
CAN with Flexible Data-Rate
Specification
Version 1.0
(released April 17th, 2012)
FD

© Copyright 2011, Robert Bosch GmbH, Robert Bosch Platz 1, 70839 Gerlingen, Germany
April 2012
page 1
Recital
The acceptance and introduction of serial communication to more and more applica-
tions has led to increasing demand for bandwidth in CAN communication and caused
system developers to look for alternative communication options in certain applications.
These applications can be realized more comfortably with the new protocol CAN FD
that allows data rates higher than 1 MBit/s and payloads longer 8 bytes per frame.
CAN FD shares the physical layer, with the CAN protocol as defined in the BOSCH
CAN Specification 2.0. The frame format however, is different. There are two new con-
trol bits in the CAN FD frame, the first enabling the new frame format with different data
length coding and the second optionally switching to a faster bit rate after the arbitration
is decided. New CRC polynomials are introduced to secure the longer CAN FD frames
with the same Hamming distance as in the proven CAN protocol.
The CAN FD frame format has been defined so that messages in CAN frame format
and in CAN FD frame format can coexist within the same network. The BOSCH CAN
Specification 2.0 remains valid without any modification as an independent, self-con-
tained CAN bus protocol specification. The coexistence is assured by the requirement,
that in order to be compatible with this CAN FD specification it is required that a
CAN FD implementation be compatible with this CAN FD specification as well as with
the BOSCH CAN Specification 2.0.
In order to be compatible with this CAN FD specification it is required that a CAN FD
implementation be compatible with this specification as well as with ISO 11898-1.
Note: CAN FD implementations that are designed according to this specification and
CAN implementations that are designed according to the BOSCH CAN Specification 2.0
can communicate with each other as long as it is not made use of the CAN FD frame
format. This enables CAN systems to migrate gradually into CAN FD systems. In the
introductory phase, it is possible to use CAN FD only in specific operation modes, e.g.
software-download at end-of-line programming, while other controllers that do not sup-
port CAN FD are kept in standby.

© Copyright 2011, Robert Bosch GmbH, Robert Bosch Platz 1, 70839 Gerlingen, Germany
April 2012
page 2
1 Introduction............................................................................................................ 3
2 Basic Concepts...................................................................................................... 5
3 Message Transfer.................................................................................................. 8
3.1 Frame Formats ...................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Frame Types.......................................................................................................... 8
3.3 Operation Modes ................................................................................................. 19
4 Message Validation ............................................................................................. 21
4.1 Message Filtering ................................................................................................ 21
5 Coding ................................................................................................................. 22
6 Error Handling...................................................................................................... 23
6.1 Error Detection..................................................................................................... 23
6.2 Error Signalling .................................................................................................... 23
7 Fault Confinement ............................................................................................... 24
8 Bit Timing Requirements ..................................................................................... 26
8.1 Transceiver Delay Compensation........................................................................ 30
9 CAN FD Implementation...................................................................................... 32
© Copyright 2011, Robert Bosch GmbH, Robert Bosch Platz 1, 70839 Gerlingen, Germany
April 2012
page 3
Introduction
1INTRODUCTION
CAN FD is a serial communications protocol which efficiently supports distributed real-
time control with a very high level of security.
The intention of this specification is to achieve compatibility between any two CAN FD
implementations. Compatibility, however, has different aspects regarding e.g. electrical
features and the interpretation of data to be transferred. To achieve design transpar-
ency and implementation flexibility CAN FD has been subdivided into different layers
according to the ISO/OSI Reference Model.
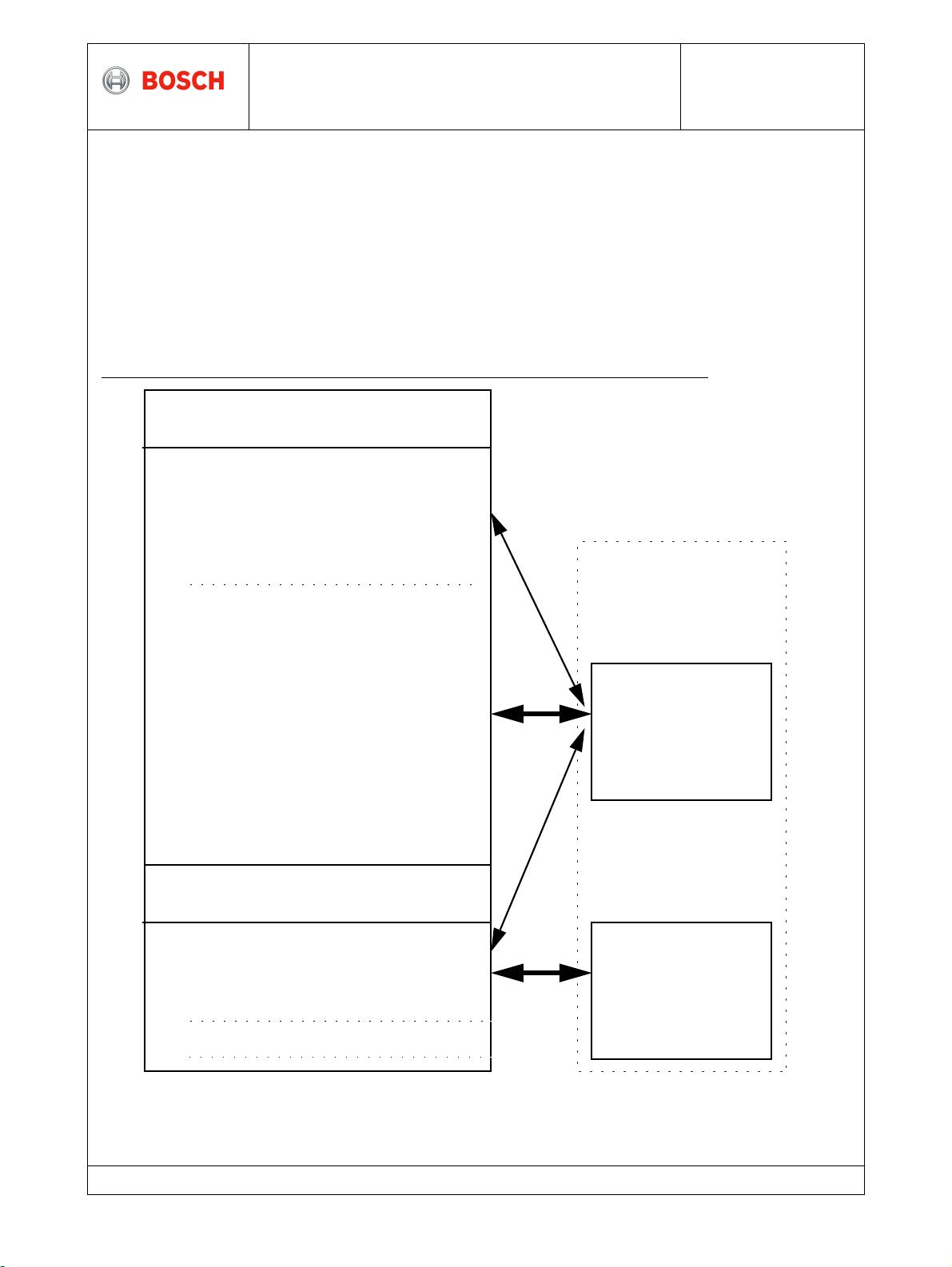
Layered Architecture of CAN FD according to the OSI Reference Model
The scope of this specification is to define the MAC sublayer and a small part of the
LLC sublayer of the Data Link Layer as well a part of the Physical Layer and to describe
the consequences of the CAN protocol on the surrounding layers.
Data Link Layer
Physical Layer
LLC Logical Link Control
MAC Medium Access Control
Acceptance Filtering
Overload Notification
Recovery Management
Data Encapsulation
/Decapsulation
Frame Coding
(Stuffing, Destuffing)
Medium Access Management
Error Detection
Error Signalling
Acknowledgment
Serialization / Deserialization
Bit Encoding/Decoding
Bit Timing
Synchronization
Driver/Receiver Characteristics
Fault
Confinement
Bus Failure
Management
Supervisor















