没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
Advances in the light field displays based on integral imaging a...
0 下载量 6 浏览量
2021-02-05
08:09:55
上传
评论
收藏 381KB PDF 举报
温馨提示
Light field displays comprise three-dimensional (3D) visual information presentation devices capable of providing realistic and full parallax autostereoscopic images. In this letter, the recent advances in the light field displays based on integral imaging (II) and holographic techniques are presented. Several advanced approaches to demonstrate the light field displays including viewing angle enhancement techniques of the II display, a fast hologram generation method using graphics processing un
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论
COL 12(6), 060005(2014) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 10, 2014
Advances in the light field displays based on integral
imaging and holographic techniques
(Invited Paper)
Nam Kim
∗
, Md. Ashraful Alam, Le Thanh Bang, Anh-Hoang Phan, Mei-Lan Piao,
and Munkh-Uchral Erdenebat
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Chungbuk National Universit y,
410 Sungbong-ro, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju, Chungbuk 361-763, Korea
∗
Corresp onding author: namkim@chungbuk.ac.kr
Received March 4, 2014; accepted April 4, 2014; posted online May 20, 2014
Light field displays comprise three-dimensional (3D) visual information presentation devices capable of
providing realistic and full parallax autostereoscopic images. In this letter, the recent advances in the light
field displays based on integral imaging (II) and holographic techniques are presented. Several advanced
approaches to demonstrate the light field displays including viewing angle enhancement techniques of the II
display, a fast hologram generation method using graphics processing unit (GPU) and multiple WRPs, and
a holographic microscopy to display the living cells are reported. These methods improve some important
constraints of the light field displays and add new features.
OCIS codes: 100.6890, 110.0110, 090.0090.
doi: 10.3788/COL201412.060005.
Nowadays, a three-dimensional (3D) light field display
has attracted a great deal of attention because of its
attractive applications. By presenting a light field using
technology that maps each sample to the appropriate ray
in physical space, one obtains an autostereoscopic visual
effect to observe the original scene. Several approaches
have been developed
[1−5]
to demonstrate a light field
display. In this letter, the recent advances in the light
field displays using techniques, such as integral imag-
ing (II), integral-floating display (IFD), holography, and
holographic microscopy of live cell, are presented.
Among numerous light field displays, II is a power-
ful autostereoscopic 3D display technique that provides
a number of attractive features such as full color, full-
parallax 3D image with continuous viewpoints in normal
room environment that distinguish the II from other
techniques. Despite a number of attractive advantages,
the II has some major drawbacks, such as limited resolu-
tion, narrow viewing angle, and small depth range, due
to the specifications of the lens array. In all of the draw-
backs of II, the narrow viewing angle is the most serious
barrier to its commercial applications. Many researches
have been conducted to overcome this problem
[6]
, but
II is still suffering for this limit. In order to develop a
wide-viewing angled II display, a new approach to the
viewing zone control of II display using a directional
projection with a directional elemental image genera-
tion and resizing (DEIGR) algorithm, was successfully
demonstrated and reported in a most recent study
[7]
.
Using this method, the point light source (PLS)
[8]
of
each elemental image (EI) shifts in terms of the projec-
tion angle, resulting in a shift in the viewing zone. The
amount of viewing zone shifting has been formulized in
terms of the projection angle. This method can con-
trol only the viewing zone of II display but it cannot
widen the viewing angle itself. If multi-directional pro-
jections of a multiple sets of EIs are used with suitable
projection angles in a sequential time-multiplex
[9]
man-
ner, a wide-viewing-angled II display can be achieved.
To implement a viewing angle enhanced II display sys-
tem, a multi-directional projection scheme is proposed.
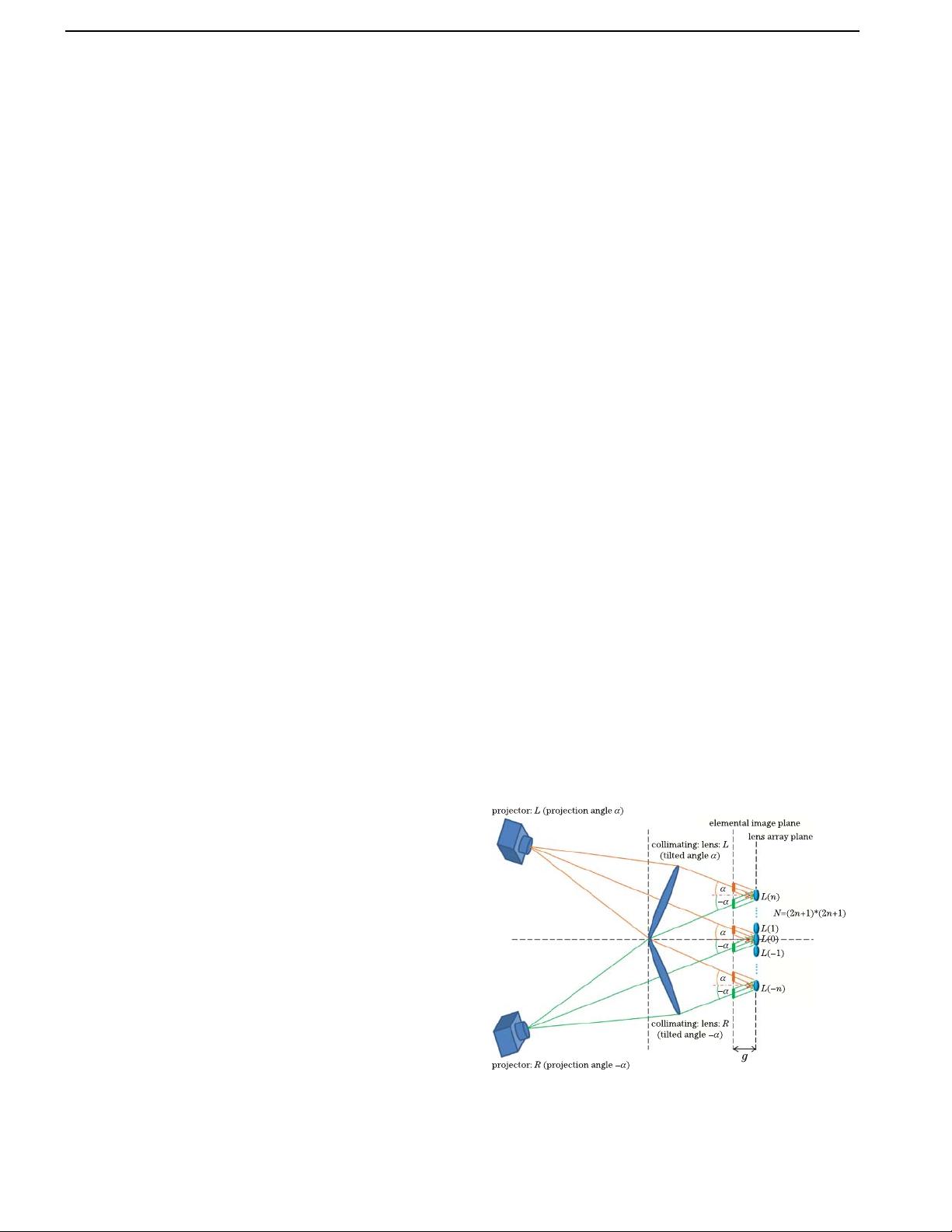
Figure 1 illustrates the basic principle of the proposed
method by using two-directional (2D) projections. In
this method, each elemental lens of the lens array col-
lects multi-directional illuminations of multiple EI sets
and produces multiple PLSs at different positions in the
focal plane; and the positions of the PLSs can be con-
trolled by the projection angles. In this case, the viewing
zone constitutes with multiple diverging ray bundles
emerging from the multi-directional projections of multi-
ple EI sets, which is wider than that of the conventional
method; whereas the conventional system produces the
Fig. 1. (Color online) Principle of the viewing angle enhance-
ment using multi-directional projections and DEIGR algo-
rithm.
1671-7694/2014/060005(5) 060005-1
c
2014 Chinese Optics Letters
资源评论

weixin_38680475
- 粉丝: 6
- 资源: 933
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功