
An energy-efficient SDN based sleep scheduling algorithm for WSNs
Yanwen Wang
a
, Hainan Chen
b,a
, Xiaoling Wu
a,b,c,d,e,
n
, Lei Shu
c
a
Guangzhou Institute of Advanced Technology, CAS, No. 1121, Haibin Rd, Nansha District, Guangzhou 511458, China
b
Guangdong University of Technology, No. 100, Huanchengxi Road, University Town, Guangzhou 510006, China
c
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Equipment Fault Diagnosis, Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology, Maoming 525000,
China
d
Information Technology Research Base of Civil Aviation Administration of China, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China
e
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, CAS, No. 1068, Xueyuan Rd, Shenzhen University Town, Nanshan District, Shenzhen 518055, China
article info
Keywords:
Energy efficiency
WSNs
Sleep scheduling
SDN-ECCKN
EC-CKN
abstract
Energy efficiency in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) has always been a hot issue and has been studied
for many years. Sleep Scheduling (SS) mechanism is an efficient method to manage energy of each node
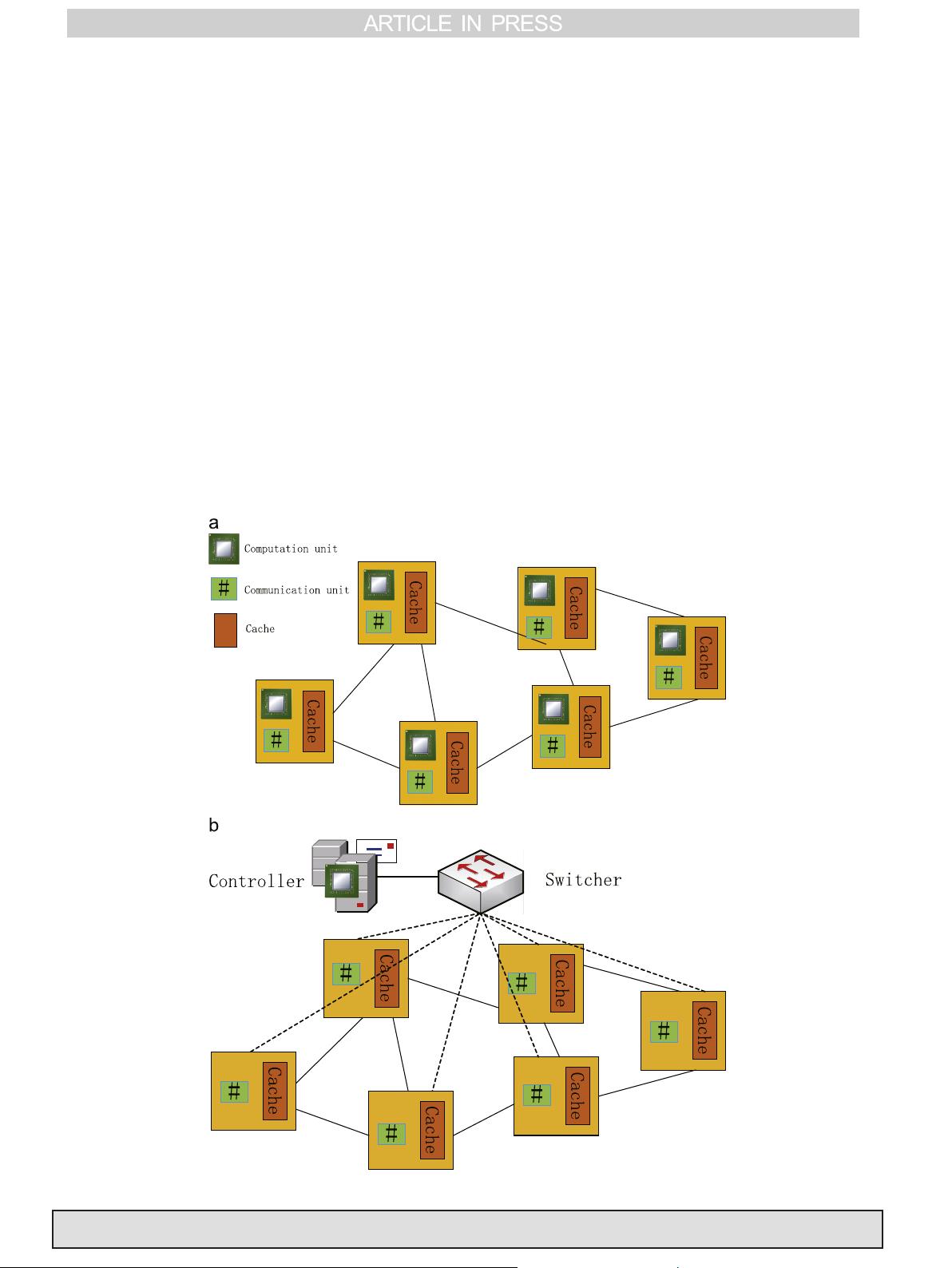
and is capable to prolong the lifetime of the entire network. In this paper a Software-defined Network
(SDN) based Sleep Scheduling algorithm SDN-ECCKN is proposed to manage the energy of the network.
EC-CKN is adopted as the fundamental algorithm when implementing our algorithm. In the proposed
SDN-ECCKN algorithm, every computation is completed in the controller rather than the sensors
themselves and there is no broadcasting between each two nodes, which are the main features of the
traditional EC-CKN technique. The results of our SDN-ECCKN show its advantages in energy manage-
ment, such as network lifetime, the number of live nodes and the number of solo nodes in the network.
& 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
1. Introduction
Wireless Sensor N etwor ks (WSNs) ha ve been widely adopt ed to
collect, process, transmit and receive on-the-spot data instead of
human labors, especially in hush en vironment. Normally, nodes in a
WSN are very hard or even impossible to be recharged or replaced.
Moreov er, for a sensor node, usually limited energy is supplied with
batteries. These challenges need high level of autonom y and self-
organization of each sensor node in the network (Baccour et al., 201 2).
Hence, each node must be capable to acquire some other nodes'
information deployed in the same region of interest. By processing
theseinformation,nodesareabletoautomaticallymakedecisionsand
change their sleep status. In recent research, many literatures about
Energy balancing techniques for W SNs ha ve been discussed
(Zhangbing et al., 2014a; Kai et al., 201 2)andthefusionofWSNs
and other network techniques is increasingly studied (Zhangbing et al.,
2014b; Luís et al., 20 14; Joel and Paulo, 20 10).
Sleep Scheduling mechanism is currently an efficient method
to manage the entire network and make the energy management
more efficient (Zhu et al., 2014). To save the energy, the key point
of Sleep Scheduling mechanism is to automatically and deliber-
ately shut down subsets of nodes while remain other nodes alive
in each given time interval. By applying SS mechanism, each node
in the network has opportunity to “sleep” instead of “being
awake” all the time, while the connectivity of the entire network
is not affected during the lifetime of the network (Zhu et al., 2012).
However, the discovery of other nodes is implemented by broad-
casting the relevant information from each node, which is called
beacon data, to all its neighbors, and all neighbors must then
broadcast their information back in every time interval, which cost
a lot of communication energy. Furthermore, in WSNs, the energy
consumption of sending a single bit of data is at least 480 times as
much as performing one addition instruction by CPU (Kimura and
Latifi,2005), which means if the total transmission times of a
network during its lifetime is reduced by one, 480 addition
instructions can be completed. How to reduce the transmission
times of a network while keeping the network connectivity
becomes a difficulty in the study of energy management in WSNs.
Motivated by the challenges above, in this paper we propose a
Software-Defined Network (SDN) based SS algorithm to reduce the
total transmission time of a network during its lifetime while
maintaining the network connectivity, hence prolong the network
lifetime. EC-CKN algorithm is regarded as the prototype of our
algorithm since the residual energy is the criterion considered by
each node when judging its status in the current interval. The rest
of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the related work
including EC-CKN algorithm and SDN technology will be briefly
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
journal h omepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jnca
Journal of Network and Computer Applications
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2015.05.002
1084-8045/& 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
n
Corresponding author.
Please cite this article as: Wang Y, et al. An energy-efficient SDN based sleep scheduling algorithm for WSNs. Journal of Network and
Computer Applications (2015), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2015.05.002i
Journal of Network and Computer Applications ∎ (∎∎∎∎) ∎∎∎–∎∎∎


 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功