没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
在介电子和di子最终状态下寻找新的共振和非共振高质量现象。 该搜索使用了36.1 fb -1的质子-质子碰撞数据,该数据是通过2015年和2016年在大型强子对撞机的ATLAS实验在s = 13 $$ \ sqrt {s} = 13 $$ TeV收集的。与标准模型无明显偏差 观察到预测。 在共振衰减为二轻子的横截面时间分支比上,设定了95%可信度的上限,然后转换为共振质量的下限,对于E 6激发的Zχ',其上限为4.1 TeV。 qqℓℓ接触相互作用标度的下限根据模型设置在2.4 TeV和40 TeV之间。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

JHEP10(2017)182
Published for SISSA by Springer
Received: July 11, 2017
Revised: September 8, 2017
Accepted: October 6, 2017
Published: October 26, 2017
Search for new high-mass phenomena in the dilepton
final state using 36 fb
−1
of proton-proton collision
data at
√
s = 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector
The ATLAS collaboration
E-mail: atlas.publications@cern.ch
Abstract: A search is conducted for new resonant and non-resonant high-mass phenom-
ena in dielectron and dimuon final states. The search uses 36.1 fb
−1
of proton-proton
collision data, collected at
√
s = 13 TeV by the ATLAS experiment at the LHC in 2015
and 2016. No significant deviation from the Standard Model prediction is observed. Upper
limits at 95% credibility level are set on the cross-section times branching ratio for reso-
nances decaying into dileptons, which are converted to lower limits on the resonance mass,
up to 4.1 TeV for the E
6
-motivated Z
0
χ
. Lower limits on the qq`` contact interaction scale
are set between 2.4 TeV and 40 TeV, depending on the model.
Keywords: Beyond Standard Model, Hadron-Hadron scattering (experiments)
ArXiv ePrint: 1707.02424
Open Access, Copyright CERN,
for the benefit of the ATLAS Collaboration.
Article funded by SCOAP
3
.
https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP10(2017)182

JHEP10(2017)182
Contents
1 Introduction 1
2 Theoretical models 3
2.1 E
6
-motivated Z
0
models 3
2.2 Minimal Z
0
models 3
2.3 Contact interactions 4
3 ATLAS detector 5
4 Data and Monte Carlo samples 5
5 Event selection 6
6 Background estimation 8
7 Systematic uncertainties 10
8 Event yields 13
9 Statistical analysis 13
10 Results 16
10.1 Z
0
cross-section and mass limits 17
10.2 Limits on Minimal Z
0
models 18
10.3 Generic Z
0
limits 18
10.4 Limits on the energy scale of contact interactions 19
11 Conclusion 21
A Dilepton invariant mass tables 22
The ATLAS collaboration 44
1 Introduction
This article presents a search for resonant and non-resonant new phenomena, based on
the analysis of dilepton final states (ee and µµ) in proton-proton (pp) collisions with the
ATLAS detector at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) operating at
√
s = 13 TeV. The
data set was collected during 2015 and 2016, and corresponds to an integrated luminosity
of 36.1 fb
−1
. In the search for new physics carried out at hadron colliders, the study of
– 1 –

JHEP10(2017)182
dilepton final states provides excellent sensitivity to a large variety of phenomena. This
experimental signature benefits from a fully reconstructed final state, high signal-selection
efficiencies and relatively small, well-understood backgrounds, representing a powerful test
for a wide range of theories beyond the Standard Model (SM).
Models with extended gauge groups often feature additional U(1) symmetries with cor-
responding heavy spin-1 bosons. These bosons, generally referred to as Z
0
, would manifest
as a narrow resonance through its decay, in the dilepton mass spectrum. Among these mod-
els are those inspired by Grand Unified Theories, which are motivated by gauge unification
or a restoration of the left-right symmetry violated by the weak interaction. Examples
considered in this article include the Z
0
bosons of the E
6
-motivated [1, 2] theories as well
as Minimal models [3]. The Sequential Standard Model (SSM) [2] is also considered due to
its inherent simplicity and usefulness as a benchmark model. The SSM manifests a Z
0
SSM
boson with couplings to fermions equal to those of the SM Z boson.
The most sensitive previous searches for a Z
0
boson decaying into the dilepton final
state were carried out by the ATLAS and CMS collaborations [4, 5]. Using 3.2 fb
−1
of
pp collision data at
√
s = 13 TeV collected in 2015, ATLAS set a lower exclusion limit at
95% credibility level (CL) on the Z
0
SSM
pole mass of 3.4 TeV for the combined ee and µµ
channels. Similar limits were set by CMS using the 2015 data sample.
This search is also sensitive to a series of other models that predict the presence of
narrow dilepton resonances. These models include the Randall-Sundrum (RS) model [6]
with a warped extra dimension giving rise to spin-2 graviton excitations, the quantum
black-hole model [7], the Z
∗
model [8], and the minimal walking technicolour model [9]. In
order to facilitate interpretation of the results in the context of these or any other model
predicting a new dilepton resonance, limits are set on the production of a generic Z
0
-like
excess.
In addition to the search for narrow resonances, results for non-resonant phenomena are
also reported. Such models of these phenomena include an effective four-fermion contact
interaction (CI) between two initial-state quarks and two final-state leptons (qq``). Unlike
resonance models, which require sufficient energy to produce the new gauge boson, the
presence of a new interaction in the non-resonant regime can be detected at a much lower
energy.
The most stringent constraints from CI searches are also provided by the ATLAS and
CMS collaborations [4, 10], for couplings between quarks and leptons. Using 3.2 fb
−1
of pp
collision data at
√
s = 13 TeV collected in 2015, ATLAS set lower limits on the qq`` CI scale
of Λ = 25 TeV and Λ = 18 TeV at 95% CL for constructive and destructive interference,
respectively, in the case of left-left interactions and assuming a uniform positive prior
probability in 1/Λ
2
. Similar limits were set by CMS using the 2015 data set. Both the
resonant and non-resonant models considered as the benchmark for this search are further
discussed in section 2.
The presented search utilises the invariant mass spectra of the observed dilepton final
states as discriminating variables. The analysis and interpretation of these spectra rely
primarily on simulated samples of signal and background processes. The interpretation
is performed taking into account the expected shape of different signals in the dilepton
– 2 –

JHEP10(2017)182
mass distribution. The use of the shape of the full dilepton invariant mass distribution
reduces the uncertainties in the background modelling, thereby increasing the sensitivity
of this search at high masses. This article is structured as follows: section 2 covers the
theoretical motivation of the models considered in this search, followed by a description
of the ATLAS detector in section 3, and a summary in section 4 of the data and Monte
Carlo (MC) samples used. The event selection is motivated and described in section 5, with
details of the background estimation given in section 6, and an overview of the systematic
uncertainty treatment given in section 7. The event yields and main kinematic distributions
are presented in section 8, followed by a description of the statistical analysis in section 9,
and the results in section 10.
2 Theoretical models
2.1 E
6
-motivated Z
0
models
In the class of models based on the E
6
gauge group [1, 2], the unified symmetry group
can break to the SM in a number of different ways. In many of them, E
6
is first broken
to SO(10) × U(1)
ψ
, with SO(10) then breaking either to SU(4) × SU(2)
L
× SU(2)
R
or
SU(5) × U(1)
χ
. In the first of these two possibilities, a Z
0
3R
coming from SU(2)
R
, where
3R stands for the right-handed third component of weak isospin, or a Z
0
B−L
from the
breaking of SU(4) into SU(3)
C
× U(1)
B−L
could exist at the TeV scale, where B (L) is the
baryon (lepton) number and (B − L) is the conserved quantum number. Both of these
Z
0
bosons appear in the Minimal Z
0
models discussed in the next section. In the SU(5)
case, the presence of U(1)
ψ
and U(1)
χ
symmetries implies the existence of associated gauge
bosons Z
0
ψ
and Z
0
χ
that can mix. When SU(5) is broken down to the SM, one of the U(1)
can remain unbroken down to intermediate energy scales. Therefore, the precise model
is governed by a mixing angle θ
E
6
, with the new potentially observable Z
0
boson defined
by Z
0
(θ
E
6
) = Z
0
ψ
cos θ
E
6
+ Z
0
χ
sin θ
E
6
. The value of θ
E
6
specifies the Z
0
boson’s coupling
strength to SM fermions as well as its intrinsic width. In comparison to the benchmark
Z
0
SSM
, which has a width of approximately 3% of its mass, the E
6
models predict narrower
Z
0
signals. The Z
0
ψ
considered here has a width of 0.5% of its mass, and the Z
0
χ
has a width
of 1.2% of its mass [11, 12]. All other Z
0
signals in this model, including Z
0
S
, Z
0
I
, Z
0
η
, and
Z
0
N
, are defined by specific values of θ
E
6
ranging from 0 to π, and have widths between
those of the Z
0
ψ
and Z
0
χ
.
2.2 Minimal Z
0
models
In the Minimal Z
0
models [3], the phenomenology of Z
0
boson production and decay is
characterised by three parameters: two effective coupling constants, g
BL
and g
Y
, and the
Z
0
boson mass. This parameterisation encompasses Z
0
bosons from many models, including
the Z
0
χ
belonging to the E
6
-motivated model of the previous section, the Z
0
3R
in a left-right
symmetric model [13, 14] and the Z
0
B−L
of the pure (B − L) model [15]. The minimal
models are therefore particularly interesting for their generality, and because couplings are
being directly constrained by the search. The coupling parameter g
BL
defines the coupling
of a new Z
0
boson to the (B − L) current, while the g
Y
parameter represents the coupling
– 3 –
JHEP10(2017)182
Z
0
B−L
Z
0
χ
Z
0
3R
γ
0
q
5
8
sin θ
W
q
41
24
sin θ
W
q
5
12
sin θ
W
cos θ
Min
1
q
25
41
1
√
5
sin θ
Min
0 −
q
16
41
−
2
√
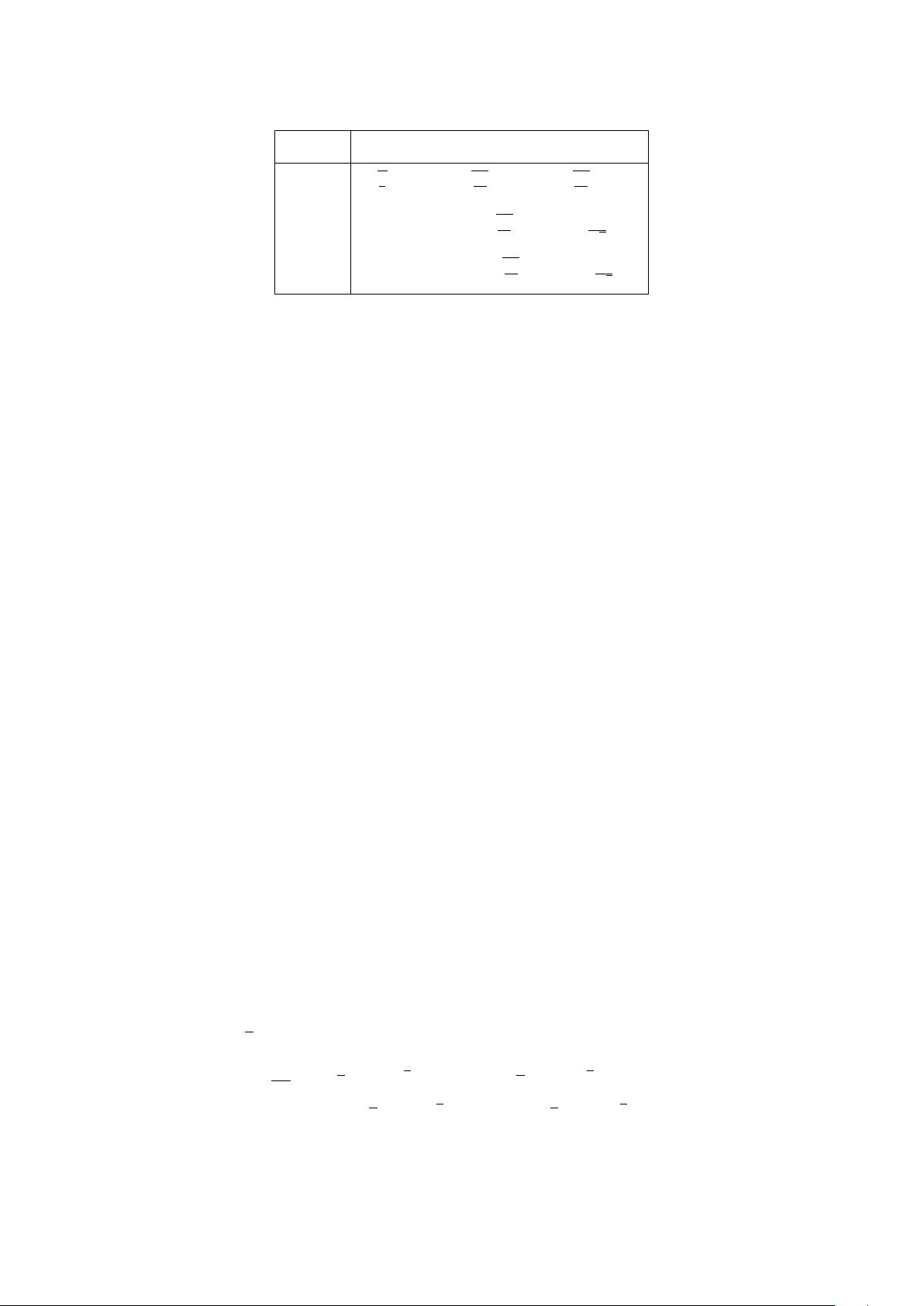
5
Table 1. Values for γ
0
and θ
Min
in the Minimal Z
0
models corresponding to three specific Z
0
bosons: Z
0
B−L
, Z
0
χ
and Z
0
3R
. The SM weak mixing angle is denoted by θ
W
.
to the weak hypercharge Y. It is convenient to refer to the ratios ˜g
BL
≡ g
BL
/g
Z
and
˜g
Y
≡ g
Y
/g
Z
, where g
Z
is related to the coupling of the SM Z boson to fermions defined by
g
Z
= 2M
Z
/v. Here v = 246 GeV is the SM Higgs vacuum expectation value. To simplify
further, the additional parameters γ
0
and θ
Min
are chosen as independent parameters with
the following definitions: ˜g
BL
= γ
0
cos θ
Min
, ˜g
Y
= γ
0
sin θ
Min
. The γ
0
parameter measures
the strength of the Z
0
boson coupling relative to that of the SM Z boson, while θ
Min
determines the mixing between the generators of the (B − L) and weak hypercharge Y
gauge groups. Specific values of γ
0
and θ
Min
correspond to Z
0
bosons in various models, as
is shown in table 1 for the three cases mentioned in this section.
For the Minimal Z
0
models, the width depends on γ
0
and θ
Min
, and the Z
0
interferes
with the SM Z/γ
∗
process. For example, taking the 3R and B − L models investigated in
this search, the width varies from less than 1% up to 12.8% and 39.5% respectively, for
the γ
0
range considered. The branching fraction to leptons is the same as for the other Z
0
models considered in this search. Couplings to hypothetical right-handed neutrinos, the
Higgs boson, and to W boson pairs are not considered. Previous limits on the Z
0
mass
versus γ
0
were set by the ATLAS experiment. For γ
0
= 0.2, the range of Z
0
mass limits at
95% CL corresponding to θ
Min
∈ [0, π] is 1.11 TeV to 2.10 TeV [16].
2.3 Contact interactions
Some models of physics beyond the SM result in non-resonant deviations from the predicted
SM dilepton mass spectrum. Compositeness models motivated by the repeated pattern of
quark and lepton generations predict new interactions involving their constituents. These
interactions may be represented as a contact interaction between initial-state quarks and
final-state leptons [17, 18]. Other models producing non-resonant effects are models with
large extra dimensions [19] motivated by the hierarchy problem. This search is sensitive to
non-resonant new physics in these scenarios; however, constraints on these models are not
evaluated in this article.
The following four-fermion CI Lagrangian [17, 18] is used to describe a new interaction
in the process qq → `
+
`
−
:
L =
g
2
Λ
2
[η
LL
(q
L
γ
µ
q
L
) (`
L
γ
µ
`
L
) + η
RR
(q
R
γ
µ
q
R
) (`
R
γ
µ
`
R
)
+ η
LR
(q
L
γ
µ
q
L
) (`
R
γ
µ
`
R
) + η
RL
(q
R
γ
µ
q
R
) (`
L
γ
µ
`
L
)] ,
– 4 –
剩余60页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

weixin_38612095
- 粉丝: 10
- 资源: 921
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 江苏省普通高校“专转本”选拔考试专业综合科目考试大纲(试行)
- C语言实现基于华为LiteOS的智慧楼宇消防系统源码+电路图+全部资料
- 基于CMLM的语义一致性数据增强方法python实现源码(提高神经机器翻译的性能、IWSLT14 DE-EN数据集验证).zip
- 静态网站首页制作,纯手工,没有使用框架
- 机器学习大作业-Python实现基于线性回归的PM2.5预测项目源码(高分期末大作业)
- 基于java开发的绿色出行的个人碳排放积分系统+源码(毕业设计&课程设计&项目开发)
- 数据结构--实验报告2.docx
- 基于python的开源文本到语音转换项目+小白使用教程(支持批量英语、中文、多情感语音合成,web界面).zip
- 本软件包是用于Windows下往云端上传代码的工具
- MySQL-server-5.6.22-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功