Performance Analysis of WBAN Based on
AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols*
Pengfei He, Xiao Li, Long Yan, Shan Yang, Boye Zhang
School of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology
Yantai University
Yantai, China
bupt_hpf@126.com
Abstract—Due to the particularity of the human body wireless
environment, there are no redundant nodes in WBAN and the
nodes energy is limited. The design of efficient routing protocol
for WBAN is crucial. In this paper, based on the human body
signs parameters measurement in the actual situation, the
wireless body area network topology model was constructed. By
the application of the classic AODV and DSDV Ad Hoc routing
protocols on this model, the end-to-end delay, packet loss rate
and throughput performance indicators were analyzed and
compared under different transmission rate and packet size. The
simulation results show that the on-demand routing protocol
AODV is more suitable for the data transmission under the
environment of human body.
Keywords—WBAN; AODV; DSDV; End-to-end Delay; Packet
Loss Rate; Throughput.
I. INTRODUCTION
Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) is a typical
application of sensor network on health care, it consists of
many elements related to the body, such as personal terminal,
body sensors and network equipments distributed around or
inside body[1]. WBAN can effectively monitor the human
body health, it is regarded as one of the key support techniques
that can solve the sharply accelerated aging population and
medical expense hyperinflation.
At present, the star topology and multi-hops tree topology
are two common topologies in WBAN[2-3]. In terms of the
energy efficiency, multi-hops tree topology is more suitable
structure for WBAN[4]. During the process of data
transmission, data packets need to pass between different nodes,
intermediate nodes in the process of this task is to forward
packets. Given the nature of WBAN and its surroundings,
sensor nodes are usually powered by battery, nodes and the
whole network are energy limited. Due to the human daily
activities, the network topology and channel quality are
constantly changing with the body movement. Therefore,
energy efficient routing protocol for WBAN is particularly
important.
In this paper, we constructed the WBAN topological
structure based on the actual human body. Two classic
Destination-Sequenced Distance-Vector Routing(DSDV) and
Ad hoc on-demand distance vector routing(AODV) routing
protocols were used on this topology model. By the network
simulation software NS2, the end-to-end transmission delay,
packet loss rate and throughput parameters of these two
protocols were obtained and compared. The applicability of
these two kinds routing protocols for WBAN data transmission
was investigated.
II. B
ODY TOPOLOGY MODEL OF WBAN
WBAN is composed of sensor nodes placed on the body,
mobile devices and remote control node, it is a distributed
network structure. All of these sensor nodes collect human
physiological information, this information will be collected
on the mobile devices together, then send integrated
information to remote control node for analysis. The sensor
nodes are spread on the human perception area, each of them
can gather and transfer data according to the settings in
advance. Based on the actual physical characteristics of the
sensor location information, human body model of WBAN is
as followed Fig.1.
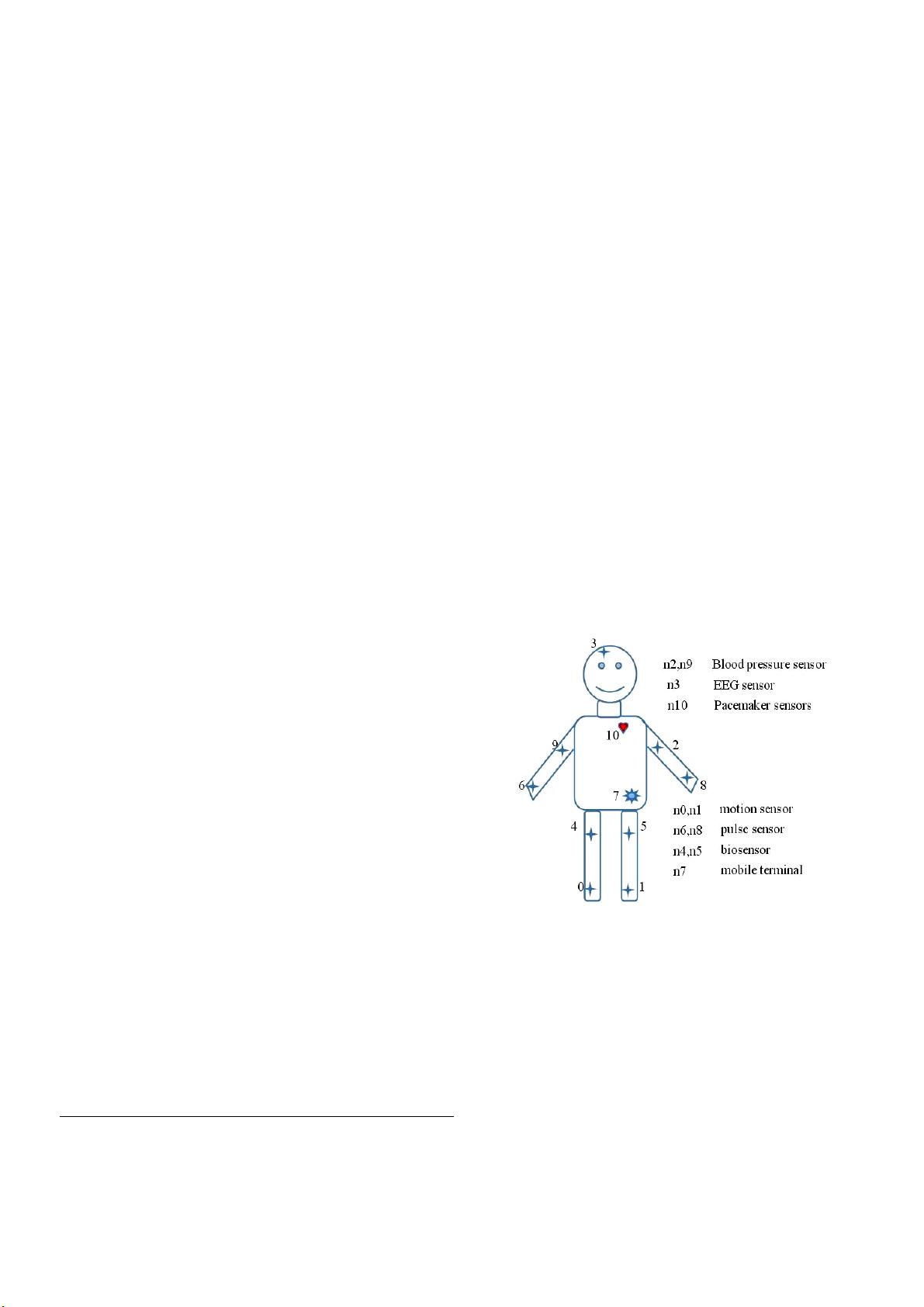
Fig. 1. Human body model of WBAN
Every sensor nodes in Fig.1 has its different functions.
Node n0 and n1 can collect real-time bounce rate of the body.
Node n6 and n8 can collect real-time acquisition of wrist pulse
which makes the monitoring of the pulse more convenient.
Node n2 and n9 monitor real-time change of blood pressure
and transmit these changes to the mobile terminal, this can
prevent harm from significantly changes of blood pressure.
Node n3 can feel the potential waveform of cerebral cortex and
translates waveform into usable output signal, it can detect
*
Project supported by National Nature Science Fund of China (No.61202399) .


 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功