Multi-AP Specification v2.0
© 2019 Wi-Fi Alliance. All Rights Reserved.
Used with the permission of Wi-Fi Alliance under the terms as stated in this document.
Page 106 of 113
19 Traffic Separation
19.1 Traffic Separation in Multi-AP Network
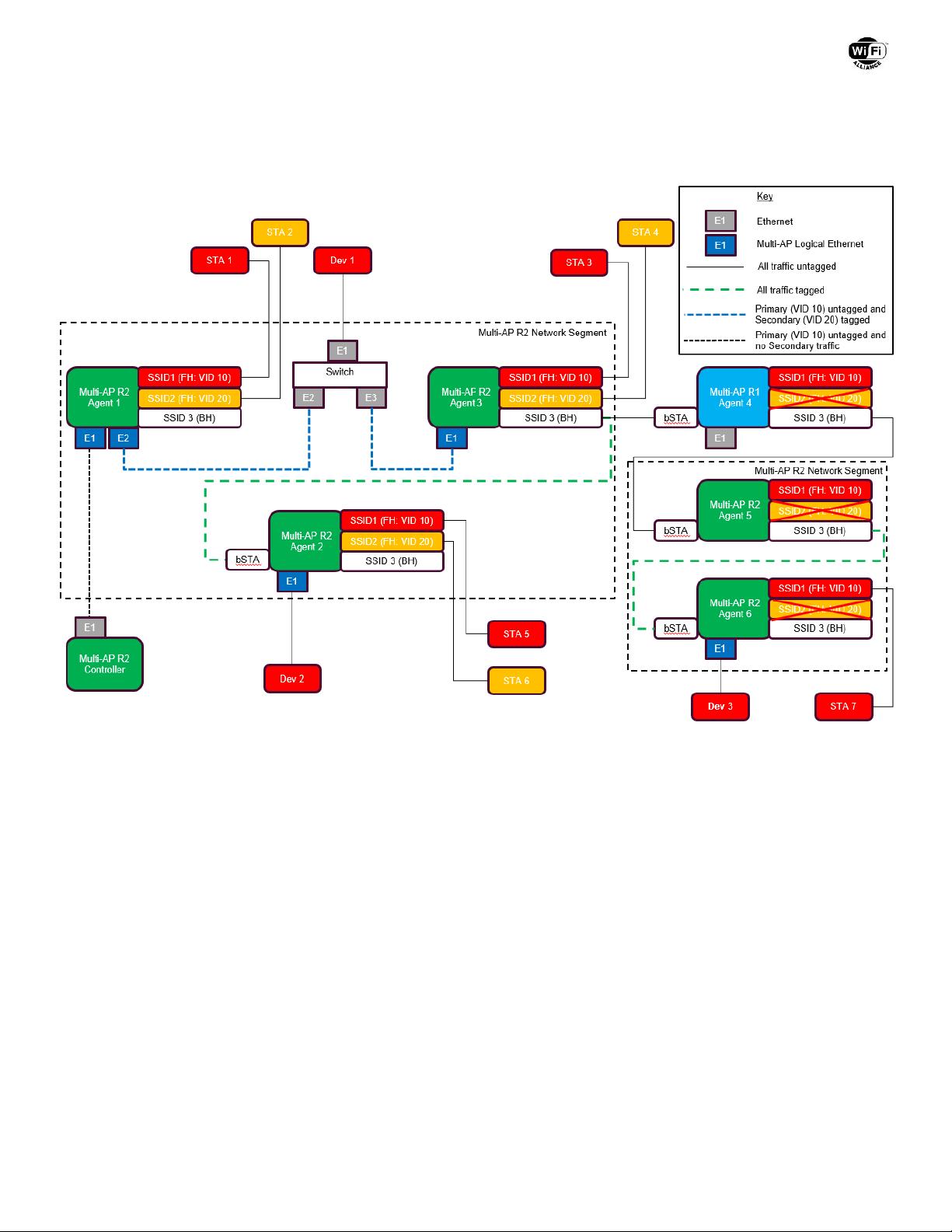
19.1.1 Traffic Separation Overview (Informative)
This informative description of traffic separation relies on terms defined in section 3.1.
A Multi-AP Controller is able to configure multiple fronthaul SSIDs in a Multi-AP network. A Multi-AP Profile-2 Network
Segment supports traffic separation for each fronthaul SSIDs using a unique VLAN. The traffic belonging to each VLAN is
distinguished using an 802.1Q C-TAG with a unique VLAN ID, or the lack of thereof.
The rules defined in section 19.1.3 ensure that traffic generated within a Multi-AP network is clearly identifiable as
belonging to one SSID. Traffic generated outside of a Multi-AP network is tagged with a VLAN ID (or untagged as
appropriate) prior to ingressing the Multi-AP network by means not defined in this specification and is expected to be
identified as belonging to an SSID.
A Multi-AP device is a layer-2 (Link Layer) logical device that can be embedded into a more complex physical device
(e.g., a router, or a gateway) that implements both a Multi-AP Agent as well as other, above layer-2, functionalities. Often
in this case, traffic generated outside of the network (e.g., ingressing thru the WAN interface) is classified by the
gateway/routing subsystem and tagged (if needed) before being forwarded to the Multi-AP device subsystem. The
abstract/logical interface between the Multi-AP subsystem and the rest of the device is considered a Multi-AP Logical
Ethernet Interface as per the definition in section 3.1.3 and the rules in section 19.1.3.
If Traffic Separation is not configured on a Multi-AP Agent that implements Profile-2, the Multi-AP Agent might behave in a
transparent manner to VLAN tags applied by other entities.
A Multi-AP Controller configures SSID to VLAN ID mapping in a Traffic Separation Policy. Each mapping from one or
many SSIDs to one VLAN ID is indicated in a Traffic Separation Policy TLV. The Multi-AP Controller distributes the Traffic
Separation Policy to all Multi-AP Agents. It is recommended that a Multi-AP Controller provides each Multi-AP Agent with
a complete list of VLAN ID to SSID mappings, including those VIDs that are mapped to SSIDs that are not configured on a
given Multi-AP Agent, to enable that traffic on all VIDs is forwarded over backhaul links. Multi-AP Agents report to the
Multi-AP Controller the maximum number of VIDs they are able to configure in the Profile-2 AP Capability TLV. A
Controller that intends to use more VIDs than those supported on some of the Multi-AP Agents it manages, may re-
arrange the topology in such a way that traffic for all VIDs downstream of a Multi-AP Agent can be forwarded by such
Agent.
For each Ingress Packet, a Multi-AP Agent adds an 802.1Q C-TAG with a VLAN ID as specified in a Traffic Separation
Policy.
For each Egress Packet, a Multi-AP Agent removes any 802.1Q C-TAG.
For a packet to be transmitted on a Multi-AP Logical Ethernet Interface, if the VLAN ID in the 802.1Q C-TAG is set to one
of the Secondary VLAN IDs, a Multi-AP Agent maintains the 802.1Q C-TAG on those packets.
Multi-AP IEEE 1905.1 management frames are carried in the Primary Network.
A Default 802.1Q Settings TLV identifies a Primary VLAN ID for tagging packets on the Primary Network.
Traffic separation is not supported across a Multi-AP Agent that implements Profile-1. Therefore, a Multi-AP Controller
should not configure any SSID that is mapped to a Secondary VLAN ID on any Multi-AP Agent that implements Profile-1
or on any Multi-AP Agent that is downstream of a Multi-AP Agent that implements Profile-1. If the location of the WAN
connection in a network managed by a Multi-AP Controller changes (e.g., in order to use a backup WAN connection in the
event the main WAN connection fails), the portions of the network where traffic separation is possible may change and the
Multi-AP Controller may need to reconfigure the entire network accordingly, including Secondary SSIDs and VLAN(s).
A Multi-AP Controller that reconfigures VLAN(s) in the entire Multi-AP Profile-2 Network Segment may reconfigure the
traffic separation policy on the Multi-AP Agents, starting from those at the very end of the data-plane tree topology and
finishing at the data-plane root. Failing to do so may result in the inability to deliver reconfiguration CMDUs to downstream
Multi-AP Agents due to Primary VLAN ID mismatch. During VLAN reconfiguration data traffic loss may occur.


 easyMesh 文档翻译.zip (3个子文件)
easyMesh 文档翻译.zip (3个子文件)  easyMesh 文档翻译
easyMesh 文档翻译  多AP规范 v2.0.md 17KB
多AP规范 v2.0.md 17KB Multi-AP_Specification_v2.0_Traffic Separation.pdf 152KB
Multi-AP_Specification_v2.0_Traffic Separation.pdf 152KB easyMesh_V2_TS.md 14KB
easyMesh_V2_TS.md 14KB

 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功