
Application Note
Construction of SMS PDU’s

First edition (June 2003)
Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications. publishes this manual without making any warranty as to the
content contained herein. Further Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications. reserves the right to make
modifications, additions and deletions to this manual due to typographical errors, inaccurate information,
or improvements to programs and/or equipment at any time and without notice. Such changes will,
nevertheless be incorporated into new editions of this manual.
All rights reserved.
© Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications., 2003

Construction of SMS PDU’s
LZT 123 7632 R1A 3
Contents
1
INTRODUCTION....................................................................................................................4
2 ABOUT SMS.......................................................................................................................... 5
3 WHAT IS A PDU?..................................................................................................................5
3.1 TRANSMISSION ORDER ...................................................................................................... 6
3.2 REPRESENTATIONS ........................................................................................................... 7
4 SMS-SUBMIT ........................................................................................................................ 8
4.1 THE SERVICE CENTER ADDRESS (SCA)............................................................................. 8
4.2 THE NEXT OCTET (TP-MTI AND FRIENDS) ......................................................................... 11
4.2.1 Message Type indicator (TP-MTI) ......................................................................... 11
4.2.2 Reject Duplicates (TP-RD) .................................................................................... 12
4.2.3 Validity Period Format (TP-VPF) ........................................................................... 12
4.2.4 Status Report Request (TP-SRR) ......................................................................... 12
4.2.5 User Data header Indicator (TP-UDHI) ................................................................. 13
4.2.6 Reply Path (TP-RP) ............................................................................................... 13
4.2.7 Back to our example – what does it mean? .......................................................... 13
4.3 MESSAGE REFERENCE FIELD (TP-MR)............................................................................. 14
4.4 DESTINATION ADDRESS (TP-DA)....................................................................................... 14
4.5 PROTOCOL IDENTIFIER (TP-PID) ..................................................................................... 15
4.6 DATA CODING SCHEME (TP-DCS).................................................................................... 16
4.7 VALIDITY PERIOD (TP-VP) ............................................................................................... 19
4.8 USER DATA LENGTH (TP-UDL) ........................................................................................ 20
4.9 USER DATA (TP-UD) ...................................................................................................... 20
5 SMS-DELIVER.....................................................................................................................25
5.1 SERVICE CENTRE ADDRESS ............................................................................................. 25
5.2 TP-MTI AND MORE FRIENDS ............................................................................................ 25
5.2.1 Message Type indicator (TP-MTI) ......................................................................... 26
5.2.2 More Messages to Send (TP-MMS) ...................................................................... 26
5.2.3 Status Report Indication (TP-SRI) ......................................................................... 26
5.2.4 User Data header Indicator (TP-UDHI) ................................................................. 26
5.2.5 Reply Path (TP-RP) ............................................................................................... 27
5.2.6 Back to our example .............................................................................................. 27
5.3 THE ORIGINATING ADDRESS (TP-OA)............................................................................. 27
5.4 PROTOCOL IDENTIFIER (TP-PID) ..................................................................................... 28
5.5 DATA CODING SCHEME (TP-DCS).................................................................................... 28
5.6 THE SERVICE CENTRE TIME STAMP (TP-SCTS) ................................................................ 28
5.7 USER DATA LENGTH (TP-UDL) ....................................................................................... 29
5.8 USER DATA (TP-UD) ................................................................................................... 29

Construction of SMS PDU’s
LZT 123 7632 R1A 4
1 Introduction
This document is to help an integrator in getting started with sending SMS
messages in the PDU format. Enough information is given here for anyone
to begin constructing the most basic PDU’s and send them, using AT
commands, from one GSM module/mobile to another.
Construction of SMS PDU’s
LZT 123 7632 R1A 5
2 About SMS
SMS, as you already probably know stands for Short Message Service.
SMS provides a means of sending messages of limited size from and to
GSM mobile stations. SMS makes use of something called a Service
Centre, which acts as a store and forward centre for the SMS messages.
Two different types of SMS services can be defined:
Mobile Originated (MO) – Mobile originated SMS will be transported from
a mobile station to the Service Centre. These may be destined for other
mobiles or may even be destined for other services which the GSM
network and Service Centre supports.
Mobile Terminated (MT) – Mobile terminated SMS will be transported from
a Service Centre to a mobile Station.
3 What is a PDU?
PDU is short for Protocol Data Unit (or it could even be Packet Data Unit,
the different meanings are in use). These data units represent how the
digital information is coded and structured when it sent over the air
interface.
When we use a mobile phone, we usually enter a text message by the
keypad of the phone, give it a phone number to be sent to, press the
“YES” button and, usually, receive a “MESSAGE SENT” notification from
the phone. With a GSM module this process has to be performed with AT
commands from a terminal of some kind, since there is no keyboard. In
some cases the module does not support text mode SMS, and the
message must be coded as a PDU.
Using the PDU mode gives the user much more power over the
information to be sent and how it is sent. For instance one may not wish to
send a text message, but may wish to send raw Data. PDU format will
allow you to do this.
There are different kinds of PDU involved in SMS messaging, from SMS-
REPORT, SMS-COMMAND etc. etc. but we will consider only two
different types here, probably the most important as well.
Related to Mobile originated SMS is the PDU of type SMS-SUBMIT. This
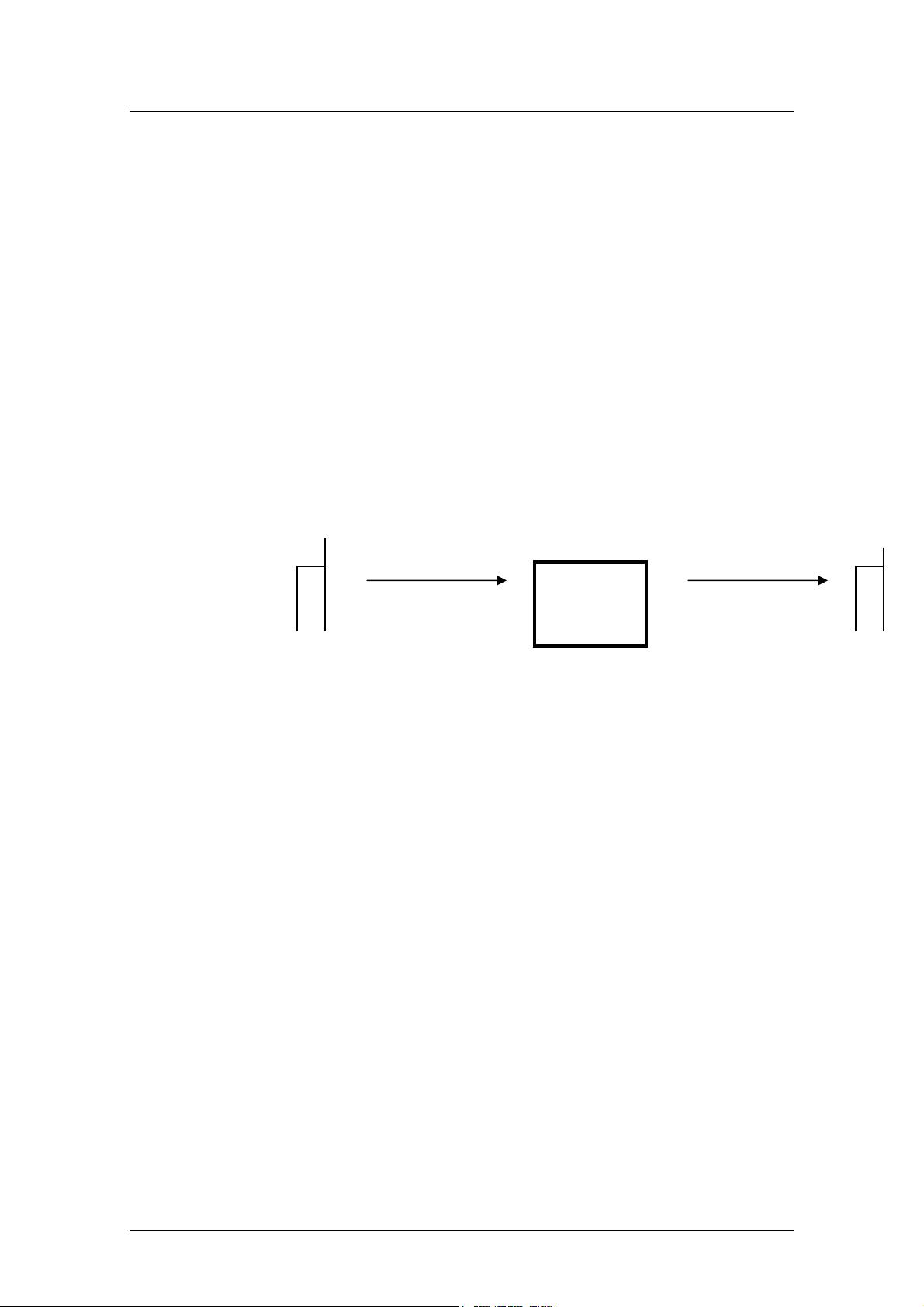
is a PDU that is sent from one Mobile terminal to the Service centre.
SMS-
SERVICE
CENTER
Mobile Station Mobile Station
MO SMS MT SMS
(
SMS-SUBMIT PDU
)
(
SMS-DELIVER PDU
)
















