信息安全研究人员、多媒体通信专家、从事视频处理及编码工作的高级技术人员。 使用场景及目标:用于版权保护、身份认证等领域,旨在为HEVC格式视频提供一种更加安全高效的数据隐藏手段,在不明显损害图像画质的情况下秘密传输信息。 其他说明:本研究涉及大量的数学模型推导和技术实现细节探讨,并借助大量实测数据证明了该算法相对于传统方法的优势所在。对于未来进一步优化此技术路线也有一定指导意义。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

RES E AR C H Open Access
Steganography algorithm based on
modified EMD-coded PU partition modes
for HEVC videos
Zhenzhen Zhang
1
, Zhaohong Li
2*
, Jindou Liu
2
, Huanma Yan
3
and Lifang Yu
1
* Correspondence: zhhli2@bjtu.edu.
cn
2
School of Electronic and
Information Engineering, Beijing
JiaoTong University, Beijing 10004 4,
China
Full list of author information is
available at the end of the article
Abstract
As High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) is a worldwide popular video coding standard,
the steganography of HEVC videos has gained more and more attention. Prediction
unit (PU) is one of the most important innovative modules of HEVC; thus, PU partition
mode-based steganography is becoming a novel branch of HEVC steganography.
However, the embedding capacity of this kind of steganography is limited by the types
of PU partition modes. To solve the problem, modified exploiting modification
direction (EMD)-coded PU partition mode-based steganography is proposed in this
paper, which can hide a secret digit in a (2
n + x
− 1)-ary notational system in a pair of PU
partition modes and thus enlarging the capacity. Furthermore, two mapping patterns
for PU partition modes are analyzed, and the one that performs the better is selected
as the final mapping pattern. Firstly, 8 × 8- and 16 × 16-sized PU partition modes are
recorded according to the optimal mapping pattern in the video encoding process.
Then, PU partition modes are modified by using the proposed method to satisfy the
requirement of secret information. Finally, the stego video can be obtained by re-
encoding the video with the modified PU partition modes. Experimental results show
that the embedding capacity can be significantly enlarged, and compared with the
state-of-the-art work, the proposed method has much larger capacity while keeping
high visual quality.
Keywords: Steganography, PU partition mode, Modified EMD, High Efficiency Video
Coding (HEVC)
1 Introduction
Steganography is a hot research issue in the field of information security. It can imper-
ceptibly conceal secret information in the carrier such as texts, images, and videos and
has extensive applications in copyright prote ction, identity authentication, covert com-
munication, and so on. Among the various branches of steganography technique, video
steganography has attracted more and more attention because video is one of the most
widely used digital media and has larger capacity for data embedding compared with
other carriers such as texts and audios.
Video steganography is closely linked to video coding standard. High Efficiency
Video Coding (HEVC) is the latest video coding standard possessing the best
© The Author(s). 2021 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which
permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the
original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or
other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit
line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by
statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain per mission directly from the copyright holder. To view a
copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
EURASIP Journal on Image
and Video Processing
Zhang et al. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing (2021) 2021:7
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13640-021-00547-5

compression efficiency compared with its predecessors such as H.264. HEVC is specif-
ically designed for the increasingly popular high-definition and ultra-high-definition
videos [1]. At present, a number of enterprises including Apple and Microsoft have de-
signed products supporting HEVC standard. Therefore, it is worthwhile to develop
steganography schemes for HEVC videos.
Modifying DCT/DST coefficients is one common approach to hide data in com-
pressed HEVC videos. Chang et al. [2] classified the blocks in intra-coded frames into 5
categories. Different perturbation patterns were introduced to the luma blocks of each
category to avoid intra-frame distortion drift. Similar ideas were taken by Liu et al. to
embed data in 4× 4 DCT blocks [3] and 4× 4 DST block s [4] of selected fram es. Ref.
[2–4] were selection-based intra drift free methods. Arige et al. [5] designed the first
cancelation-based intra drift free method for HEVC videos which was more general
than Ref. [2–4]. Besides 4 × 4 blocks, 8 × 8 blocks, and 16 × 16 blocks which satisfy cer-
tain coarseness conditions were also employed as carriers in Ref. [6], which made its
embedding capacity enlarged.
Intra-prediction mode (IPM)-based steganography is also a hot topic for HEVC vid-
eos. Wang et al. [7] proposed an IPM-based stegography method by introducing (4, 3)
standard array decoding table. The method achieved satisfying embedding capacity
while modifying IPMs as few as possible. After that, the authors designed a new map-
ping table between the angle differences of IPMs and secret information to embed data
[8]. The study in [9] explored diamond coding to increase the embedding capacity and
could conceal 2–3 bits data by modifying 2 IPMs at most. Wang et al. [10] summarized
the existing IPM-based steganography methods and proposed a cover selecting rule by
analyzing the probability distribution of 4 × 4 IPMs.
Besides DCT/DST coefficients and IPM, motion vector and quantization parameter
(QP) are another two popular carriers to hide secret information. Van et al. [11 ] pro-
posed a low complexity steganography method by modifying the motion vector differ-
ences and DCT coefficients selected from the frames classified by the inter-prediction
dependencies between them. An efficient steganography method based on motion vec-
tor space encoding was presented in [12]. Since not every CTU could be used as car-
rier, the capacity of the method was limited. In the aspect of QP based steganography
methods, Zuo et al. [13] combined the just noticeable coding distortion model and
exploiting modification direction method to modify the optimal QP values for each
coding unit (CU) and embed secret information.
The aforementioned HEVC steganography methods are based on the traditional car-
riers that are the same with previous video coding standards such as MPEG-4 and
H.264. However, HEVC has developed some innovative technologies including flexible
quatree partition architecture (CU, PU, and transform unit (TU)) and sample adaptive
offset. The innovative technologies also offer abunda nt carrie rs to embed secret infor-
mation, thus they opened up a new research field for HEVC steganography.
Shanableh [14] utilized the flags indicating the partition of 16 × 16 sub-CUs as car-
riers to embed data, where up to an average payload of 32.6K bit/s can be achieved.
Tew et al. [15] divided the prediction block (PB) into two categories. One indicated “0”
and the other indicated “1.” Data were hidden by mod ifying the partition mode of PBs.
Inspired by Ref. [15], Xie et al. [16] classified the PU partition mode into 3 categories
except for “N × N”and “
2N ×2N” mode, which enl arged the embedding capacity. By
Zhang et al. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing (2021) 2021:7 Page 2 of 20

modifying Ref. [16], a multi-level steganography method was designed in Ref. [17],
where the embedding capacity can be adjusted according to the actual requirement.
Exploiting modification direction (EMD) was applied to PU partition mode in Ref. [18]
to further enlarge the embedding capaci ty. These PU partitioning mode based stega-
nography methods have achieved excellent visual quality, but their capacities are rela-
tively low for the limited number of CUs. Even the method of [18], which has
improved the capacity a lot compared with [15–17], still required three consecutive
CUs to form a group to hide a digit in 7-ary notational system. Stimu lated by this, we
adopt a modified EMD coding method [19] which only required two elements in each
group to pre-code PU partition modes. By modifying the characteristic value function
and designing a new codebook, a high-performance HEVC video steganography is pro-
posed in this paper.
CUs with differen t sizes own different PU partition modes, which have an impact on
embedding capacity; thus, we investigate the variety of PU partition modes for different
sized CUs and select CUs with sizes of 16 × 16 and 8 × 8 to hide information. Further-
more, it is essential to map PU partition modes into integers for PU partition modes
based steganography, and two mapping patterns are discussed in this paper. After that,
PU partition modes of 16 × 16-sized CUs and 8 × 8-sized CUs are forced to be altered
according to the modified EMD rules to embed secret data. The experimental results
show that the proposed method has much larger capacity than the state-of-the-art
works while keeping high visua l quality.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. CU and PU partition modes in HEVC
are demonstrated in Section 2. Section 3 discusses the modified EMD method for PU
partition modes and the designed mapping patterns. Detailed description of the pro-
posed steganography method is also presented in Section 3. Experimental results are il-
lustrated in Section 4, and Section 5 summarizes the paper.
2 Background of CU and PU partition modes in HEVC
HEVC was jointly released by ITU-T [20] and ISO/IEC [21] and has brought in various
new techniques to increase compression efficiency. One of the key techniques is the
introduction of quadtree partition structure. In the quadtree partition structure, CU,
PU, and TU are introduced. CU is the basic coding unit, and PU and TU are the basic
units for intra/inter prediction and transform/quantization, respectively.
In encoding process, an image is firstly divided into non-overlapping coding tree unit
(CTU) whose size is set by the user with 64 × 64 as default. Then each CTU is recur-
sively divided into square shapes in a quadtree structure. Every leaf node of a CTU is
called a CU which is the basic coding unit in HEVC. There are 4 allowed types of CUs:
64 × 64, 32 × 32, 16 × 16, and 8 × 8. As shown in Fig. 1 b, the quadtre e structure of the
left top CTU surrounded by red square in Fig. 1a is displayed. In Fig. 1a, the white lines
indicate the boundary of CUs, and the digit denote s the coding order of each CU. We
can see that the quadtree partition of CTU is closely related to the image texture. In
the region with simple texture such as the tree trunk in Fig. 1a, larger-sized CUs are
adopted. While in the region with complex texture such as the border between the tree
trunk and the road, more detailed CUs are adopted.
When performing CTU quadtree tree partition, PU partition mode is determined for
each CU in the traversal way according to the rate distortion function. PU partition
Zhang et al. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing (2021) 2021:7 Page 3 of 20
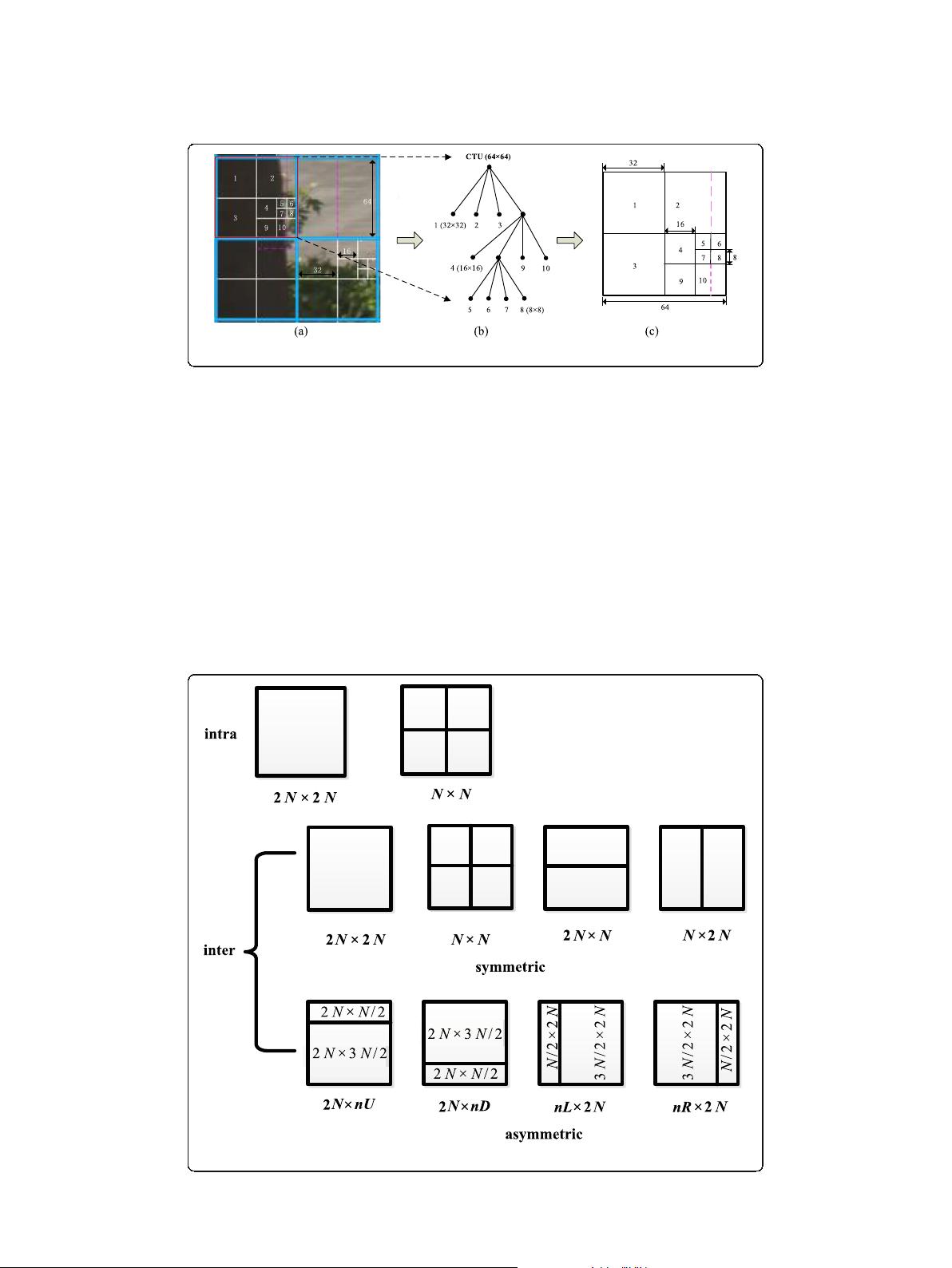
modes are different under different prediction mode, as presented in Fig. 2. In intra
prediction mode, one 2N ×2N (N = 4, 8, 16, 32) CU can be encoded as one single PU
or be further split into 4 PUs with equal size (N × N). In inter prediction mode, the CU
can be divided into symmetric or asymmetric PUs. Both symmetric and asymmetric
PUs are composed of 4 partition modes. Figure 1c shows the PU partition mode of the
left top CTU marked red in Fig. 1a. The black line implies that the PU has the same
size as the corresponding CU, and the purple line means that the CU needs to be sub-
divided into two PUs in order to get minimum rate distortion.
From Fig. 2, we can see that more various PU partition modes are available in inter pre-
diction mode than in intra prediction mode. Since we aim to hide information by modify-
ing the PU partition mode, we select the PU partition mode in inter prediction mode,
which means that P pictures are adopted to hide information in this paper. Li et al. [18]
Fig. 1 Example of quadtree partition of CTU into CUs and PUs. a CTU partition. b CU partition quatree. c PU partition
Fig. 2 PU partition modes in different prediction modes
Zhang et al. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing (2021) 2021:7 Page 4 of 20
剩余19页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

码流怪侠
- 粉丝: 2w+
- 资源: 557
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 西门子全自动定长裁切机PLC程序:高精度切割,简洁注释,适合新手编程练习,威纶通触摸屏控制,13西门子200PLC全自动定长度裁切机设备程序(含威纶通触摸屏程序)该程序已经在设备上应用,切割长度精度高
- 基于双闭环控制策略的Buck变换器:Pi控制实现电压稳定与动态优化,输出功率达百瓦级,支持输入电压调整与输出电压自定义,Matlab仿真文件下载链接 ,Buck变器,双闭环控制策略,电压环和电流环均采
- 成熟稳定运行的智能立体仓库管理系统案例:西门子PLC控制下的堆垛机与输送机联动实践,立体仓库 堆垛机 输送机 智能物流 项目是本人以前做的工程项目案例,是成熟的并且稳定的运行在客户现场的程序,项目有
- Matlab Simulink单相光伏储能模型:高效太阳能发电与蓄电池储能系统仿真,MPPT电导增量法跟踪,并网等级与个人使用需求解决方案,Matlab simulink模型,单相光伏储能模型 可再生
- 掌握COMSOL激光烧蚀技术:精通脉冲激光打孔包与动网格固体传热模块的应用艺术 ,comsol激光烧蚀脉冲激光打孔包会 掌握一个等于学会一整套 COMSOL 主要涉及模块:动网格、固体传热 ,核心关
- 西门子1200 PLC程序与项目模板:从硬件选型到HMI界面设计的全面指南,西门子1200程序和项目模板,适用初学者 本资料从一个项目出发,包含了 1.如何进行硬件设备的选型; 2.电气原理图绘制标准
- 雪豹速清v2.1.8.apk
- 基于Simulink的汽车LAR-LQG半主动与主动悬架系统研究,汽车lar lqg 半主动 主动悬架 simulink ,核心关键词:汽车; LAR; LQG; 半主动悬架; 主动悬架; Simu
- 基于车辆运动学模型的Hybrid-Astar路径规划算法实现研究,25混合A星算法路径规划Hybrid-Astar 以车辆的运动学模型为节点,以当前点到终点的Astar距离和RS距离两者最大的距离作为
- 光储电压电流双环并网控制MATLAB仿真详解:涵盖光伏阵列、MPPT升压回路等模块及讲解文档,光储电压电流双环并网控制MATLAB仿真,包含光伏阵列模型、MPPT升压回路、储能电池模型、电压电流双环控
- 模块化多电平换流器MMC-HVDC直流输电系统仿真研究:载波移相调制与换流站控制策略详解(附参考文献与参数计算,适合初学者),模块化多电平流器,MMC-HVDC直流输电系统,单个桥臂4个子模块(5电平
- 基于LQR最优控制算法的车辆轨迹跟踪控制模型 基于质心侧偏角等动力学参数建立模型,优化误差实现实时轨迹跟踪,仿真效果优异 ,基于LQR最优控制算法实现的轨迹跟踪控制,建立了基于车辆的质心侧偏角、横摆角
- 基于模型预测控制(MPC)的车速控制算法研究:燃油汽车上下层控制器设计与实现,可应用于代码生成与实车试验,适用于多种车速需求场景,附复现资料 ,基于模型预测MPC实现的车速控制,控制目标为燃油汽车,采
- "PMSM永磁同步电机的自抗扰控制策略与matlab Simulink仿真实现",【PMSM自抗扰控制】 PMSM 永磁同步电机 ADRC 自抗扰控制 matlab simulink 仿真 (1)采
- PFC单轴压缩下声发射模拟演化规律及胶结破坏能实时监测分析,PFC单轴压缩声发射模拟演化规律及胶结破坏能监测 ,PFC; 压缩声发射; 模拟演化规律; 胶结破坏; 监测,PFC单轴压缩声发射:胶结破
- COMSOL针-板正流注放电模型:基于流体方程的光电离过程参考模型,[COMSOL针-板正流注放电模型]采用流体方程,包含光电离过程,有需要的可以拿去作为参考 ,核心关键词:COMSOL针-板正流
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功