没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
TI-TL16C450.pdf

试读
31页
UART收发器TI-TL16C450.pdf
UART(Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter)是一种异步串行通信接口标准,广泛应用于计算机、通信设备和其他电子系统之间的数据交换。TI-TL16C450是一款高性能的UART收发器芯片,由Texas Instruments公司生产,具有丰富的功能特性和高-speed数据传输能力。
可编程的串行通信接口
TI-TL16C450采用可编程的串行通信接口,支持5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-Bit字符长度、Even-, Odd-, or No-Parity位生成和检测、1-, 1 1/2-, or 2-Stop位生成等多种串行通信模式。该芯片还可以生成内部16倍时钟,以满足高速数据传输的需求。
高speed数据传输
TI-TL16C450支持高达256 Kbit/s的高速数据传输速率,满足高速数据传输的需求。同时,芯片还具有False Start Bit检测能力,可以检查串行数据流中的错误。
独立的接收器时钟输入
TI-TL16C450具有独立的接收器时钟输入,允许用户独立地控制接收器时钟频率。这使得该芯片能够在各种异步通信系统中发挥作用。
全面状态报告能力
TI-TL16C450具有全面状态报告能力,可以报告串行数据流中的错误,包括溜带、奇偶校验、溜带、数据溜带等。该芯片还可以生成线路中断信号,以便及时地响应串行数据流中的错误。
三态TTL驱动能力
TI-TL16C450具有三态TTL驱动能力,可以驱动双向数据总线和控制总线,满足各种异步通信系统的需求。
内部诊断能力
TI-TL16C450具有内部诊断能力,可以模拟串行数据流中的错误,包括溜带、奇偶校验、溜带、数据溜带等。这使得用户可以快速地检测和isolated串行数据流中的错误。
完全优先中断系统
TI-TL16C450具有完全优先中断系统,可以根据不同的中断优先级来控制串行数据流中的错误。这使得该芯片能够在各种异步通信系统中发挥作用。
调制解调器控制功能
TI-TL16C450具有调制解调器控制功能,可以控制串行数据流中的调制解调器信号,满足各种异步通信系统的需求。
易于接口到流行的微处理器
TI-TL16C450可以轻松地接口到流行的微处理器,例如Intel、Motorola、Zilog等。这使得该芯片可以广泛应用于各种电子系统中。
TI-TL16C450是一款功能强大且高性能的UART收发器芯片,能够满足各种异步通信系统的需求。
SLLS037C − MARCH 1988 − REVISED JANUARY 2006
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D Programmable Baud Rate Generator Allows
Division of Any Input Reference Clock by 1
to (2
16
−1) and Generates an Internal 16×
Clock
D Full Double Buffering Eliminates the Need
for Precise Synchronization
D Standard Asynchronous Communication
Bits (Start, Stop, and Parity) Added or
Deleted to or From the Serial Data Stream
D Independent Receiver Clock Input
D Transmit, Receive, Line Status, and Data
Set Interrupts Independently Controlled
D Fully Programmable Serial Interface
Characteristics:
− 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-Bit Characters
− Even-, Odd-, or No-Parity Bit Generation
and Detection
− 1-, 1 1/2-, or 2-Stop Bit Generation
− Baud Generation (dc to 256 Kbit/s)
D False Start Bit Detection
D Complete Status Reporting Capabilities
D 3-State TTL Drive Capabilities for
Bidirectional Data Bus and Control Bus
D Line Break Generation and Detection
D Internal Diagnostic Capabilities:
− Loopback Controls for Communications
Link Fault Isolation
− Break, Parity, Overrun, Framing Error
Simulation
D Fully Prioritized Interrupt System Controls
D Modem Control Functions (CTS, RTS, DSR,
DTR
, RI, and DCD)
D Easily Interfaces to Most Popular
Microprocessors
D Faster Plug-In Replacement for National
Semiconductor NS16C450
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications o
f
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
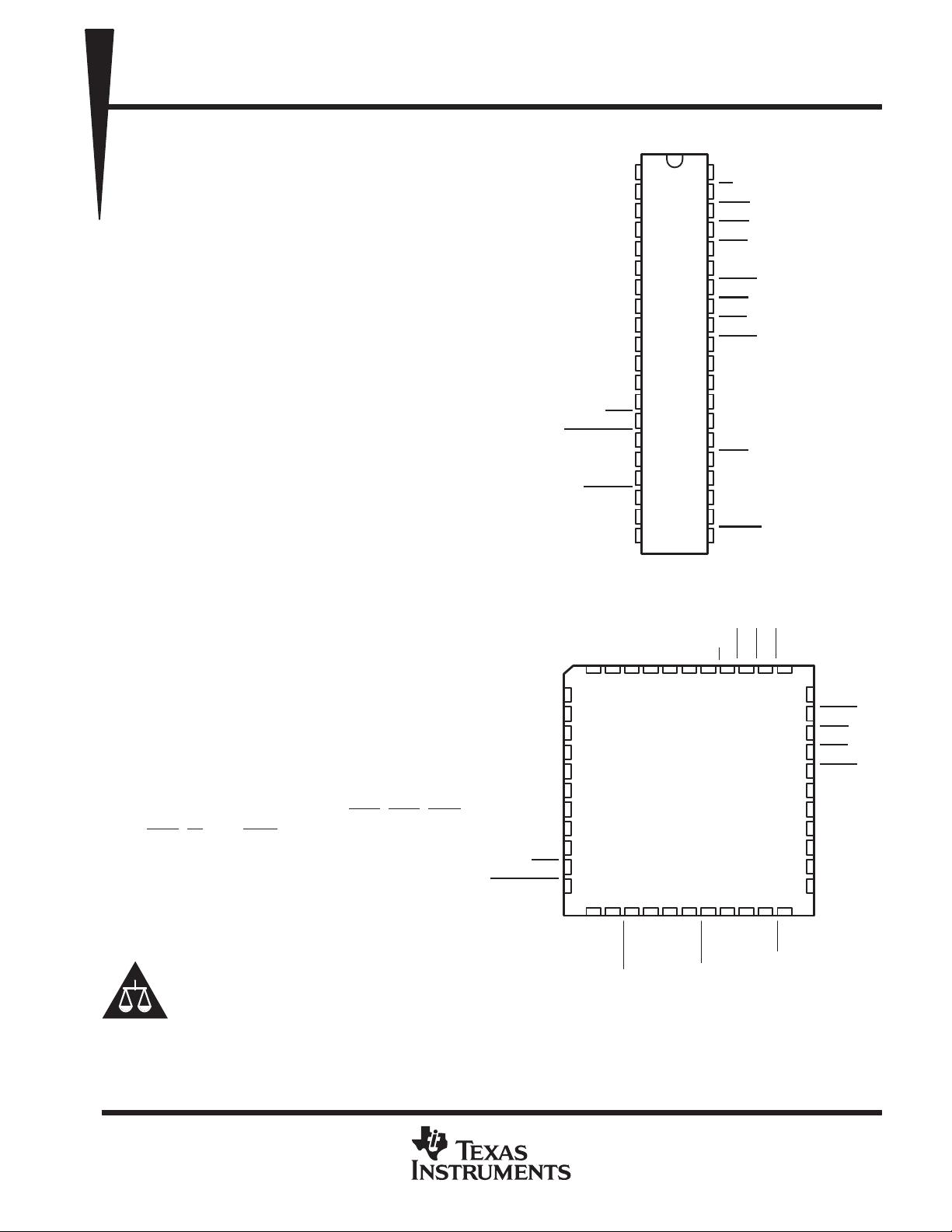
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
RCLK
SIN
SOUT
CS0
CS1
CS2
BAUDOUT
XTAL1
XTAL2
DOSTR
DOSTR
V
SS
V
CC
RI
DCD
DSR
CTS
MR
OUT1
DTR
RTS
OUT2
INTRPT
NC
A0
A1
A2
ADS
CSOUT
DDIS
DISTR
DISTR
N PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
MR
OUT1
DTR
RTS
OUT2
NC
INTRPT
NC
A0
A1
A2
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
18 19
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
D5
D6
D7
RCLK
SIN
NC
SOUT
CS0
CS1
CS2
BAUDOUT
20 21 22 23
FN PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
RI
DCD
DSR
CTS
54 321644
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
NC
DISTR
DDIS
CSOUT
ADS
XTAL1
XTAL2
DOSTR
DOSTR
NC
DISTR
42 41 4043
24 25 26 27 28
NC − No internal connection
V
CC
V
SS
NOTE: 40-pin DIP (N package) will be obsoleted as of 7/30/2006. Please
contact your local distributor or TI Sales Office for more information.
!" #!$% &"'
&! #" #" (" " ") !"
&& *+' &! #", &" ""%+ %!&"
", %% #""'
Copyright 1988 − 2006, Texas Instruments Incorporated

SLLS037C − MARCH 1988 − REVISED JANUARY 2006
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
description
The TL16C450 is a CMOS version of an asynchronous communications element (ACE). It typically functions
in a microcomputer system as a serial input/output interface.
The TL16C450 performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data received from a peripheral device or modem and
parallel-to-serial conversion on data received from its CPU. The CPU can read and report on the status of the
ACE at any point in the ACE’s operation. Reported status information includes the type of transfer operation
in progress, the status of the operation, and any error conditions encountered.
The TL16C450 ACE includes a programmable, on-board, baud rate generator. This generator is capable of
dividing a reference clock input by divisors from 1 to (2
16
−1) and producing a 16× clock for driving the internal
transmitter logic. Provisions are included to use this 16× clock to drive the receiver logic. Also included in the
ACE is a complete modem control capability and a processor interrupt system that may be software tailored
to the user’s requirements to minimize the computing required to handle the communications link.
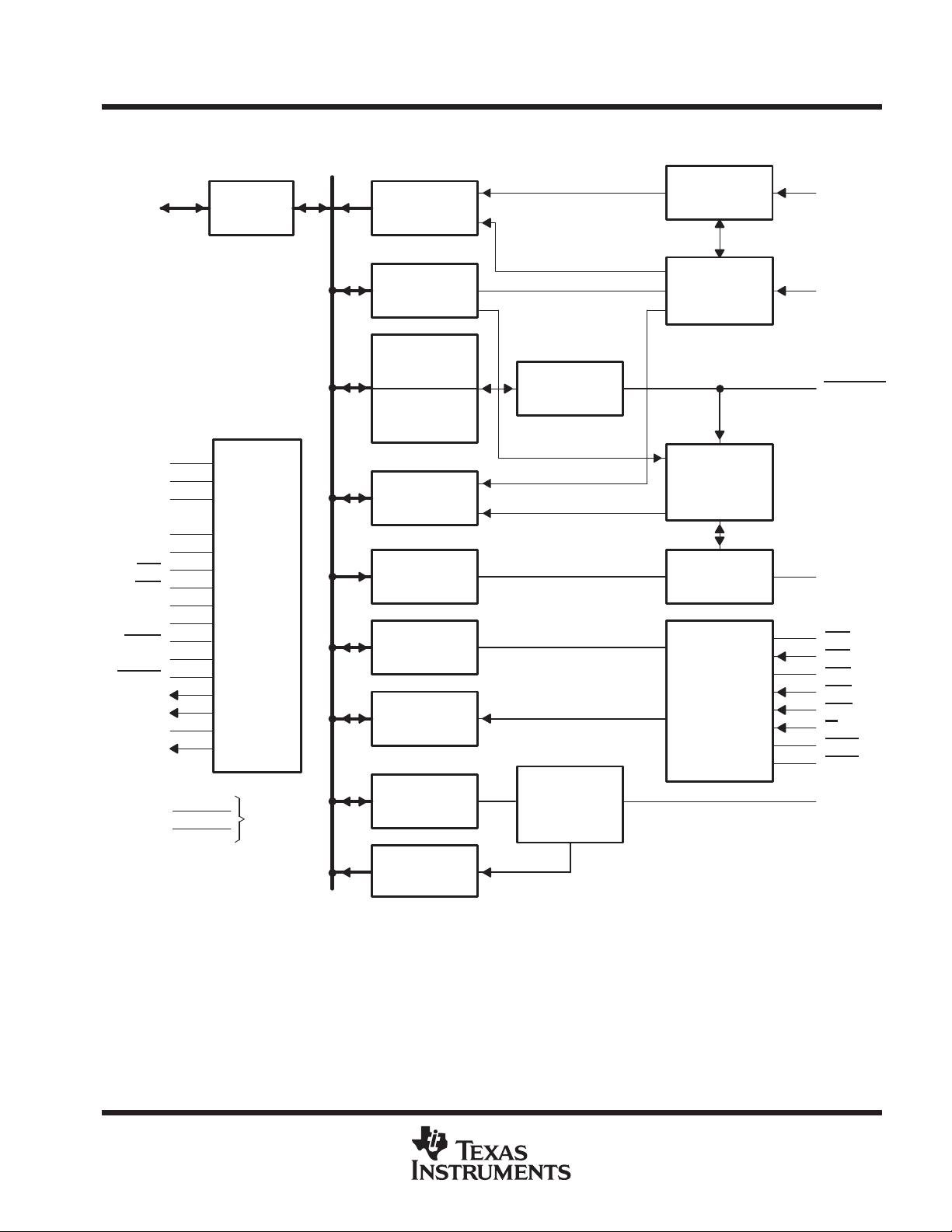
SLLS037C − MARCH 1988 − REVISED JANUARY 2006
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
block diagram
Receiver
Buffer
Register
Line
Control
Register
Divisor
Latch (LS)
36
40
37
41
42
43
38
35
13
17
10
11
31
30
29
14
15
16
28
39
25
24
21
20
26
27
18
19
2 − 9
33
A0
A1
A2
CS0
CS1
CS2
ADS
MR
DISTR
DISTR
DOSTR
DOSTR
CSOUT
XTAL1
XTAL2
D7−D0
DDIS
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
DCD
RI
OUT1
OUT2
SOUT
BAUDOUT
RCLK
SIN
INTRPT
V
CC
V
SS
44
22
Divisor
Latch (MS)
Line
Status
Register
Transmitter
Holding
Register
Modem
Control
Register
Modem
Status
Register
Interrupt
Enable
Register
Interrupt
I/O
Register
Interrupt
Control
Logic
Baud
Generator
Receiver
Shift
Register
Receiver
Timing and
Control
Data
Bus
Buffer
Internal
Data Bus
Transmitter
Timing and
Control
Transmitter
Shift
Register
Modem
Control
Logic
Power
Supply
Select
and
Control
Logic
Terminal numbers shown are for the FN package.
SLLS037C − MARCH 1988 − REVISED JANUARY 2006
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
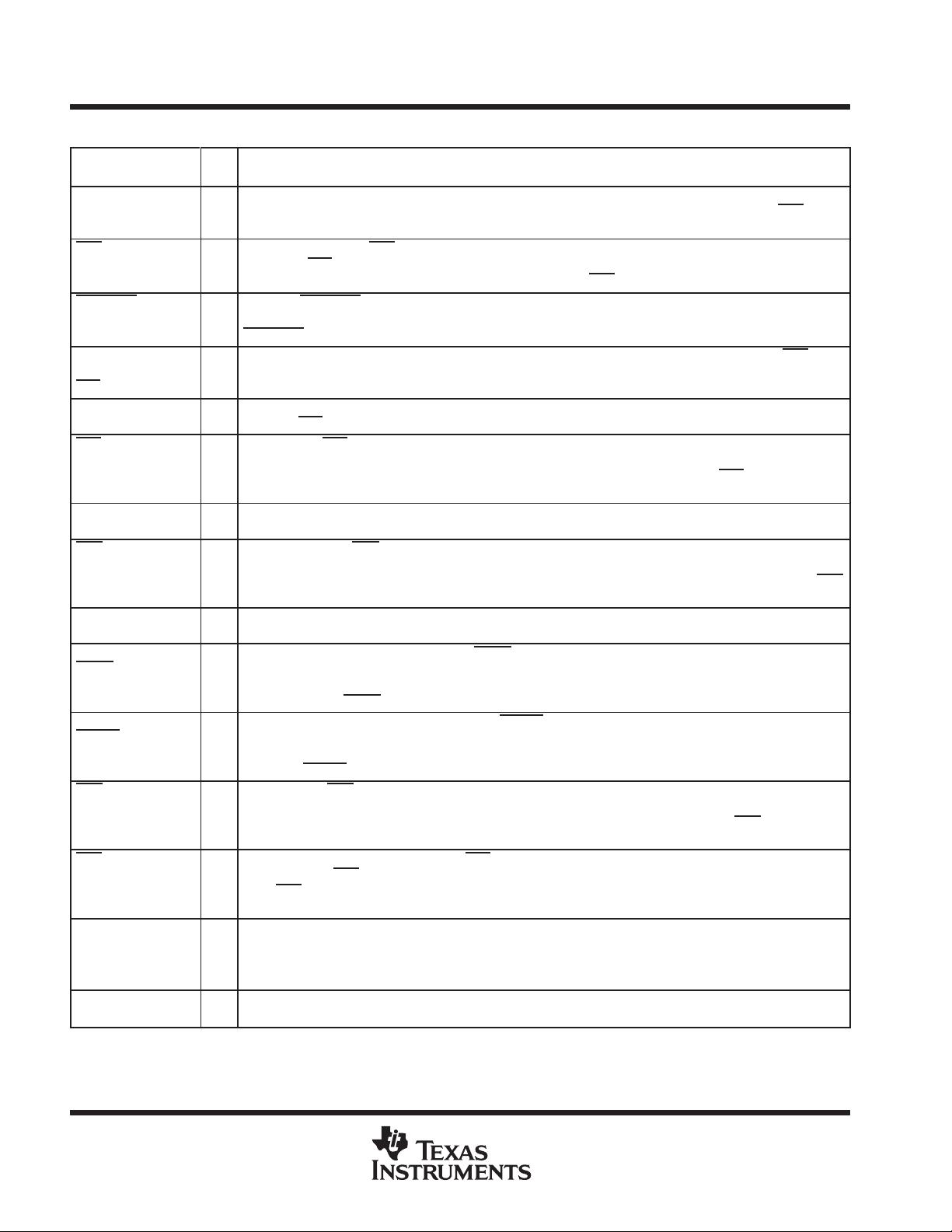
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
I/O
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
†
I/O
DESCRIPTION
A0
A1
A2
31
30
29
I Register select. A0, A1, and A2 are three inputs used during read and write operations to select the ACE register
to read from or write to. Refer to Table 1 for register addresses, also refer to the address strobe (ADS
) signal
description.
ADS
28 I
Address strobe. When ADS is active (low), the register select signals (A0, A1, and A2) and chip select signals
(CS0, CS1, CS2
) drive the internal select logic directly; when high, the register select and chip select signals are
held in the state they were in when the low-to-high transition of ADS
occurred.
BAUDOUT
17 O
Baud out. BAUDOUT is a16× clock signal for the transmitter section of the ACE. The clock rate is established
by the reference oscillator frequency divided by a divisor specified by the baud generator divisor latches.
BAUDOUT
may also be used for the receiver section by tying this output to the RCLK input.
CS0
CS1
CS2
14
15
16
I
Chip select. When CSx is active (high, high, and low respectively), the ACE is selected. Refer to the ADS signal
description.
CSOUT 27 O Chip select out. When CSOUT is high, it indicates that the ACE has been selected by the chip select inputs (CS0,
CS1, and CS2
). CSOUT is low when the chip is deselected.
CTS
40 I
Clear to send. CTS is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 4 (CTS) of the modem
status register. Bit 0 (DCTS) of the modem status register indicates that this signal has changed states since the
last read from the modem status register. If the modem status interrupt is enabled when CTS changes state, an
interrupt is generated.
D0 − D7 2 − 9 I/O Data bus. D0 − D7 are 3-state data lines that provide a bidirectional path for data, control, and status information
between the ACE and the CPU.
DCD
42 I
Data carrier detect. DCD is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 7 (DCD) of the
modem status register. Bit 3 (DDCD) of the modem status register indicates that this signal has changed states
since the last read from the modem status register. If the modem status interrupt is enabled when the DCD
changes state, an interrupt is generated.
DDIS 26 O Driver disable. DDIS is active (high) when the CPU is not reading data. When active, this output can disable an
external transceiver.
DISTR
DISTR
25
24
I
Data input strobes. When either DISTR or DISTR is active (high or low respectively) while the ACE is selected,
the CPU is allowed to read status information or data from a selected ACE register. Only one of these inputs is
required for the transfer of data during a read operation. The other input should be tied in its inactive state (i.e.,
DISTR tied low or DISTR
tied high).
DOSTR
DOSTR
21
20
I
Data output strobes. When either DOSTR or DOSTR is active (high or low respectively), while the ACE is
selected, the CPU is allowed to write control words or data into a selected ACE register. Only one of these inputs
is required to transfer data during a write operation. The other input should be tied in its inactive state (i.e., DOSTR
tied low or DOSTR
tied high).
DSR
41 I
Data set ready. DSR is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 5 (DSR) of the modem
status register. Bit 1 (DDSR) of the modem status register indicates that this signal has changed state since the
last read from the modem status register. If the modem status interrupt is enabled when the DSR changes state,
an interrupt is generated.
DTR
37 O
Data terminal ready. When active (low), DTR informs a modem or data set that the ACE is ready to establish
communication. DTR
is placed in the active state by setting the DTR bit of the modem control register to a high
level. DTR
is placed in the inactive state either as a result of a master reset or during loop mode operation or
clearing bit 0 (DTR) of the modem control register.
INTRPT 33 O Interrupt. When active (high), INTRPT informs the CPU that the ACE has an interrupt to be serviced. The four
conditions that cause an interrupt are: a receiver error, received data is available, the transmitter holding register
is empty, or an enabled modem status interrupt. The INTRPT output is reset (inactivated) either when the interrupt
is serviced or as a result of a master reset.
MR 39 I Master reset. When active (high), MR clears most ACE registers and sets the state of various output signals.
Refer to Table 2 for ACE reset functions.
†
Terminal numbers shown are for the FN package.
SLLS037C − MARCH 1988 − REVISED JANUARY 2006
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
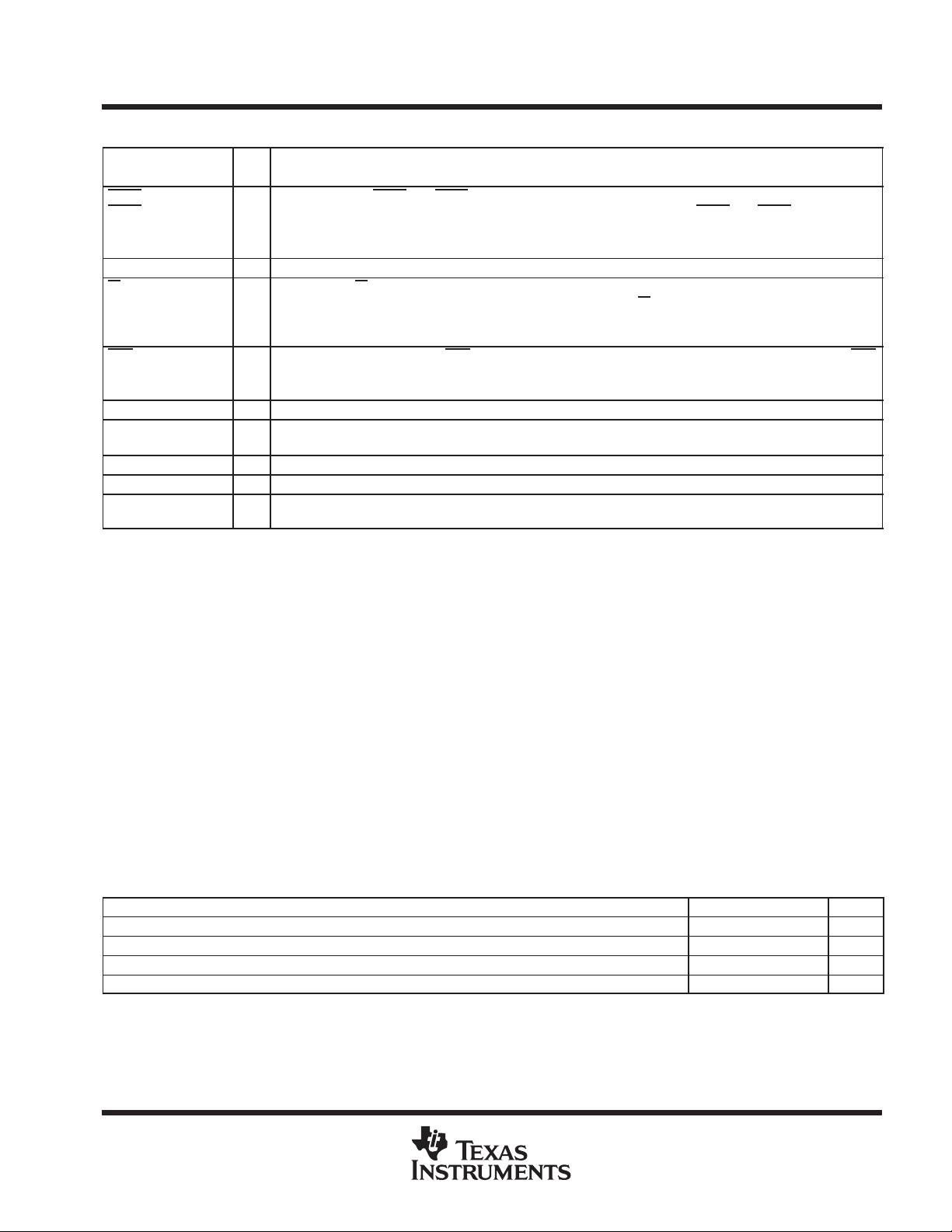
Terminal Functions (continued)
TERMINAL
I/O
DESCRIPTION
NAME NO.
†
I/O
DESCRIPTION
OUT1
OUT2
38
35
O
Outputs 1 and 2. OUT1 and OUT2 are user-designated output terminals that are set to their active states by
setting their respective modem control register bits (OUT1 and OUT2) high. OUT1
and OUT2 are set to their
inactive (high) states as a result of master reset or during loop mode operations or by clearing bit 2 (OUT1) or
bit 3 (OUT2) of the MCR.
RCLK 10 I Receiver clock. RCLK is the 16× baud rate clock for the receiver section of the ACE.
RI
43 I
Ring indicator. RI is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 6 (RI) of the modem status
register. Bit 2 (TERI) of the modem status register indicates that the RI
input has transitioned from a low to a high
state since the last read from the modem status register. If the modem status interrupt is enabled when this
transition occurs, an interrupt is generated.
RTS
36 O
Request to send. When active, RTS informs the modem or data set that the ACE is ready to transmit data. RTS
is set to its active state by setting the RTS modem control register bit and is set to its inactive (high) state either
as a result of a master reset or during loop mode operations or by clearing bit 1 (RTS) of the MCR.
SIN 11 I Serial input. SIN is the serial data input from a connected communications device.
SOUT 13 O Serial output. SOUT is the composite serial data output to a connected communication device. SOUT is set to
the marking (set) state as a result of MR.
V
CC
44 5-V supply voltage
V
SS
22 Supply common
XTAL1
XTAL2
18
19
I/O External clock. XTAL1 and XTAL2 connect the ACE to the main timing reference (clock or crystal).
†
Terminal numbers shown are for the FN package.
absolute maximum ratings over free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage range, V
CC
(see Note 1) −0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage range at any input, V
I
−0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage range, V
O
−0.5 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total power dissipation at (or below) 70°C free-air temperature: FN package 1100 mW. . . . . . .
N package
‡
800 mW. . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
A
0°C to 70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
−65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Case temperature for 10 seconds, T
C
: FN package 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds: N package
‡
260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
‡
The N package in Not Recommended for New Designs.
NOTE 1: All voltage values are with respect to V
SS
.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
CC
4.75 5 5.25 V
High-level input voltage, V
IH
2 V
CC
V
Low-level input voltage, V
IL
−0.5 0.8 V
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
0 70 °C
剩余30页未读,继续阅读
资源推荐
资源评论
162 浏览量
125 浏览量
105 浏览量
144 浏览量
130 浏览量
134 浏览量
197 浏览量
175 浏览量
176 浏览量
2019-12-16 上传
196 浏览量
141 浏览量
2021-09-25 上传
2021-02-10 上传
资源评论

 qq_335607272023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整
qq_335607272023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整 m0_745259962023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整
m0_745259962023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整 CSDN_1872023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整
CSDN_1872023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整 2301_763960562023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整
2301_763960562023-02-13#完美解决问题 #运行顺畅 #内容详尽 #全网独家 #注释完整
不觉明了
- 粉丝: 7238
- 资源: 5764
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- Keras 基于LSTM、CNN、SVM、MLP 进行语音情感识别项目源码
- windows,windows,windows
- 基于springboot+vue的疫情下图书馆管理系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的音乐网站(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的疫情隔离管理系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 【有参考文献】事件触发模型 可实现倒立摆控制仿真实验 simulink模型可直接运行 含详细参考文献
- 基于springboot+vue的英语知识应用网站的设计与实现(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的在线课程管理系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的在线教育系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的在线问卷调查系统的设计与实现(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的智慧图书管理系统设计与实现(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的智能无人仓库管理(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的中小企业人事管理系统代码(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的中国陕西民俗网(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的智能学习平台系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
- 基于springboot+vue的作业管理系统(Java毕业设计,附源码,部署教程).zip
安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功