没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
时延容忍的移动网络具有间歇性连接性,巨大的传输延迟,节点移动性等特点。通常在网络中没有端到端路径,这对DTMN中的路由提出了巨大挑战。 本文首先介绍了DTMN的体系结构,包括DTMN的特性,路由挑战以及度量和移动性模型。 然后,讨论并分析了DTMN的最新路由协议。 路由策略分为三类:基于非知识的方法,基于知识的方法和基于社会的方法。 最后,介绍了有关DTMN的一些研究问题。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

Hindawi Publishing Corporation
International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks
Volume 2013, Article ID 145727, 16 pages
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/145727
Review Article
Study on Routing Protocols for Delay Tolerant Mobile Networks
Haigang Gong and Lingfei Yu
School of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
Correspondence should be addressed to Haigang Gong; hggong@uestc.edu.cn
Received 11 October 2012; Accepted 6 December 2012
Academic Editor: Nianbo Liu
Copyright © 2013 H. Gong and L. Yu. is is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License,
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Delay tolerant mobile networks feature with intermittent connectivity, huge transmission delay, nodal mobility, and so forth. ere
is usually no end-to-end path in the networks and it poses great challenges for routing in DTMNs. In this paper, the architecture
of DTMNs is introduced at �rst, including the characteristics of DTMNs, routing challenges, and metric and mobility models.
And then, the state-of-the-art routing protocols for DTMNs are discussed and analyzed. Routing strategies are classi�ed into three
categories: nonknowledge-based approach, knowledge-based approach, and social-based approach. Finally, some research issues
about DTMNs are presented.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of low-power wireless commu-
nication technology and integrated circuit technology, there
emerge a large number of low-cost, portable wireless devices.
ese devices are organized into a wireless ad hoc network
and communicate with each other by multihop transmis-
sions, which have great potential for many applications. For
example, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) [1], composed of
densely deployed low-power, low-cost sensor nodes, could be
applied in scenarios such as military surveillance [2], disaster
relief [3], health monitoring [4], environment monitoring
[5], and smart home [6]. Another example is vehicular ad
hoc networks (VANETs), in which vehicles equip with short
range RF modules and exchange data when they meet, widely
used in traffic safety [7], traffic efficiency [8], and information
service [9].
Data gathering and routing is one of the fundamental
functions of the low-power wireless ad hoc network and
there have been lots of research works on routing issues
[10–14].However,authorsassumethatthenetworkisfull
connected in these works, that is to say, there exists an
end-to-end path between the source node and destination
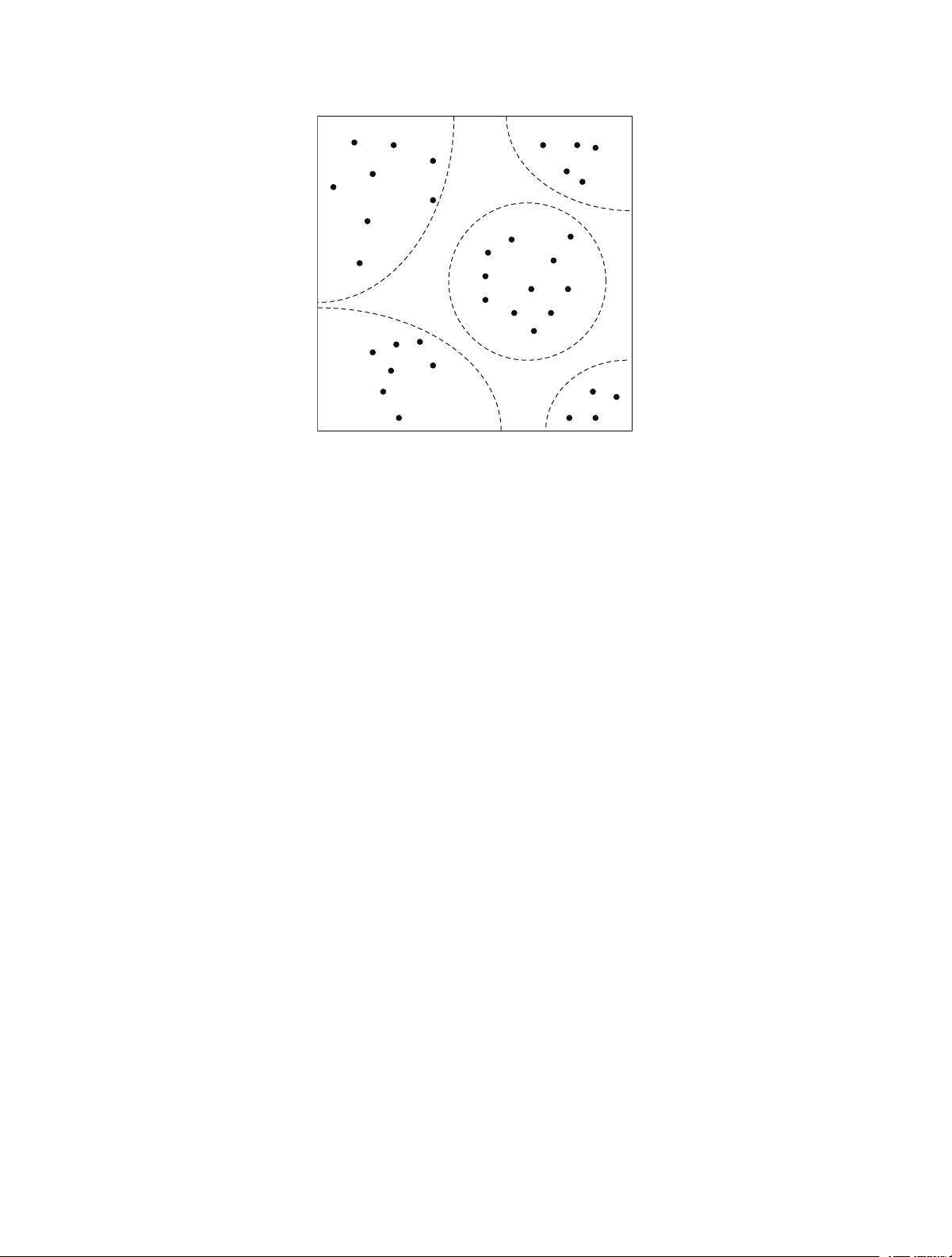
node, which is unreasonable in the real environment. In fact,
if nodes are deployed randomly in the region, the density
of nodes in some subregions would be higher than other
subregions, leading to the phenomena of network partition,
as shown in Figure 1.Oncethenetworkispartitioned,itisnot
fully connected any more. Secondly, the environment oen
has great impacts on the low-power communication. For
instance, if there are electromagnetic �elds or some obstacles,
nodes will not communicate with each other even if they are
within the transmission range, disconnecting the network.
irdly, nodes are oen powered by batteries, which is hard
to rechargeable. When the energy of the battery exhausts,
nodes cannot transmit data any more, degrading the network
connectivity. Moreover, if nodes move with animals such
as ZebraNet [15] and SWIM [16], data transmission only
occurs when nodes meet each other. e mobility of nodes
introduces opportunistic connectivity and there is not a
stable end-to-end path in the network, leading to partially
connected network.
Aboveall,thenetworkisoennotfullyconnected
in the real environments and the network connectivity is
intermittent and opportunistic, which is the characteristic
of delay tolerant networks (DTNs) [17]. DTNs feature with
sparse and intermittent connectivity, long and variable delay,
high latency, high error rates, highly asymmetric data rate,
and no stable end-to-end path. Obviously, traditional routing
protocols are not well suitable for DTNs. For example, on-
demand routing protocols such as AODV [18]andDSR[19]
for MANET try to �nd an end-to-end path and table-driven
routing protocols such as DSDV [20] and WRP [21] need
tobuildroutetable.eyarebothhardtobeadaptiveto
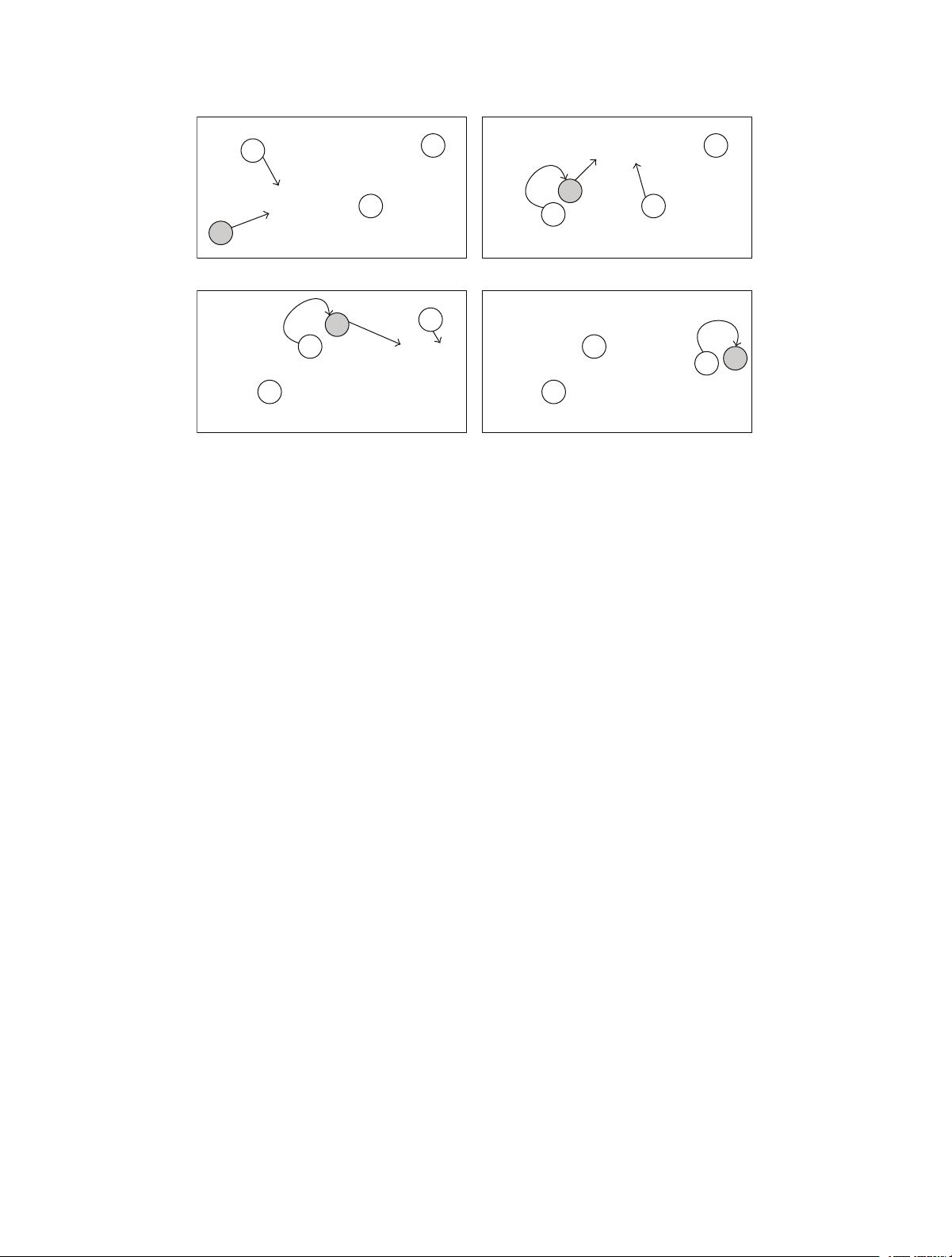
A
B
C
D
T1
C
D
B
A
T2
Contact,
send data
B
D
A
C
Contact,
send data
T3
B
C
A
D
Destination
T4
2. Network Architecture
2.1. Characteristics of DTMNs.
2.2. Routing Challenges.
2.2.1. Intermittent Connectivity.
剩余15页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

weixin_38682076
- 粉丝: 6
- 资源: 917
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功