没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
Compared with the traditional image intensifier with phosphor screen readout, the photon-counting imaging detector with charge induction readout is more beneficial in several aspects (e.g., good imaging properties and time resolution) to astronomy, reconnaissance, bioluminescence, and materials research. However, the annealing temperature during the tube-making process can affect the properties of the Ge film, and consequently impair the performance of the detector. Therefore, the influence of a
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论
April 10, 2010 / Vol. 8, No. 4 / CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS 361
Influence of annealing te mperature on the performance
of Ge film and p hoton-counting imaging syste m
Feifei Zhao (
ëëë
)
1,2∗
, Baosheng Zhao (
ëëë
,,,
)
1
, Xiaofeng Sai (
mmm
¹¹¹
)
1
,
Xinghua Zhang (
ÜÜÜ
,,,
uuu
)
1,2
, Yonglin Wei (
[[[
)
1
, and Wei Zou (
qqq
UUU
)
1
1
State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics,
Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2
Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
∗
E-mail: free.ff@163.com
Received July 22, 2009
Compared with the traditional image intensifier with phosph or screen readout, the photon-counting imag-
ing detector with charge induction readout is more beneficial in several aspects (e.g., good imaging proper-
ties and time resolution) to astronomy, reconnaissance, bioluminescence, and materials research. However,
the annealing temperature during the tube-making process can affect the properties of the Ge film, and
consequently impair the performance of the detector. Therefore, the influence of annealing temperature
on Ge film and on the detector is studied in order to determine th e cru cial parameters. The Ge films
are prepared on ceramic and qu artz glass by the use of an electron gun. They are analyzed by scanning
electron microscope (SEM), high-resistance meter, and X-r ay diffraction (XRD). The results show that the
optimum sub strate and annealing temperature are ceramic plate and 250
◦
C, respectively.
OCIS codes: 160.6000, 030.5260, 110.2970, 100.0100.
doi: 10.3788/COL20100804.0361.
The world space observatory-ultraviolet (WSO-UV) is a
space telescope project led by Russia, with contributions
from several other countries. The mission involving a
long-slit spectrograph instrument provides low-resolution
sp e ctra in the range of 102–320 nm in China. Therefore,
the study on two photon-counting detectors in the ranges
of 102–170 and 160–320 nm is carried out.
The photon-counting imaging detector, which is char-
acterized by both high time resolution and good imaging
properties, is superior to the traditional image intensi-
fier with phospho r screen readout
[1]
as well as to hy-
brid sensors, such as intensified charge-coupled devices
(ICCDs)
[2]
and electron-multiplying charge-coupled de-
vices (EMCCDs)
[3,4]
in the field of imaging at very
low flux level and in the solar-blind ultraviolet (UV)
range. Compared with the sealed imaging detector tubes
with position-sensitive anode
[5−7]
, the photon-counting
detector
[8−10]
with charge induction readout is beneficial
in several aspects, such as the abilities to avoid image
distortion produced by secondary electron, eliminate
noise due to quantized charge collection, simplify the
electronic design requirements, and so on. However, the
annealing temperature during the encapsulation process
and photocathode preparatio n may affect the properties
of the Ge film, and consequently impair the performance
of the detector (e.g., the position resolution). Therefore,
the objectives of this study are to research the influence
of annealing temperature on Ge film and on the detector
and to determine the crucial parameters.
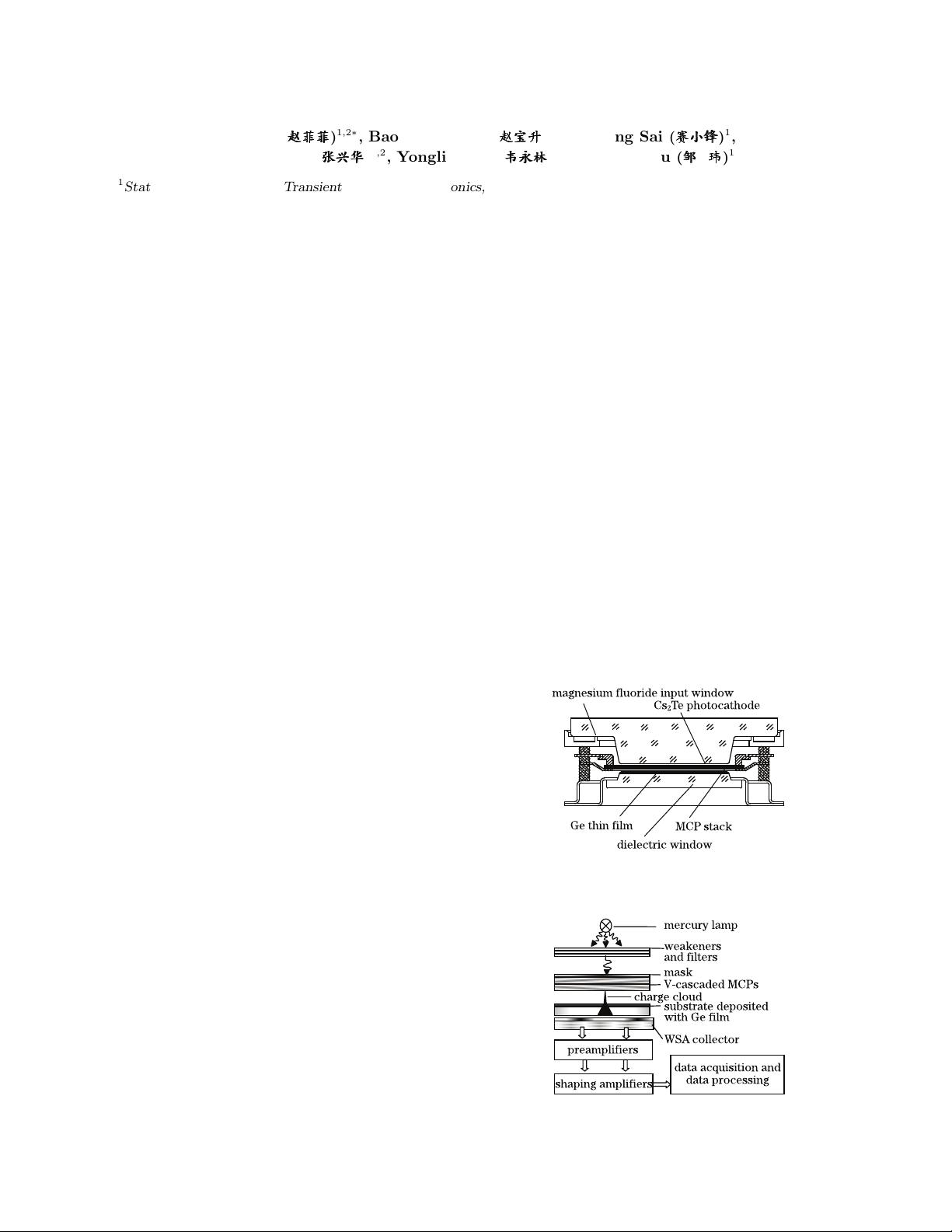
Figure 1 shows the schematic cross-section of a near-
UV (NUV) sealed tube imaging detector. The compo-
nents of the detector a re sealed in a vacuum tube, which
is required for their operation. A semitransparent cesium
telluride photocathode is deposited on the input window
to accommodate the wavelength range of 160–320 nm.
During the technological process, these tube parts are
annealed in a vacuum chamber for 40 h prior to the
preparation of the photocathode. The entire proce ss of
preparing a sealed tube creates many problems, one of
which is the influence of annealing temperature on the
Ge films. To simplify the experiment, a photon-counting
imaging system is used, who se configuration and opera t-
ing flow are shown in Fig. 2.
This system utilizes a chevron stack o f microchan-
nel plates (MCPs), each with a length-to-diameter ratio
Fig. 1. Schematic cross-section of NUV sealed tube. MCP:
microchannel plate.
Fig. 2. Sketch of experimental photon- counting imaging sys-
tem. WSA: wedge and strip anode.
1671-7694/2010/040361-04
c
2010 Chinese Optics Letters
资源评论

weixin_38667920
- 粉丝: 3
- 资源: 909
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功