
© 2013 ANSYS, Inc. May 21, 2013
1
Release 14.5
Lecture 3:
Static Magnetic Solvers
ANSYS Maxwell V16
Training Manual
© 2013 ANSYS, Inc. May 21, 2013
2
Release 14.5
A. Magnetostatic Solver
a. Selecting the Magnetostatic Solver
b. Material Definition
c. Boundary Conditions
d. Excitations
e. Parameters
f. Analysis Setup
g. Solution Process
B. Eddy Current Solver
a. Selecting the Eddy Current Solver
b. Material Definition
c. Boundary Conditions
d. Excitations
e. Parameters
f. Analysis Setup
g. Solution Process
Content
© 2013 ANSYS, Inc. May 21, 2013
3
Release 14.5
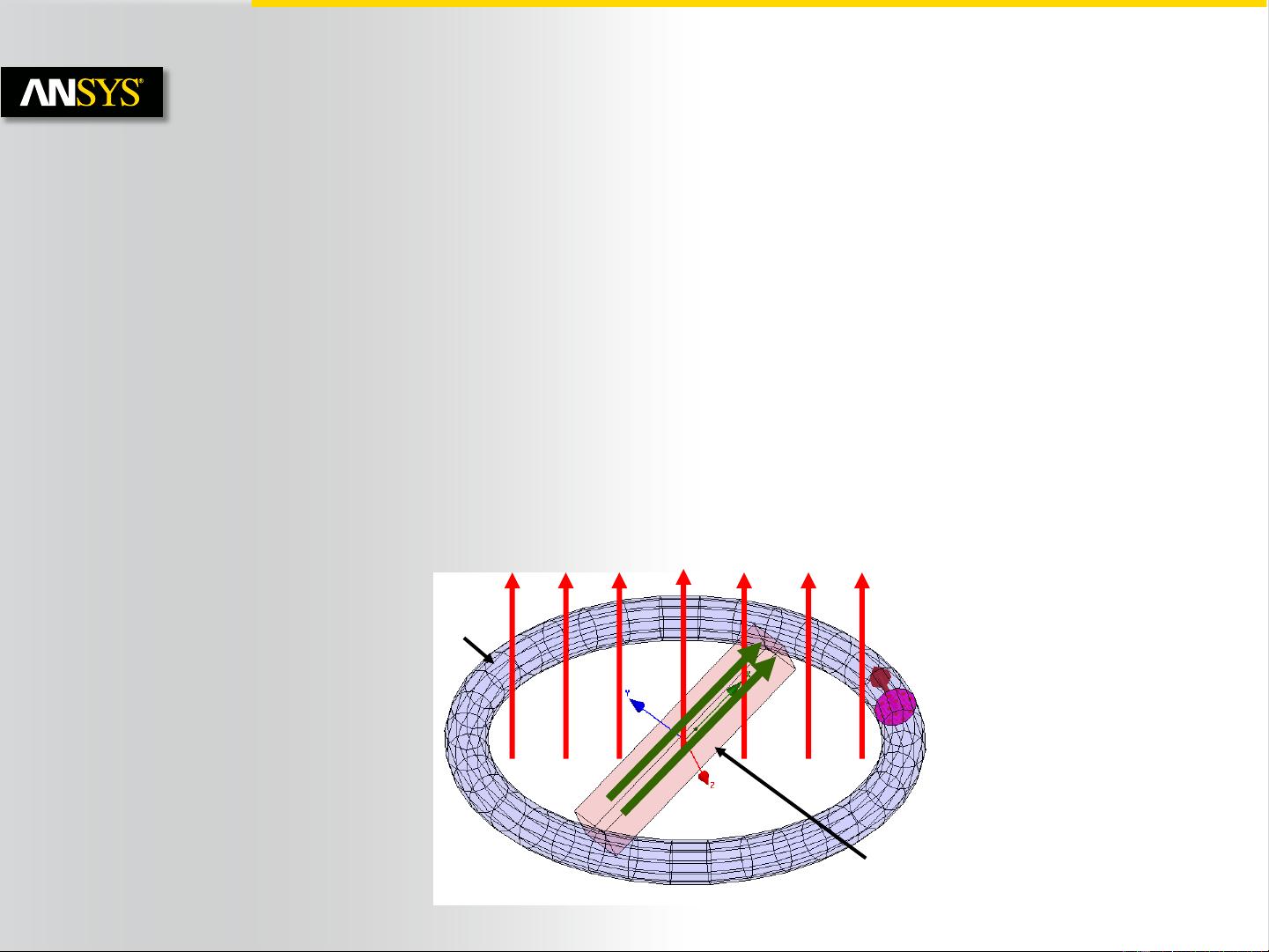
A. Magnetostatic Solver
Magnetostatic Solver
– In the Magnetostatic Solver, a static magnetic field is solved resulting from a DC
current flowing through a coil or due to a permanent magnet
– The Electric field inside the current carrying coil is completely decoupled from
magnetic field
– Losses are only due to Ohmic losses in current carrying conductors
– The Magnetostatic solver utilizes an automatic adaptive mesh refinement
technique to achieve an accurate and efficient mesh required to meet defined
accuracy level (energy error).
Magnetostatic Equations
– Following two Maxwell’s equations are solved with Magnetostatic solver
p
r
MHMH(μB
B
JH
000
)
0
)),((
1
),(
0
yxAyxJ
z
r
z
Maxwell 3D
Maxwell 2D
© 2013 ANSYS, Inc. May 21, 2013
4
Release 14.5
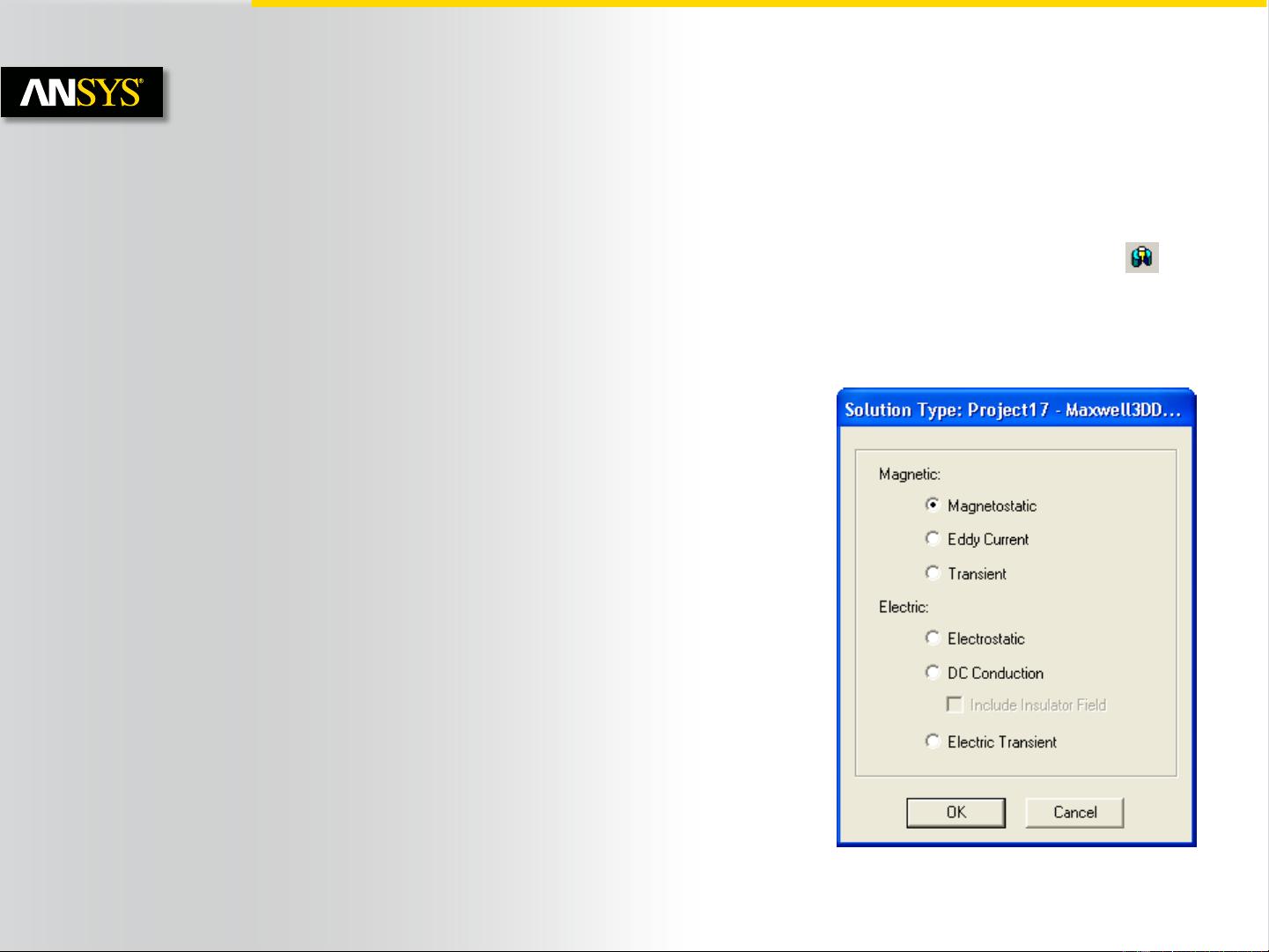
a. Selecting the Magnetostatic Problem
Selecting the Magnetostatic Solver
– By default, any newly created design will be set as a Magnetostatic problem
– Specify the Magnetostatic Solver by selecting the menu item Maxwell 2D/3D
Solution Type
– In Solution type window, select Magnetic> Magnetostatic and press OK
Maxwell 3D
Maxwell 2D
© 2013 ANSYS, Inc. May 21, 2013
5
Release 14.5
b. Material Definition
Magnetostatic Material Properties
– In a Magnetostatic simulation, the following parameters may be defined for a
material (by clicking on the pull-down menu under Type and Value)
Magnetic Coercivity:
• Used to define permanent magnetization of magnetic
materials.
• Requires magnitude and direction specification.
• Direction specified is with respect to Orientation CS
of bodies to which material is assigned
Composition:
• Can be Solid or Lamination
• Setting Composition to Lamination creates an
anisotropic magnetization effect.
Relative Permeability:
• Permeability (µ) is defined as µ
0
*µ
r
• Relative permeability(µ
r
) along with the Magnetic Coercivity determine the magnetic
properties of the material.
• Relative permeability can be Simple(linear µ
r
) or Nonlinear(BH Curve) or/and anisotropic
Bulk Conductivity:
• Used to determine the current distribution in current carrying conductors
• Does not have any impact on magnetic part of analysis
• Can be Simple or Anisotropic




















评论20