Introduction to Wireless Sensor Networks
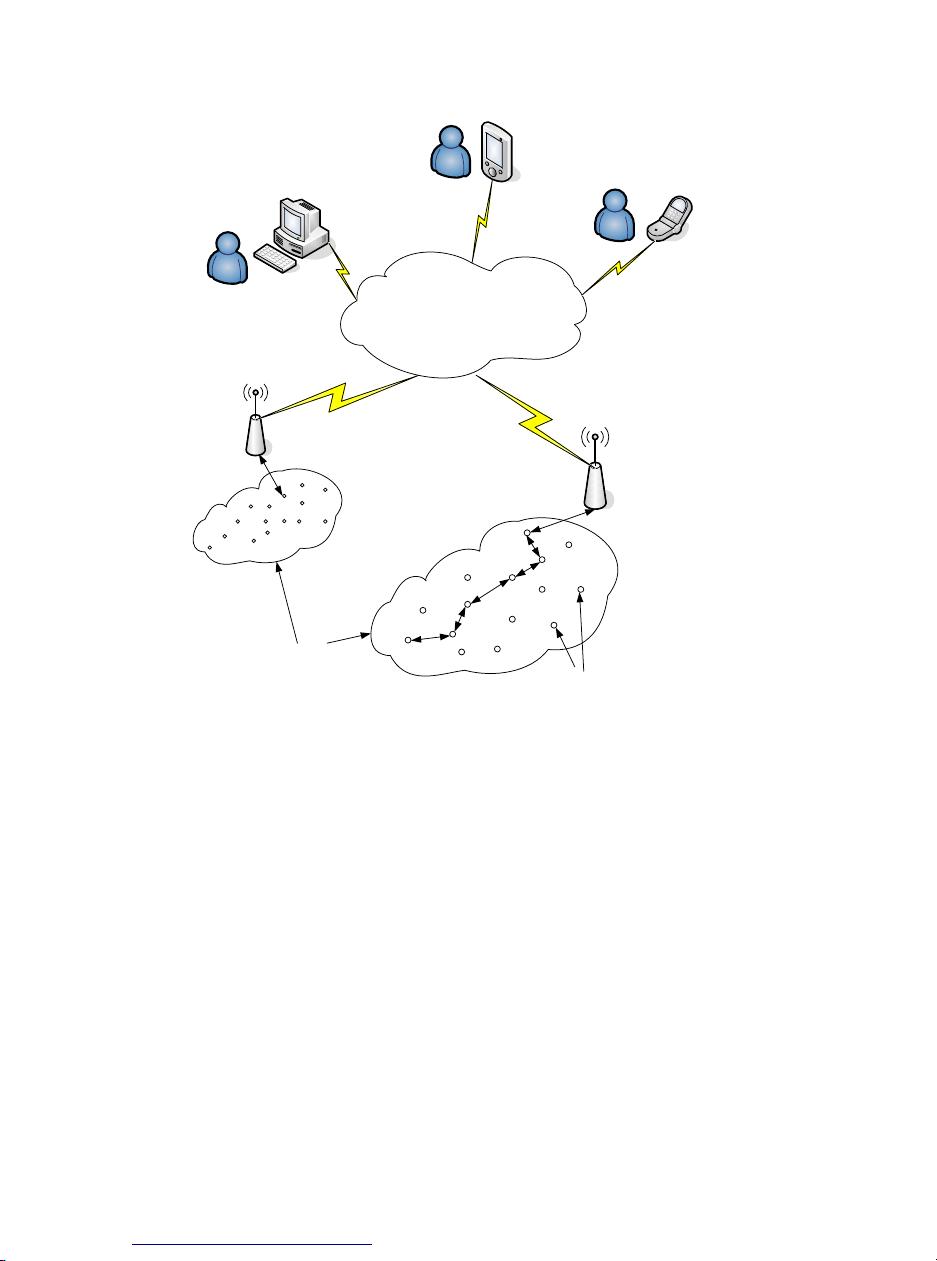
无线传感器网络(Wireless Sensor Networks,简称WSN)是一种由大量小型、低成本、低功耗的传感器节点组成的网络,这些节点能够感知环境信息,并通过无线通信进行数据传输和信息共享。WSN是现代信息技术发展的一个重要方向,尤其在后PC时代,随着笔记本电脑、手机、个人数字助理(PDA)、全球定位系统(GPS)、射频识别(RFID)以及智能电子设备的普及,计算设备变得更为便携、分布广泛且深入日常生活的方方面面。 ### WSN的关键组件 一个典型的无线传感器节点主要包括以下几个部分: 1. **传感组件**:用于采集环境数据,如温度、湿度、光照强度等。 2. **计算组件**:负责数据处理与存储,通常集成有微处理器和内存。 3. **通信组件**:支持无线通信,实现与其他节点的数据交换。 4. **执行组件**:根据处理后的信息执行特定操作,如开关阀门、调整电机等。 5. **电源组件**:为整个节点供电,常见的是采用电池供电,设计时需考虑节能策略以延长工作时间。 ### WSN的应用场景 WSN的应用范围极其广泛,涵盖了多个领域: - **环境监测与生态研究**:部署于野外,监测气候、动物活动等自然现象。 - **军事侦察**:战场上的隐蔽部署,用于情报收集和监视。 - **应急救援**:灾难发生时快速部署,协助搜救行动。 - **工业维护**:工厂中的设备监控,实现基于状态的维修策略。 - **建筑健康监测**:评估建筑物结构安全,预防潜在风险。 - **智能家居**:家庭自动化控制,提升居住舒适度。 - **医疗监护**:患者体征监测,及时反馈健康状况。 ### WSN的技术挑战 尽管WSN具有广阔的应用前景,但其技术实现也面临诸多挑战: 1. **能源限制**:传感器节点通常依赖电池供电,如何优化能量消耗,延长网络寿命是关键问题。 2. **通信效率**:无线通信信道的不稳定性与多跳传输机制增加了数据传输的复杂性。 3. **安全性**:开放的无线环境易受干扰与攻击,确保数据的安全传输是另一大挑战。 4. **大规模部署**:成千上万的传感器节点自组织形成网络,如何高效管理与协调是亟待解决的问题。 ### 结论 无线传感器网络作为信息技术领域的一项重大突破,正逐步改变我们对环境的认知与管理方式。通过将微型传感器节点广泛部署,不仅可以收集到前所未有的海量数据,还能实现远程监控与智能化决策。然而,WSN的发展同样面临着能源、通信、安全及管理等方面的挑战,未来的研究将致力于克服这些障碍,推动WSN技术向更成熟、更广泛应用的方向发展。



剩余20页未读,继续阅读

 yin556633282014-03-07学习无线传感器的经典资料
yin556633282014-03-07学习无线传感器的经典资料
- 粉丝: 5
- 资源: 45
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 西工大noj 116题及答案word版.doc
- 模拟采访ppt封面(英文版)
- Django开发中常见问题与解决方案的全面指南
- 基于51单片机的波形发生器设计(protues仿真)-毕业设计
- 安卓开发注意事项及踩坑示例:从环境搭建到性能优化全面指南
- 车辆船只检测5-YOLO(v5至v9)、COCO、CreateML、Darknet、Paligemma、TFRecord、VOC数据集合集.rar
- Questasim仿真脚本
- Questasim仿真脚本2
- 基于51单片机的正弦波方波锯齿波振幅频率可调波形发生器设计(protues仿真)-毕业设计
- 西工大noj 题及答案word版.docx
- 计算机视觉与机器学习的OpenCV开发资源指南
- YOLO目标检测算法学习与开发资源全面整理
- 基于51单片机的定时插座数码管设计(protues仿真)-毕业设计
- 车辆船只检测8-YOLO(v5至v9)、COCO、CreateML、Darknet、Paligemma、TFRecord、VOC数据集合集.rar
- mp3转换器小程序-音频20241222115740.mp3
- 汇编语言学习开发资源指南:计算机科学基础与实践


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功