没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

1
MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of
Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC)
Data User’s Guide
Collection 6 (ver. of June 2018)
Version 2.0
Principal Investigator: Alexei Lyapustin
Correspondence e-mail address:
Yujie.Wang@nasa.gov; Alexei.I.Lyapustin@nasa.gov;
Prepared by Alexei Lyapustin and Yujie Wang
Published: June 2018

2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Introduction …………………….............................................................................................. 3
2. Overview of MAIAC products ........................................................................................... 3
2.1 Tiled File Structure and Naming Convention ................................................................... 3
2.2 MAIAC Products: General Description ............................................................................ 4
2.2.1 Atmospheric Properties File (MCD19A2).................................................................. 4
2.2.2 Surface Reflectance File (MCD19A1) ...................................................................... 5
2.2.3 Surface BRDF File (MCD19A3) …………………………………………..………. 8
3. QA-related Comments (please read) ………………………….................................................... 9
3.1 Change in reported AOD for MAIAC AOD users ………………………………….……9
3.2 Use of Adjacency Mask .................................................................................................... 9
3.3 Selecting Best Quality BRF and AOD .............................................................................. 9
4. MAIAC Data Specification ………………………………………………………………..… 10
4.1. Surface Reflectance (MCD19A1) ............................................................................... 10
4.2 Status QA definition for MCD19A1 (16-bit unsigned integer) …………...…………… 11
4.3 Aerosol Optical Depth (MCD19A2) …..……….………………………………………. 12
4.4 AOD QA definition for MCD19A2 (16-bit unsigned integer) ………………………… 13
4.5 8-day BRDF model parameters (MCD19A3) ………………………………………..… 14
5. Caveats and Known Problems …………………………………………………………….… 14
6. Community Validation and Analysis of MAIAC …………………………………………… 15
7. Data ordering (browsing) ………………………………………………………………….… 15
7.1 Data Access…………………………………………………………………………………..15
References ............................................................................................................................... 16

3
1. Introduction
MAIAC is a new advanced algorithm which uses time series analysis and a combination of pixel-
and image-based processing to improve accuracy of cloud detection, aerosol retrievals and
atmospheric correction (Lyapustin et al., 2011a,b; 2012; publication on current MAIAC is under
preparation). The underlying physical idea behind MAIAC is simple: because surface changes
slowly in time compared to aerosols and clouds given the daily rate of global MODIS observations,
we focus on extensive characterization of the surface background in order to improve all stages of
MAIAC processing. MAIAC starts with gridding MODIS measurements (L1B data) to a fixed grid
at 1km resolution in order to observe the same grid cell over time and work with polar-orbiting
observations as if they were “geostationary”. In this regard, this approach is fundamentally different
from the conventional swath-based processing where the footprint changes with orbit and view
geometry (scan angle) making it difficult to characterize an always changing surface background.
To enable the time series analysis, MAIAC implements the sliding window technique by storing
from 4 (at poles) to 16 (at equator) days of past observations in operational memory. This helps us
retrieve surface BRDF from accumulated multi-angle set of observations, and detect seasonal (slow)
and rapid surface change. A detailed knowledge of the previous surface state also helps MAIAC’s
internal dynamic land-water-snow classification including snow detection and characterization.
Consistently with the entire C6 MODIS land processing, the top-of-atmosphere (TOA) L1B
reflectance includes standard C6 calibration (Toller et al., 2014) augmented with polarization
correction for MODIS Terra (Meister et al., 2012), residual de-trending and MODIS Terra-to-
Aqua cross-calibration (Lyapustin et.al, 2014). The L1B data are first gridded into 1km MODIS
sinusoidal grid using area-weighted method (Wolfe et al., 1998). Due to cross-calibration, MAIAC
processes MODIS Terra and Aqua jointly as a single sensor.
2. Overview of MAIAC products
MAIAC provides a suite of atmospheric and surface products in HDF4 format, including: (1) daily
MCD19A1 (spectral BRF, or surface reflectance), (2) daily MCD19A2 (atmospheric properties),
and (3) 8-day MCD19A3 (spectral BRDF/albedo).
2.1 Tiled File Structure and Naming Convention
Products are generated on a 1km sinusoidal grid. The sinusoidal projection is not optimal due to
distortions at high latitudes and off the grid-center, but it is a tradeoff made by the MODIS land
team for the global data processing. The gridded data are divided into 1200x1200km
2
standard
MODIS tiles shown in Figure 1.
The current dataset presents data per orbit (we do not provide a daily composite image as in
standard MODIS surface reflectance product MOD09). Each daily file name follows the standard
MODIS name convention, for instance:
MCD19A1.DayOfObservation.TileNumber.Collection.TimeOfCreation.hdf.
DayOfObservation has the format “AYYYYDDD”, where YYYY is year, DDD is Julian day.
TileNumber has the standard format, e.g. h11v05 for the east coast USA.
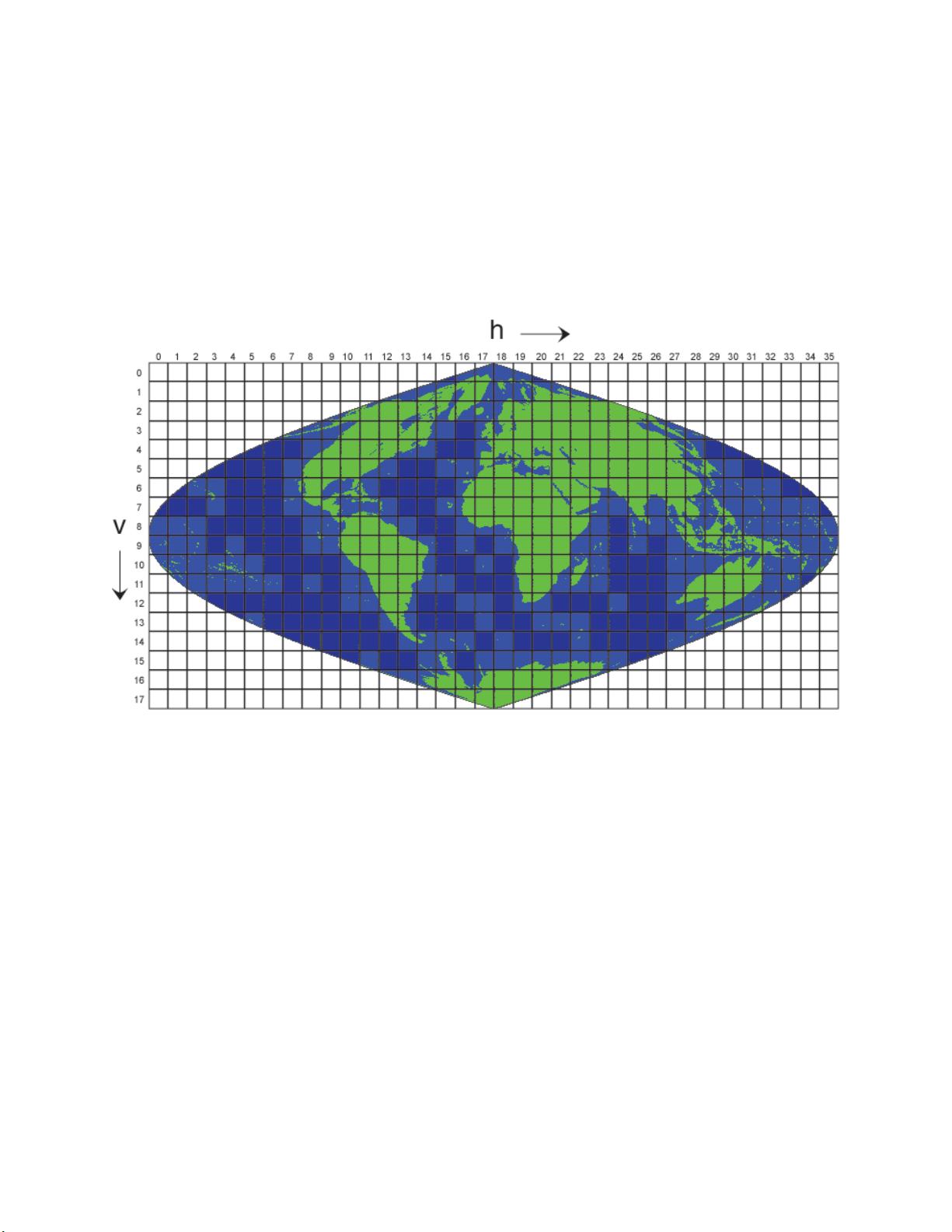
4
Each daily file usually contains multiple orbit overpasses (1-2 at equator and up to 30 in polar
regions for combined Terra and Aqua) which represents the third (time) dimension of MAIAC
daily files. The orbit number and the overpass time of each orbit are saved in global attributes
“Orbit_amount” and “Orbit_time_stamp” sequentially. The Orbit_time_stamp is in the format of
“YYYYDDDHHMM[T/A]”, where YYYY is year, DDD is Julian day, HH is hour MM is minute,
T stands for Terra and A stands for Aqua. At high latitudes, only the first 16 orbits with largest
coverage are selected for processing per day in order to limit the file size.
Figure 1. Illustration of MODIS Sinusoidal Tiles.
2.2 MAIAC Products: General Description
In Version 6, MAIAC spectral BRF and BRDF are considered “standard” products while aerosol
optical depth (AOD) and other output fields are reported as “internal”. MAIAC processing is limited
to global land tiles and land-containing ocean tiles (green and light blue colors in Fig. 1).
Over inland, coastal and open ocean waters, MAIAC reports AOD, fine mode fraction, and spectral
reflectance of underlight (or equivalent reflectance of water-leaving radiance).
2.2.1 Atmospheric Properties File (MCD19A2)
For each orbit, MAIAC daily MCD19A2 (atmospheric properties) file includes:
Over land:
-
column water vapor (CWV) retrieved from MODIS near-IR bands B17-B19 at 0.94
m
(in cm). CWV is reported for both clear and cloudy pixels. In the latter case, it represents
剩余18页未读,继续阅读
资源评论


此星光明
- 粉丝: 8w+
- 资源: 1323
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 白色简洁风格的宠物美容服务整站网站源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的创意画展模板下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的宠物收养所源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的出租车公司整站网站源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的创意室内设计模板下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的创意生活家居整站网站源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的创意设计网站模板下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的创意图片设计模板下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的大学图书教育整站网站模板.zip
- 白色简洁风格的大型机械卡车运输企业网站模板.zip
- 白色简洁风格的当代网站CSS3模板.zip
- 白色简洁风格的单页面背景信息源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的地产实业公司企业网站源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的登录页源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的登山探险装备网店整站网站源码下载.zip
- 白色简洁风格的电话通讯公司模板下载.zip
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功