Guaranteed Cost Fault-Tolerant Control for Networked Control Sys...
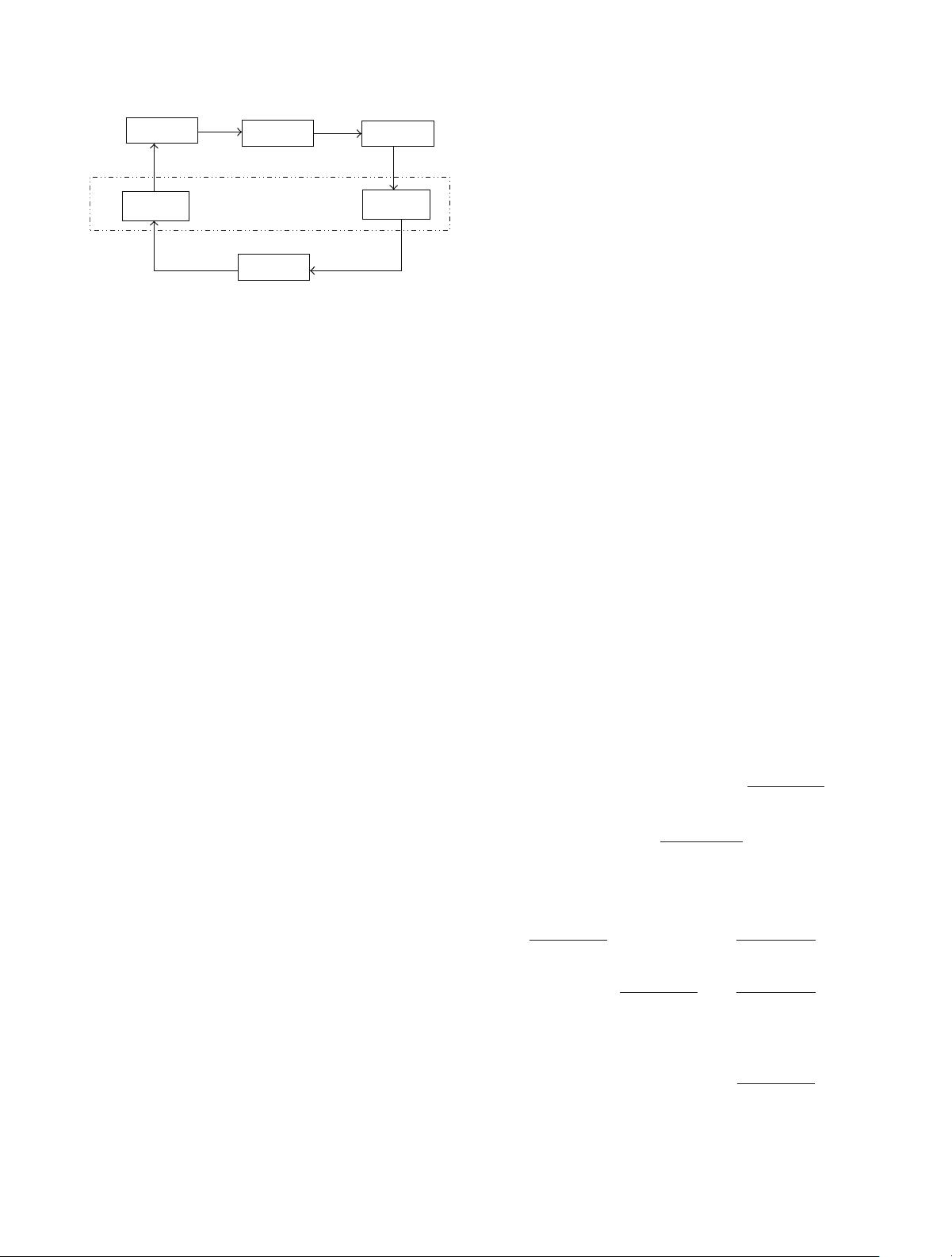
在网络化控制系统(NCS)的研究领域,传感器故障问题是影响系统稳定性和性能的关键因素之一。传感器故障包括但不限于损坏、噪声干扰、数据丢失或错误读数等问题,它们可能会导致整个控制系统的性能下降甚至完全失效。考虑到网络化控制系统通常具有大规模和复杂的结构,在恶劣的工作环境中,时变传感器故障无可避免地会出现。因此,研究如何设计一个能够保证系统成本并在传感器故障情况下仍能保持系统稳定性的容错控制器成为了该领域的一个重要课题。 文章“Guaranteed Cost Fault-Tolerant Control for Networked Control Systems with Sensor Faults”中,作者提出了针对含有时变传感器故障的网络化控制系统进行容错控制的研究。研究工作的基础是网络传输环境中的时延特性,即网络传输延迟和数据包丢失等现象。通过这一特性,作者将含传感器故障的网络化控制系统建模为具有不确定参数的离散时间系统,并将该模型与传感器故障的边界值联系起来。模型的准确构建是确保后续控制器设计有效性的前提。 文章中提到的控制理论基础是基于Lyapunov稳定性理论。Lyapunov稳定性理论是控制理论中用于分析系统稳定性的强大工具。它提供了一种不需要解系统微分方程的方法,通过构造Lyapunov函数或Lyapunov泛函来证明或估算系统的动态行为。在本研究中,通过Lyapunov函数的构建和分析,可以判断系统的稳定性并为后续的控制器设计提供理论基础。 文章还使用了线性矩阵不等式(LMI)方法来验证所设计的具有成本保证的容错控制器能够使得含传感器故障的网络化控制系统渐近稳定。线性矩阵不等式方法是数学优化领域用于解决多变量系统的稳定性问题的一种技术。通过转化为凸优化问题,LMI能够在多项式时间内给出系统的稳定性判据和控制器参数的设计准则,这在设计复杂系统控制器时尤为有用。 文章最后通过仿真来展示理论结果的正确性。仿真测试是验证理论和模型有效性的重要手段,它能够在受控的环境中复现真实世界中可能发生的各种情况,进而观察和验证控制器的实际表现是否符合预期的性能指标。 在应用背景方面,网络化控制系统广泛应用于信息技术、生命科学、航空航天技术等领域。这些领域的实时控制需求推动了NCS的发展,同时也要求控制系统在故障情况下依然能够保持一定的性能水平。因此,保证成本的容错控制策略对于实现上述目标尤为重要。 这篇文章为网络化控制系统在面对传感器故障时如何设计和实现一个稳定且具有成本保证的容错控制器提供了理论支持和设计方法。其研究不仅具有理论深度,同时对实际应用也有着重要的指导意义。

剩余9页未读,继续阅读

- 粉丝: 3
- 资源: 949
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- ShellTransition学习笔记
- 5G+AI智慧高校大数据顶层规划设计及应用方案(67页PPT).pptx
- 基于PWM的 三色灯RGB模块调色 标准库 代码
- 基于Simulink仿真的光储并网直流微电网模型研究:MPPT最大功率输出与混合储能系统的协同优化,基于Simulink仿真的光储并网直流微电网模型研究:MPPT最大功率输出与混合储能系统的协同优化
- JAVA实现有趣的迷宫小游戏(附源码).zip
- 基于NRBO-Transformer-BILSTM的深度学习模型:多特征分类预测与性能评估的Matlab实现,基于NRBO-Transformer-BILSTM的多特征分类预测模型与性能评估的Matl
- 磁链观测器在VESC中的应用方法及其代码、文档、仿真模型的对应关系以及附送翻译的Lawicel CANUSB驱动,磁链观测器在VESC中的应用:实现0速闭环启动,代码、文档、仿真模型供学习,磁链观测器
- 基于多智能体一致性算法的电力系统分布式经济调度策略:迭代优化与仿真验证,基于多智能体一致性算法与迭代计算的电力系统分布式经济优化调度策略(MATLAB实现),MATLAB代码基于多智能体系统一致性算
- 2013.8.5-2025.3.5碳排放权交易数据(日度).xlsx
- 中断上下文详细解析PDF详细内容
- VC-redist.x64-14.42.34438.0.7z
- MATLAB实现基于BiGRU-AdaBoost双向门控循环单元结合AdaBoost多输入分类预测(含模型描述及示例代码)
- Matlab实现KOA-CNN-GRU-selfAttention多特征分类预测(自注意力机制)(含模型描述及示例代码)
- MATLAB实现SSA-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention多变量时间序列预测(SE注意力机制)(含模型描述及示例代码)
- 基于磁耦合谐振的无线电能传输设计:MATLAB仿真中的PWM控制与过零检测模块探讨及二极管与同步整流技术的结合应用 ,基于Matlab Simulink仿真的无线电能传输设计:磁耦合谐振与PWM MO
- 博图16立体车库控制系统:PLC运行效果视频展示与接线图详解,深度解析:4x5立体车库控制系统的博图16版本,含PLC运行效果视频、详细接线图及IO表,4x5立体车库控制系统 博图16 带PLC运行效


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功