Research Article
Dihadron Azimuthal Correlations in 200 GeV Au-Au and
2.76 TeV Pb-Pb Collisions
G. X. Zhang,
1
Y. C. Qian,
2
and B. C. Li
2
1
Institute of eoretical Physics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2
College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030000, China
Correspondence should be addressed to B. C. Li; bcli
th@yeah.net
Received June ; Revised August ; Accepted August ; Published August
Academic Editor: Chen Wu
Copyright © G. X. Zhang et al. is is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License,
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. e
publication of this article was funded by SCOAP
.
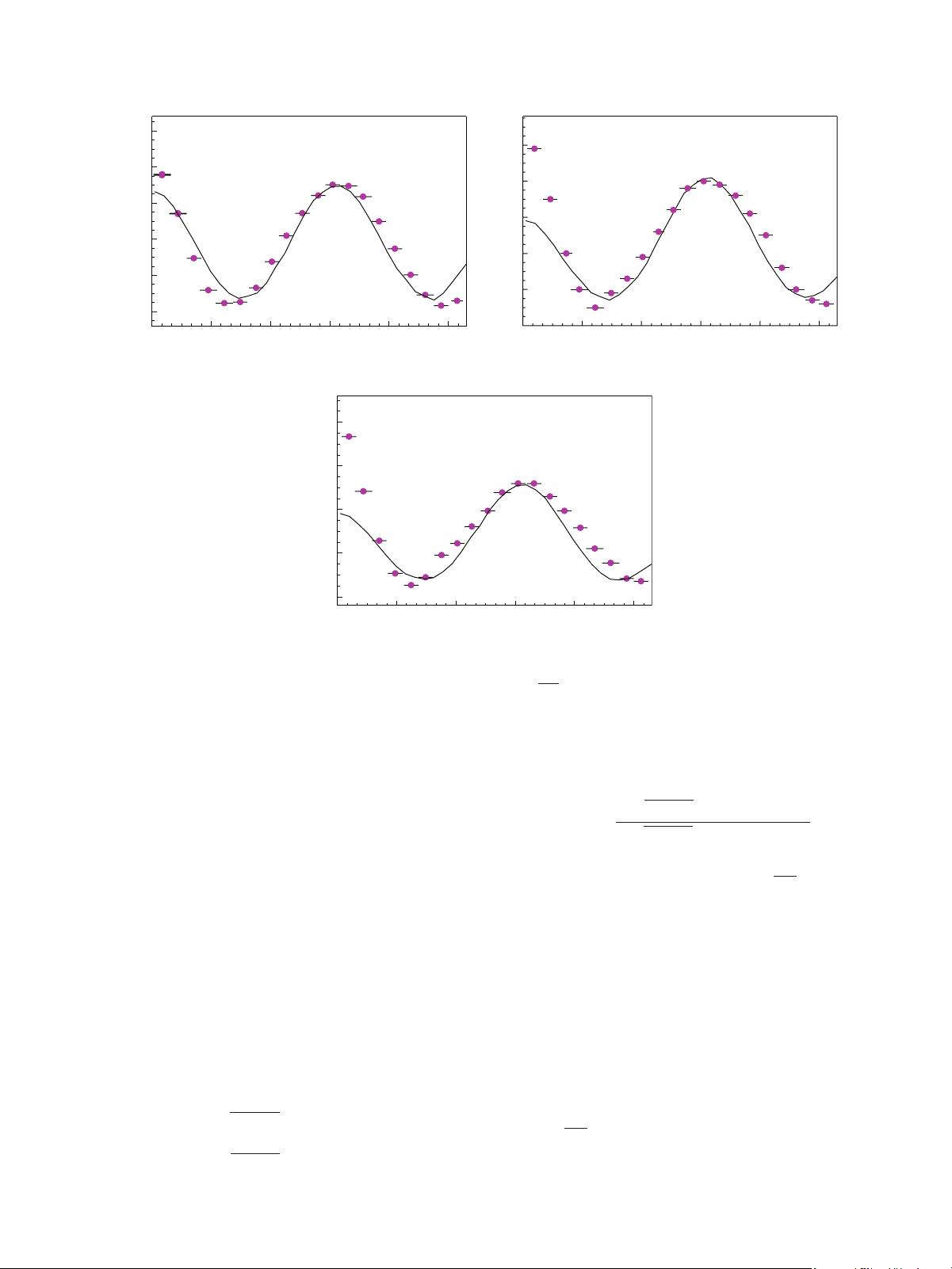
In a multisource thermal model, we detailedly show dihadron azimuthal correlations for –% and –% in Au-Au collisions
at
NN
= 200GeV and over a centrality range from –% to –% in Pb-Pb collisions at
NN
= 2.76TeV. e model can
approximately describe the azimuthal correlations of particles produced in the collisions. e
𝑥
amplitude of the corresponding
source is magnied, and the source translates along the direction. e factor
𝑥
, in most cases, increases with the increase of the
centrality in Pb-Pb collisions at
NN
=2.76TeV.
1. Introduction
An important subject of high energy physics is to discuss
the strongly interacting matter and nuclear matter at high
temperature and high density by heavy-ion collisions at
ultrarelativistic energies [, ]. In the initial stage of the
collision, tremendous amounts of energy are accumulated
at a nite zone in a short time. en, they result in the
creation of a nearly perfect quark-gluon plasma (QGP),
which will undergo the hadronization and freeze-out and
will nally produce lots of observed particles []. As we
know, a description of strong nuclear interactions is quantum
chromodynamics (QCD). Studying QCD phase transition
and properties of quark matter is a main target of heavy-ion
collisions at relativistic heavy ion collider (RHIC) and large
hadron collider (LHC) []. But the evolution of the heavy-ion
collisions and the production of hadrons are very complicated
for us. In general, we can extract the evolution informa-
tion of the colliding system by analyzing the properties of
observable quantities, which contain multiplicity, transverse
momentum, polar and elliptic ow, and angular correlation,
and so on.
In recent years, a dihadron correlation has been one of
the hot topics in particle and nuclear physics. Experimen-
tally, RHIC and LHC have observed or will observe the
dihadron azimuthal correlations in proton-proton, proton-
nucleus, and nucleus-nucleus collisions. Some theoretical
investigations [–]givemanyvaluableandinteresting
results to explain the ridge phenomena, which were regarded
as a contribution from jet-medium interactions. In these
works, various models have been proposed. In this paper, we
would like to apply a multisource thermal model to discuss
azimuthal correlations of dihadron for dierent associated
transverse momentum
assoc
𝑇
intervals in –% and –
%, which are measured in Au-Au collisions at
NN
=
200GeV []. For a comparison, we will also use the model to
discuss the azimuthal correlations of the dihadron for a wide
centrality range in Pb-Pb collisions at
NN
=2.76TeV [].
2. Dihadron Azimuthal Correlation in
the Model and Experiments
As a presupposition in the multisource thermal model
[–], the observed particles are projected isotropically
Hindawi Publishing Corporation
Advances in High Energy Physics
Volume 2014, Article ID 870614, 6 pages
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/870614