
U16 APPLICATIONS OF POWER
ELECTRONICS
U16 – 1 Controlled and uncontrolled rectification

SUB UNIT OUTLINE
Measurement techniques : safety considerations in a
heavy current power environment (eg in systems
where V > 50 V); use of isolated differential voltage
attenuator probes; Hall effect current probes; power
oscilloscope
Standard configurations: half wave and full wave
bridge circuits; resistive and inductive loads, flywheel
diodes
Signal parameters: eg average and root-mean-square
(rms) values, pulse number, waveforms, harmonics
Device protection : protection of power semiconductors
(eg over-voltage, over-current, transients)
5/7/2010
2
U16 Applications of Power Electronics

SUB UNIT OUTLINE
Measurement techniques : safety considerations in a
heavy current power environment (eg in systems
where V > 50 V); use of isolated differential voltage
attenuator probes; Hall effect current probes; power
oscilloscope
Standard configurations: half wave and full wave
bridge circuits; resistive and inductive loads, flywheel
diodes
Signal parameters: eg average and root-mean-square
(rms) values, pulse number, waveforms, harmonics
Device protection : protection of power semiconductors
(eg over-voltage, over-current, transients)
5/7/2010
3
U16 Applications of Power Electronics
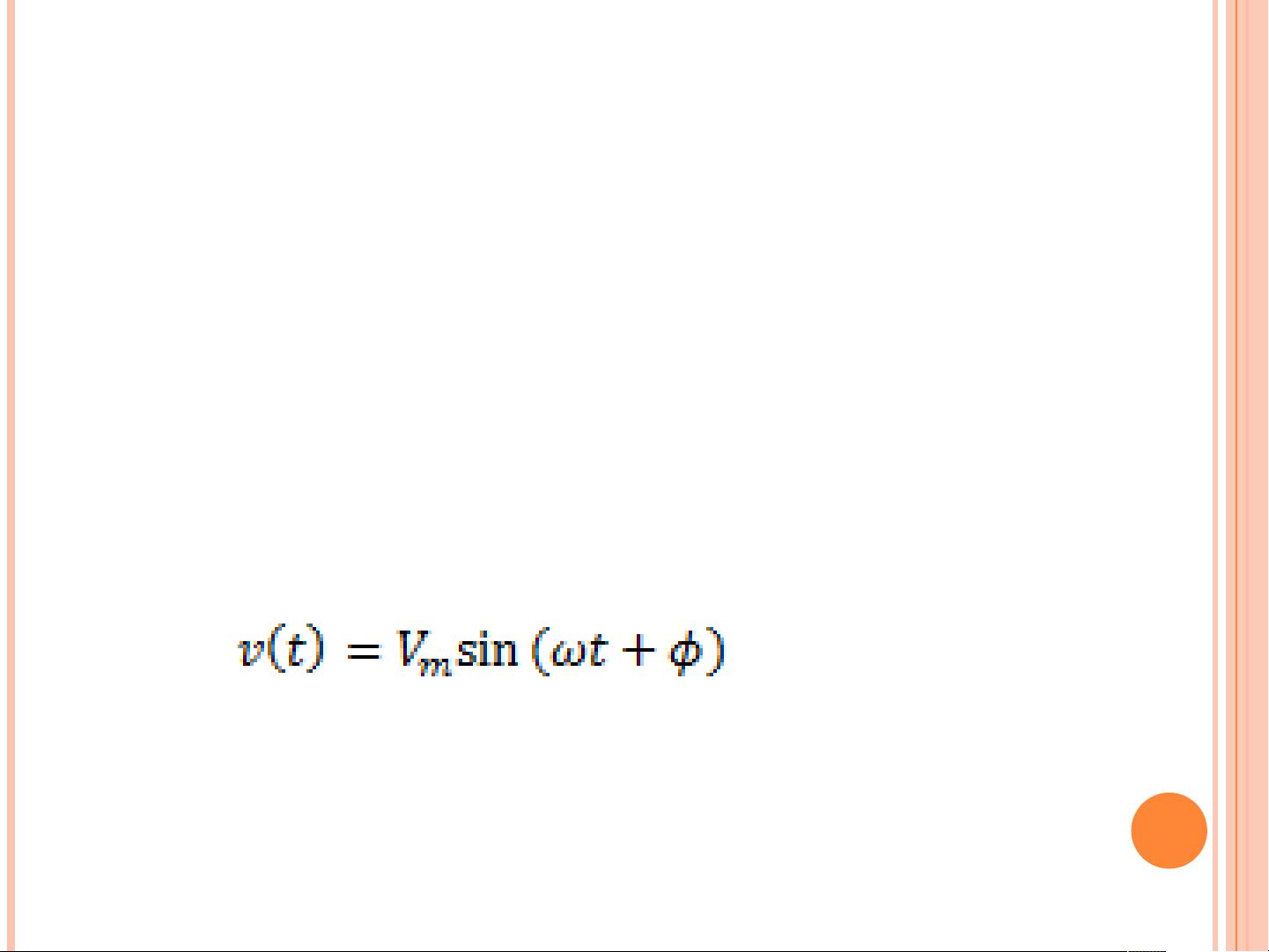
ALTERNATIVE CURRENT (AC)
AC waveform is a periodic waveform which
alternate between positive and negative values.
Amplitude is varying instance to instance.
Example
Sinusoidal Voltage waveform

INSTANTANEOUS VALUE
The vale of the waveform at any given instance of
time.
It is a time variable.
For a sinusoidal, Instantaneous value















