LTspice build in VDmos model.
Introduction (from the help file)
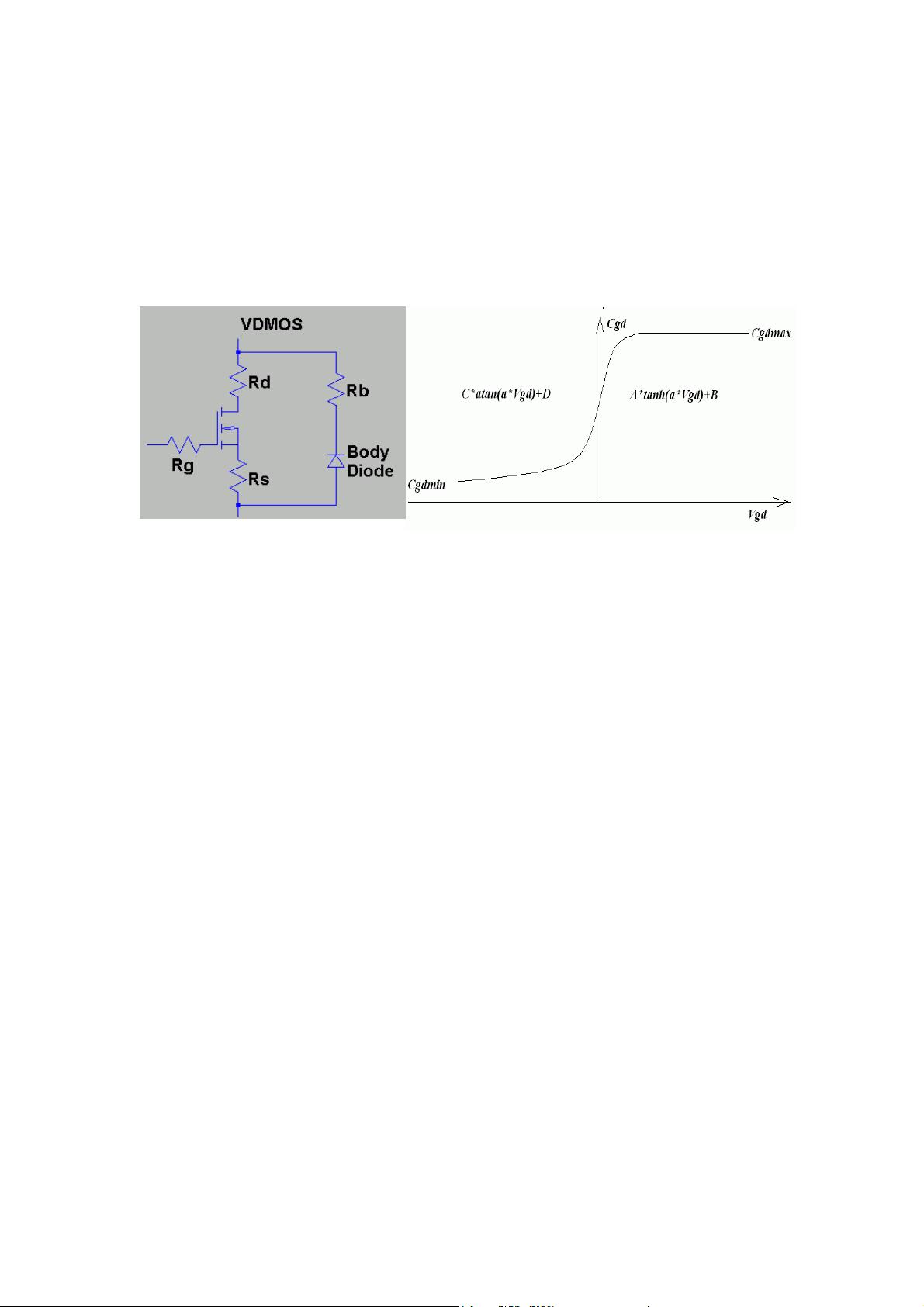
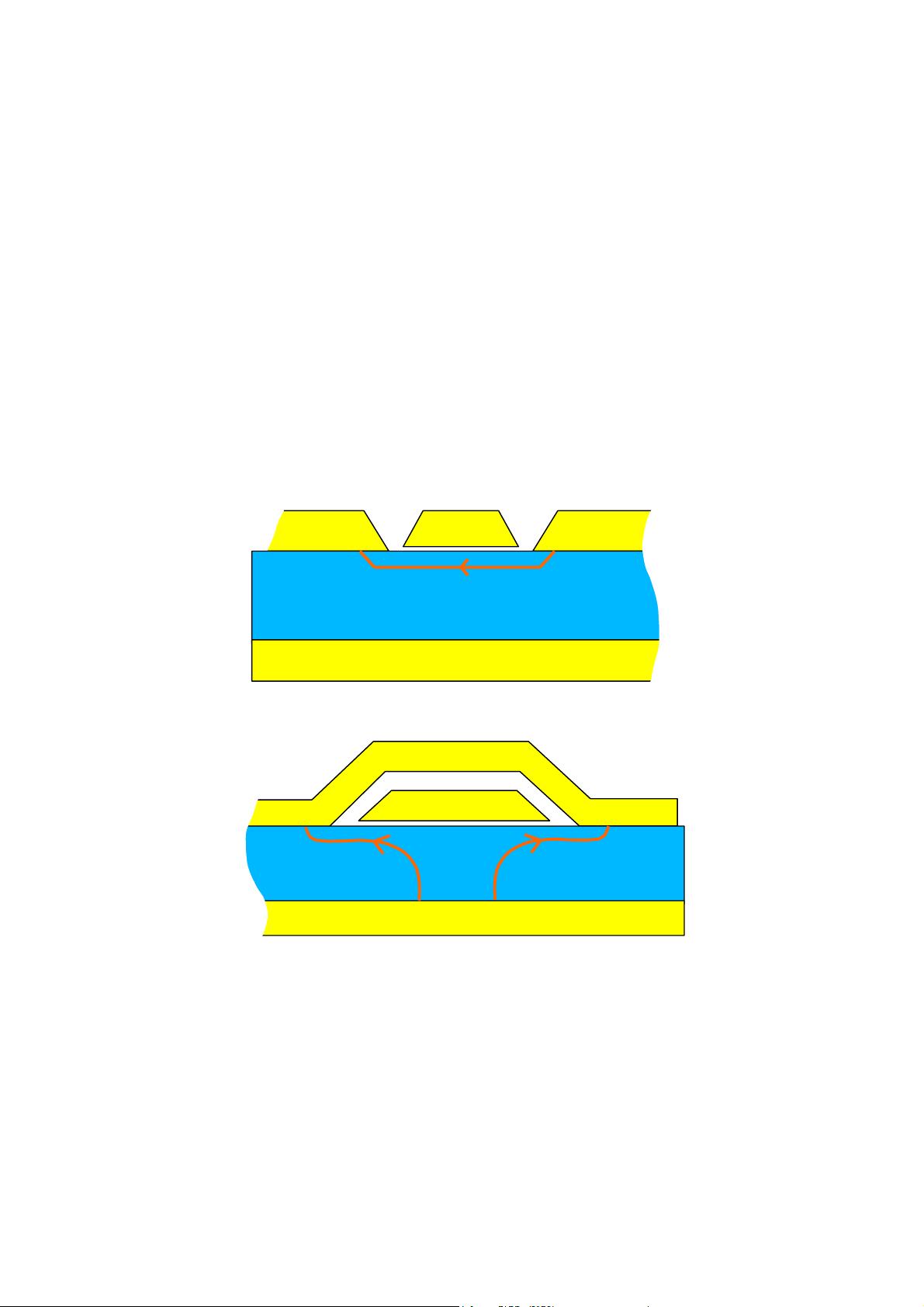
The discrete vertical double diffused MOSFET transistor (VDMOS) popularly used in
board level switch mode power supplies has behavior that is qualitatively different
than the monolithic MOSFET models. In particular, (i) the body diode of a VDMOS
transistor is connected differently to the external terminals than the substrate diode of
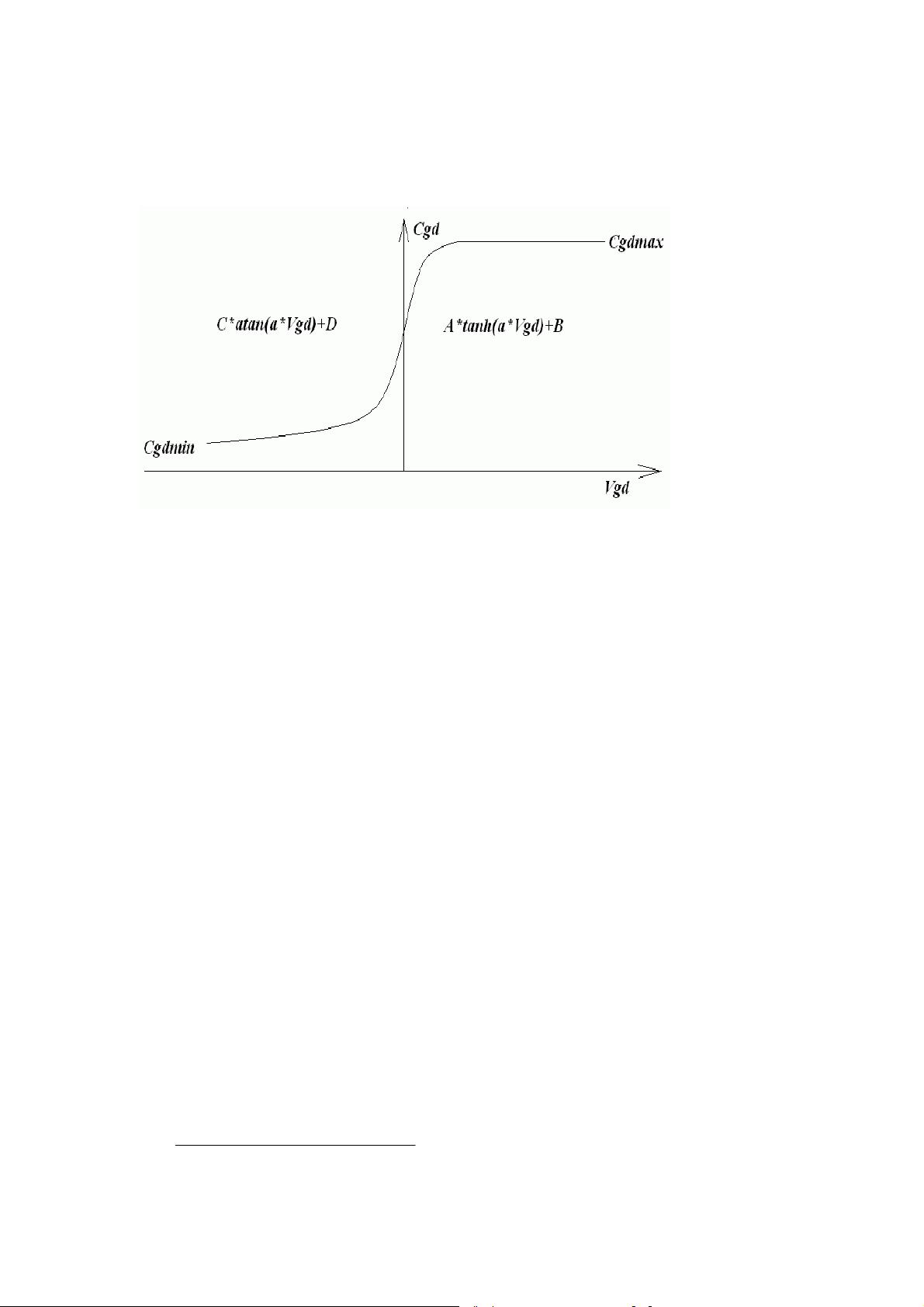
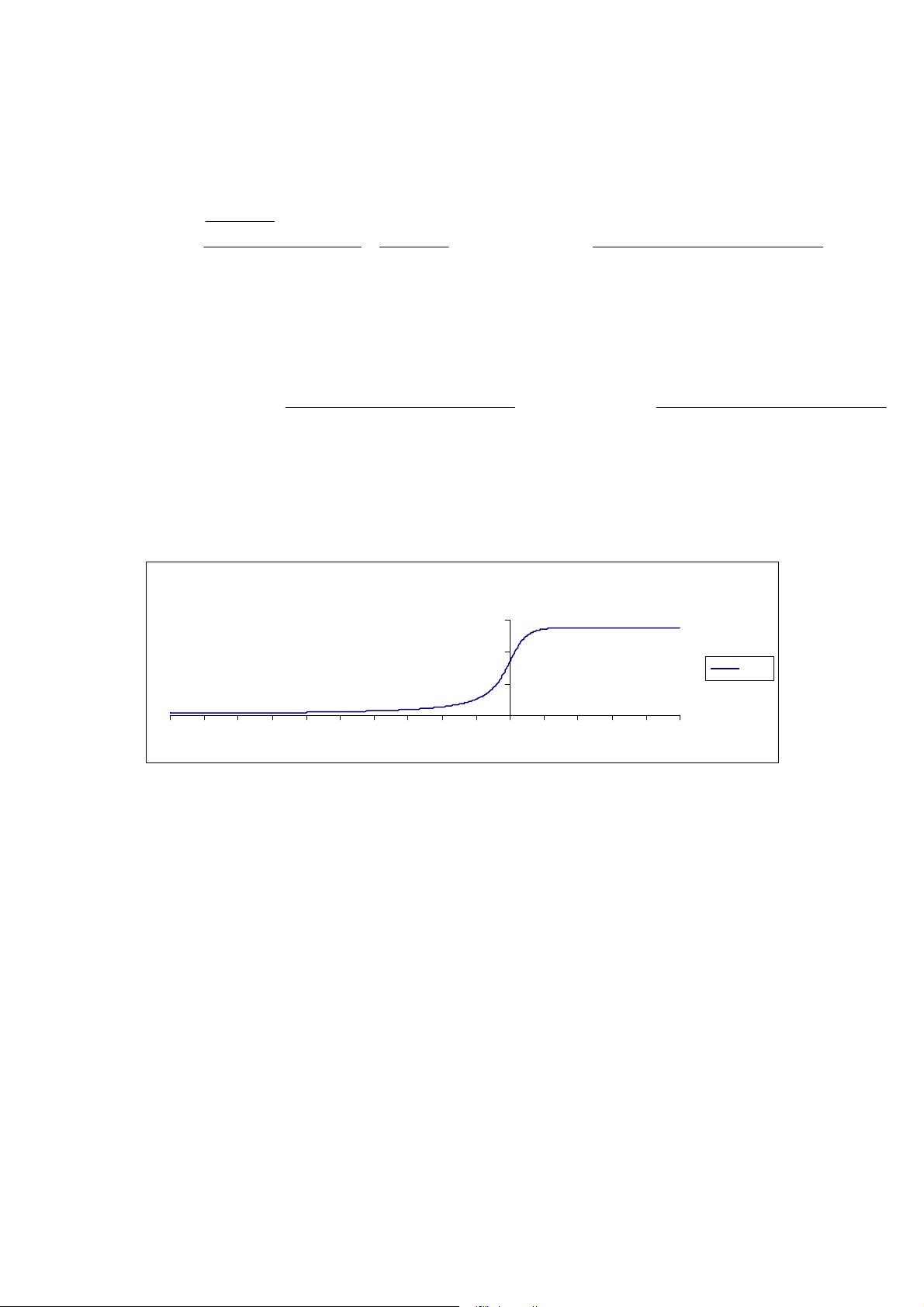
a monolithic MOSFET and (ii) the gate-drain capacitance (Cgd) non-linearity cannot
be modeled with the simple graded capacitances of monolithic MOSFET models. In a
VDMOS transistor, Cgd abruptly changes about zero gate-drain voltage (Vgd). When
Vgd is negative, Cgd is physically based a capacitor with the gate as one electrode
and the drain on the back of the die as the other electrode. This capacitance is fairly
low due to the thickness of the non-conducting die. But when Vgd is positive, the die
is conducting and Cgd is physically based on a capacitor with the thickness of the gate
oxide.
Normal Monolithic MOSFET
(Used in IC’s)
VDMOS
(Discrete Power MOSFET)
Source
Gate
Bulk
(
Substrate
)
Drain
Source
Gate
Drain