没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
随着对风能的需求持续以指数级的速度增长,降低运行和维护(O&M)成本并提高可靠性已成为风力涡轮机维护策略中的重中之重。 在风力涡轮机故障达到灾难性阶段之前对其进行预测对于降低由于不必要的定期维护而导致的运维成本至关重要。 利用基于SCADA数据的状态监视系统,该系统利用了已经在风力涡轮机控制器处收集的数据,是一种经济高效的方法,可以监视风力涡轮机以进行故障预警。 本文提出了一种基于人工神经网络(ANN)的基于存储的SCADA数据的风力发电机主轴承故障预测和自动生成警告和警报的方法。 建立了汽轮机主轴承正常行为的ANN模型,然后计算出该参数的估计值与实际值之间的偏差。 此外,已经开发了一种用于产生预警和警报并且避免基于该偏差的误报和警报的方法。 通过这种方式,风电场运营商能够有足够的时间来计划维护,因此,可以避免意外停机,并可以降低运维成本。

Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 2018, 8, 211-225
http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojapps
ISSN Online: 2165-3925
ISSN Print: 2165-3917
Automatic Fault Prediction of Wind Turbine
Main Bearing Based on SCADA Data and
Artificial Neural Network
Zhenyou Zhang
Renewables & Utilities, Kongsberg Digital AS, Trondheim, Norway
Abstract
As the demand for wind energy continues to grow at exponential rate, redu
c-
ing operation and maintenance (O & M) costs and improving
reliability have
become top priorities in wind turbine maintenance strategies. Prediction of
wind turbine failures before they reach a catastrophic stage is critical to reduce
the O & M cost due to unnecessary scheduled maintenance. A SCADA-
data
based condition monitoring system, which
takes advantage of data already
collected at the wind turbine controller, is a cost-
effective way to monitor
wind turbines for early warning of failures. This article proposes a methodo
l-
ogy of fault prediction and automatical
ly generating warning and alarm for
wind turbine main bearings based on stored SCADA data using Artificial
Neural Network (ANN). The ANN model of turbine main bearing
normal
behavior is established and then the deviation between estimated and actual
values of the parameter is calculated. Furthermore, a method has been deve
l-
oped to generate
early warning and alarm and avoid false warnings and
alarms based on the deviation. In this way, wind farm operators are able to
have enough time to plan maintenance, and
thus, unanticipated downtime
can be avoided and O & M costs can be reduced.
Keywords
Artificial Neural Network, SCADA Data, Wind Turbine, Automatic Fault
Prediction
1. Introduction
Power production from renewable sources becomes more and more important
globally to meet the increasing demand of power and reduce the effect of the
energy production on the environments, such as water and air, ecological system
How to cite this paper:
Zhang, Z.Y. (2018
)
Automatic Fault Prediction of Wind Tu
r-
bine Main Bearing Based on SCADA Data
and Artificial Neu
ral Network.
Open Jou
r-
nal of Applied Sciences
,
8
, 211-225.
https://doi.org/10.4236/ojapps.2018.86018
Received:
May 2, 2018
Accepted:
June 25, 2018
Published:
June 28, 2018
Copyright © 201
8 by author and
Scientific
Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative
Commons Attribution International
License (CC BY
4.0).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Open Access
DOI: 10.4236/ojapps.2018.86018 Jun. 28, 2018 211 Open Journal of Applied Sciences
Z. Y. Zhang
and climate change. Wind power is one of the most developed renewable energy
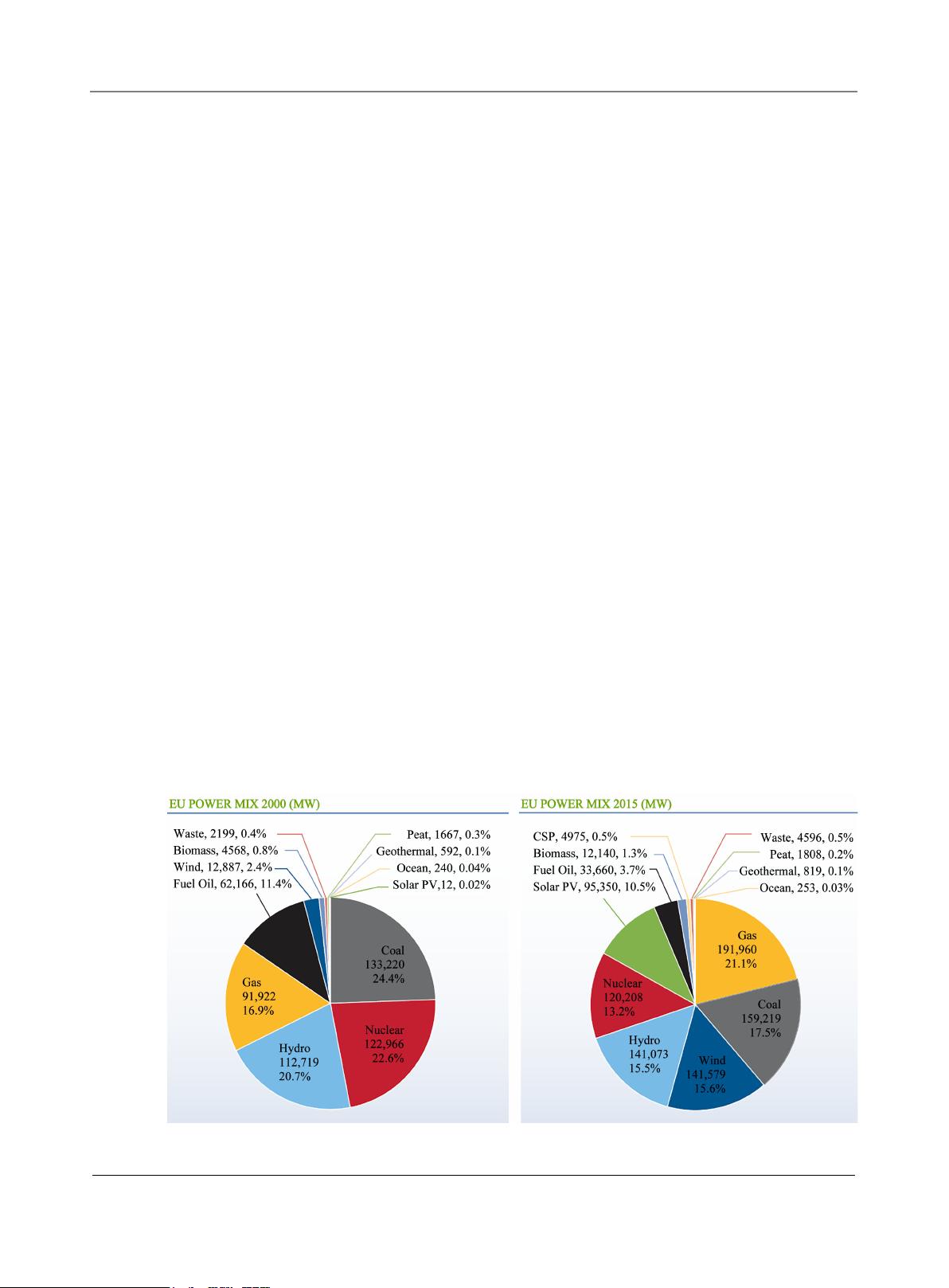
technologies worldwide with 432.491 GW installed capacity at the end of 2015
[1]. It has overtaken hydro as the third largest source of power generation in the
EU with a 15.6% share of total power capacity as seen in
Figure 1 which has
been increased remarkably from just tiny 2.4% in 2000 [2]. If the trend remains,
it is no doubt that the target of 20% wind energy share of energy production in
Europe will be met in 2020 [3] [4]. However, to achieve this target, the Levelised
cost of wind energy still should be reduced further. Today, large wind turbines
(2 - 10 MW) for both onshore and offshore from some wind equipment OEMs,
such as Siemens and Vestas, are designed, tested and manufactured as economi-
cally viable alternatives to traditional fossil-fueled power generation. At the same
time, the cost of wind energy has decreased sharply in last two decades which
makes both onshore and offshore wind power more competitive than conven-
tional power generation sources, such as coal and gas, and other renewable
energy [5]. Even though, the cost of wind power production, especially for off-
shore wind power, need to be reduced further to make it more competitive to
other resources. Operations and Maintenance (O & M) has been estimated at up
to 20% - 30% of overall lifetime costs for energy [6] [7]. It is really making sense
to reduce the O & M cost by reducing unanticipated downtime through an au-
tomatic condition monitoring system.
The best way to reduce the O & M cost of wind energy is to reduce downtime
through online condition monitoring to enable the operators to plan mainten-
ance action when and only when it needed. Wind turbines often operate in se-
vere and remote environments which make the limitation of accessibility when
the maintenance actions are needed. Therefore, unscheduled maintenance due
to unexpected failures, even just small issues, can be very costly, not only for
maintenance actions but also for lost production time. From the operators’ view, it
Figure 1. Comparison of EU Power Mix in 2000 and 2015 [2].
DOI: 10.4236/ojapps.2018.86018 212 Open Journal of Applied Sciences

Z. Y. Zhang
is, therefore, worth increasing effort spent to monitor the wind turbine condition
in order to reduce unanticipated downtime and thus reduce the maintenance
cost and production time loss. Therefore, prediction of faults of wind turbines as
early as possible becomes the key part of condition monitoring. In the other
hand, false critical alarms may cause even more cost due to lots of resources
maybe used for the maintenance that is not needed.
SCADA system, which is installed with almost all wind turbines, mainly logs
the performance parameters of wind turbines. It would be beneficial for the
wind farm owners if the SCADA data can be analysed and interpreted auto-
matically to predict faults early enough to help them to do the maintenance ac-
tions just when it is needed.
There are mainly two methodologies for fault prediction of wind turbines:
model-based or data-based. The model-based methods require a comprehensive
physical or mathematical model which is usually unavailable. Data-based methods
are based on the history data and data mining technologies are used to find the
relations among variables in the data. Wind turbine mathematical/physical
models are normally unavailable but the data has been collected and stored via
SCADA system, and thus data-based technologies are preferred [8]. There are
some works in literature to use SCADA data analysis to detect faults of wind
turbine components with model-based or data-driven methodologies [9] [10]
[11] [12] [13], however, none of them consider to design a mechanism to avoid
false warning and false alarms due to sudden changes of wind turbine running
condition which the model may be not fast enough to capture these changes.
This paper describes the methodology to automatically predict incipient faults
of wind turbine main bearings by analyzing SCADA data based on Artificial
Neural Network (ANN), which has been implemented in EmPower® developed
by Kongsberg Digital AS. The ANN model of turbine main bearing normal be-
haviour is established firstly and then the deviation between estimated and ac-
tual values of the parameter is calculated.The deviation is used to be an indicator
of abnormal behavior of main bearing. To avoid the false warning/alarm, a time
interval (
i.e.
a week) is used to calculate the percentage of time that the deviation
is above warning/alarm threshold. In this way, incipient faults are detected in
advance and false warning/alarm is avoided, and thus, only actual warn-
ings/alarms are sent to the operator.
The remaining sections of this paper are organized as follows. Section 2 de-
scribes the principle of Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Section 3 proposes the
procedure of fault prediction and warning/alarm generation. Section 4 describes
how the normal behavior ANN model is established based on SCADA data. Sec-
tion 5 proposes how the warning and alarm can be generated automatically
based on established normal behavior ANN model. Section 6 describes how the
proposed procedure to be applied in online monitoring for wind turbines and
some cases are shown. Section 7 gives the conclusions and indicates some future
works.
DOI: 10.4236/ojapps.2018.86018 213 Open Journal of Applied Sciences
剩余14页未读,继续阅读
资源推荐
资源评论
2020-09-07 上传
2021-11-12 上传
2021-09-25 上传
2021-07-14 上传
101 浏览量
161 浏览量
105 浏览量
178 浏览量
197 浏览量
2016-03-15 上传
2021-08-08 上传
167 浏览量
2022-06-02 上传
111 浏览量
资源评论

weixin_38554781
- 粉丝: 6
- 资源: 884
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- YOLOv11边缘计算部署指南-TensorRT加速与NVIDIAJetson优化实践.pdf
- YOLOv11边缘计算部署指南-无人机巡检实时目标检测优化策略.pdf
- YOLOv11+SlowFast-工业生产中的高危动作识别系统开发.pdf
- YOLOv11船舶检测实战-MMShip数据集1.9%mAP提升秘籍.pdf
- YOLOv11边缘计算实战-无人机巡检中的输电线路缺陷实时检测.pdf
- YOLOv11多传感器融合-自动驾驶场景下的行人检测与轨迹预测.pdf
- YOLOv11多任务学习-病理切片细胞分类与病灶区域分割联合训练.pdf
- YOLOv11多任务优化-同时实现零售货架商品检测与OCR识别.pdf
- YOLOv11多任务实战-目标检测+距离测量+三维姿态估计一体化方案.pdf
- YOLOv11工业级缺陷检测实战-基于PCB板瑕疵识别的轻量化模型优化.pdf
- YOLOv11工业质检-高精度缺陷检测与实时分类解决方案.pdf
- YOLOv11工业缺陷检测实战-从模型训练到生产线部署全流程.pdf
- YOLOv11工业质检-零缺陷检测系统搭建与模型部署全攻略.pdf
- YOLOv11工业质检实战-基于表面缺陷检测的模型优化与部署指南.pdf
- YOLOv11跨平台部署实战-从TensorRT到ONNX的工业级优化.pdf
- YOLOv11模型轻量化-从TensorRT部署到边缘计算性能调优全攻略.pdf
安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功