没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
Excited-state population distributions of alkaline-earth metal i...
0 下载量 13 浏览量
2021-02-04
01:33:06
上传
评论
收藏 617KB PDF 举报
温馨提示
The intensities of fluorescence spectral lines of Ca atoms and Sr atoms in two different hollow cathode lamps (HCLs) are measured by element-balance-detection technology. In the wavelength range of 350–750 nm in the visible spectral region, using the individual strongest line (Ca 422.67 nm, Sr 460.73 nm) as the bench mark, the population ratios between the excited states of Ca atoms and Sr atoms are calculated by rate equations and the spontaneous transition probabilities. The HCLs with populati
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论
Excited-state population distributions of alkaline-earth
metal in a hollow cathode lamp
Pengyuan Chang (常鹏媛), Bo Pang (逄 博), Yisheng Wu (吴一胜),
and Jingbiao Chen (陈景标)*
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication System and Network, School of Electronics
Engineering and Computer Science, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
*Corresponding author: jbchen@pku.edu.cn
Received October 22, 2017; accepted January 4, 2018; posted online March 7, 2018
The intensities of fluorescence spectral lines of Ca atoms and Sr atoms in two different hollow cathode lamps
(HCLs) are measured by element-balance-detection technology. In the wavelength range of 350–750 nm in
the visible spectral region, using the individual strongest line (Ca 422.67 nm, Sr 460.73 nm) as the bench mark,
the population ratios between the excited states of Ca atoms and Sr atoms are calculated by rate equations
and the spontaneous transition probabilities. The HCLs with populations at excited states can be used to realize
the frequency stabilization reference of the laser frequency standard.
OCIS codes: 300.6210, 020.1335, 260.2510.
doi: 10.3788/COL201816.033001.
Hollow cathode lamps (HCLs) with alkaline-earth
metal are attracting growing attention nowadays as
sources of intense atomic spectral lines in various physical
devices applied in atomic absorption and emission spec-
troscopy
[1–3]
. Furthermore, the atom unit most frequently
employed in a traditional Faraday anomalous dispersion
optical filter (FADOF)
[4]
is a vapor cell with atomic den-
sity determined by thermal equilibrium
[5–8]
. Hence, the
samples of atomic filters have to be heated to high temper-
atures to get an atomic density high enough to guara ntee
the transmittance
[9,10]
. To overcome this limitation , an
innovative method of utilizing an HCL to realize a Sr
element FADOF was proposed, as the HCLs can provide
the high atomic density at room temperature
[11]
. Moreover,
since the state-of-the-art HCLs cover about 70 kinds of
high melting point metal elements, we believe that, due
to its rich spectral lines, without heating, scalability,
low fabrication cost, and potential applications in various
atomic spectra
[12–16]
they can be used in submarine commu-
nication systems as well as excited-state FADOFs without
the use of a pump laser
[5,6]
.
Basic knowledge about HCLs is meaningful for
the exploration of further applications
[17,18]
. The HCLs
have rich atomic spectral lines; nevertheless, the spectral
measurements are often contaminated by buffer gas-line
interference
[14–23]
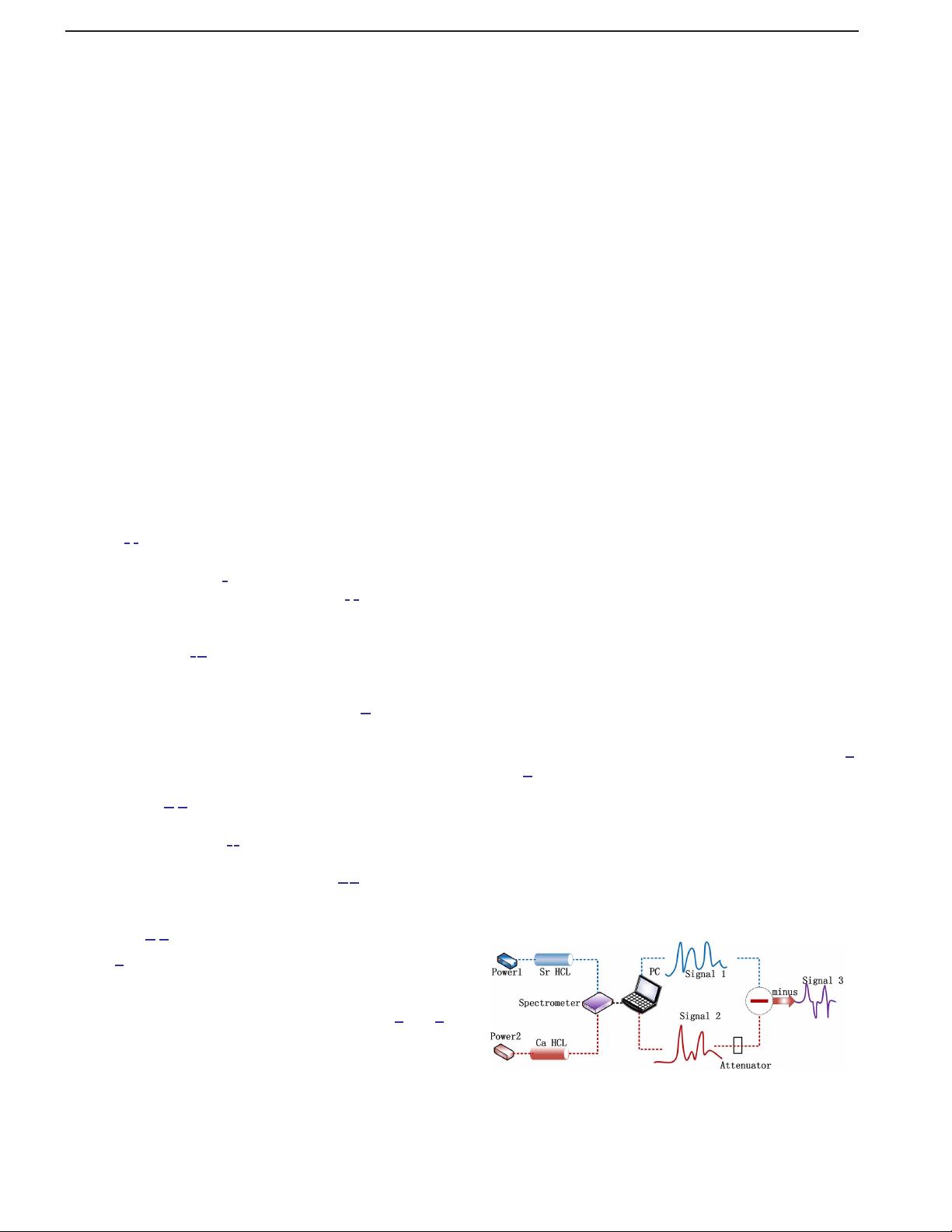
. A new method of measurement, as shown
in Fig.
1, element-balance-detection technology, is intro-
duced by us, whi ch can remove the effect of the buffer
gas-line via the subtraction relation between two spectral
signals of Ca HCL and Sr HCL, as shown in Figs.
2 and 3.
This method is simply described as follows: two spectral
signals of Ca HCL and Sr HCL both include the buffer
gas-line; in order to distinguish the atom lines between
the spectral signals, we conduct a subtraction operation
of two signals to make the buffer gas-lines offset each
other. Although the components of the buffer gas may
be different, the results imply that the subtraction pro-
cedure is coping better with this problem. Hence, the
element-balance-detection technology is applicable for
similar situations in atomic spectroscopy measurement,
which exists in the interference of impurity lines.
In this Letter, we measured the intensities of fluores-
cence spectral lines of Ca and Sr atoms in two different
HCLs, respectively. In the wavelength range of 350–
750 nm in the visible spectral region, using the individual
strongest line (Ca 422.67 nm, Sr 460.73 nm) as the bench
mark, we calculated the population ratios between the ex-
cited states by rate equations and spontaneous transition
probabilities. The measured results showed that the inten-
sities of the spectral lines of Ca and Sr atoms are signifi-
cantly different.
The measurement setup is schematically shown in Fig.
1.
Figure
2 shows the energy diagrams of the transitions re-
lated to the Ca and Sr atoms’ spectral signal. The Sr HCL
and Ca HCL are powered by Power1 and Power2 (gener-
ating a current range of 0 to 20 mA), respectively, which
are placed across the cathode and anode terminals. The
intensities of the fluorescence spectral lines of Ca and
Sr atoms were strikingly different along with the current
increase. The USB2000+ spectrometer in connection with
Fig. 1. Experimental schemes of Ca HCL and Sr HCL in the con-
figuration of element-balance-detection technology for spectrum
research.
COL 16(3), 033001(2018) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS March 10, 2018
1671-7694/2018/033001(5) 033001-1 © 2018 Chinese Optics Letters
资源评论

weixin_38635794
- 粉丝: 7
- 资源: 935
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 毕业设计JAVAWEB校园订餐系统项目源码
- html css js分页按钮
- Comsol多孔板相场断裂模型:一种高效的数值模拟工具,好的,以下是根据您提供的“comsol多孔板相场断裂模型”提炼出的一个标题: COMSOL多孔板相场模拟与断裂分析模型 此标题涵盖了您提供
- Vcredist运行库【2005、2008、2010、2012、2013、2015-2022】X86+X64集合打包
- 六轴EtherCAT总线伺服涂布收卷机程序:动态测量与同步控制,具备参考值的六个伺服+变频器+编码器方案,六轴EtherCAT总线伺服涂布收卷机高级编程:伺服、变频器与编码器的协同控制及动态测量频率转
- springboot接入InfoSuiteAs
- 命令行界面构建库 :CmdForge
- 电力系统风储协同调频策略的MATLAB仿真模型:基于四机两区系统的频域模型与控制策略优化分析,MATLAB仿真模型:风储联合一次调频在四机两区电力系统的应用与优化,电力系统风储联合一次调频MATLAB
- 【微信小程序源码】笑话
- 「三菱R系列PLC应用:ST、RD77MS定位与触摸屏配方功能实现异地操作及快速通信」,三菱R系列PLC案例详解:高级应用与CClink通信实现机器人远程操作及触摸屏配方功能,三菱R系列PLC案例程序
- 【微信小程序源码】滑动选项卡
- Video_59564296397953.mp3
- 使用c++开发相机的示例CameraDS,引用DirectShow技术
- 贪吃蛇 web版 支持python启动
- 基于NRBO优化算法的Transformer-BiLSTM回归模型Matlab代码:适用于多变量时序预测的电力负荷与光伏功率预测,NRBO-Transformer结合BiLSTM神经网络的时序数据回归
- 【微信小程序源码】京东白条
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功