没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
数据包络分析中技术和规模无效率估计的若干模型
需积分: 9 2 下载量 20 浏览量
2017-07-24
19:47:48
上传
评论
收藏 1.76MB PDF 举报
温馨提示
Some models for estimating the inefficiency of technology and scale in data envelopment analysis 数据包络分析中技术和规模无效率估计的若干模型
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论
http://www.jstor.org
Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis
Author(s): R. D. Banker, A. Charnes, W. W. Cooper
Source:
Management Science,
Vol. 30, No. 9 (Sep., 1984), pp. 1078-1092
Published by: INFORMS
Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2631725
Accessed: 22/08/2008 13:55
Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use, available at
http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp. JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use provides, in part, that unless
you have obtained prior permission, you may not download an entire issue of a journal or multiple copies of articles, and you
may use content in the JSTOR archive only for your personal, non-commercial use.
Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at
http://www.jstor.org/action/showPublisher?publisherCode=informs.
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed
page of such transmission.
JSTOR is a not-for-profit organization founded in 1995 to build trusted digital archives for scholarship. We work with the
scholarly community to preserve their work and the materials they rely upon, and to build a common research platform that
promotes the discovery and use of these resources. For more information about JSTOR, please contact support@jstor.org.

MANAGEMENT SCIENCE
Vol. 30, No. 9, September 1984
Printed
in
U.S.A.
SOME MODELS FOR ESTIMATING TECHNICAL
AND
SCALE INEFFICIENCIES
IN DATA
ENVELOPMENT
ANALYSIS*
R. D.
BANKER,
A.
CHARNES
AND W. W.
COOPER
School
of Urban
and Public
Affairs, Carnegie-Mellon University,
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15213
Graduate School
of Business, University of Texas, Austin,
Texas 78712
In
management contexts, mathematical programming is usually used to evaluate a collec-
tion
of
possible
alternative courses
of
action en route
to selecting
one which is best.
In
this
capacity, mathematical programming serves
as a
planning aid to management. Data
Envelop-
ment Analysis reverses this role and employs mathematical programming to obtain ex
post
facto evaluations
of
the relative efficiency
of
management accomplishments, however
they
may
have been
planned
or
executed. Mathematical programming
is
thereby extended
for use
as a
tool
for
control and evaluation of past accomplishments as well as a tool to aid in
planning
future activities. The
CCR ratio
form
introduced by Charnes, Cooper and Rhodes,
as
part of
their Data
Envelopment Analysis approach, comprehends
both
technical and scale inefficien-
cies
via the
optimal
value
of
the ratio
form,
as
obtained directly
from
the data without
requiring
a
priori specification of weights and/or explicit delineation of assumed functional
forms
of relations
between inputs
and
outputs.
A
separation into technical and
scale
efficien-
cies
is
accomplished by
the methods
developed
in
this paper
without
altering the
latter
conditions
for
use
of DEA
directly
on
observational data.
Technical
inefficiencies
are
identified
with
failures to achieve best
possible output levels and/or usage
of excessive
amounts
of
inputs.
Methods
for
identifying and correcting
the
magnitudes
of
these
inefficien-
cies,
as
supplied
in
prior work,
are illustrated. In the
present paper,
a
new separate
variable
is
introduced
which
makes it
possible
to
determine whether operations were conducted
in
regions
of
increasing,
constant or
decreasing returns to
scale
(in multiple input
and
multiple
output
situations).
The
results
are discussed and related not
only
to classical
(single output)
econom-
ics
but
also
to more
modern versions
of
economics which are identified with "contestable
market theories."
(EFFICIENCY;
TECHNICAL
INEFFICIENCY; RETURNS
TO
SCALE;
MATHEMATI-
CAL
PROGRAMMING;
LINEAR
PROGRAMMING)
1. Background
Charnes, Cooper and Rhodes (CCR) (1978a, 1979) introduced a ratio definition
of
efficiency,
also called the CCR
ratio
definition,
which
generalizes
the
single-output
to
single-input
classical
engineering-science ratio definition
to
multiple
outputs
and
inputs
without
requiring preassigned weights.
This is
done via
the
extremal
principle
incorporated
in
the following model:
s2=rYO
iUrYrj
maxh =h
subject
to
1
>
, j =
1,
..., n,
with
(1)
Ur, Vi
>
O,1
..=
.
m;
r
1....
s.
Here the
yrj,
xii
>
0
represent output
and
input
data
for
decision
making
unit
(DMU)
j
*Accepted by
Arie
Y.
Lewin; received December 11, 1981. This paper has been with the
authors
42
months for
2
revisions.
'See
Charnes, Cooper, Lewin, Morey,
and
Rousseau
for an exact non-Archimedean
expression
of this
"positivity"
with
necessary algebraic closure.
1078
0025-1 909/84/3009/
1
078$O
l
.25
Copyright
?
1984, The Institute of
Management Sciences
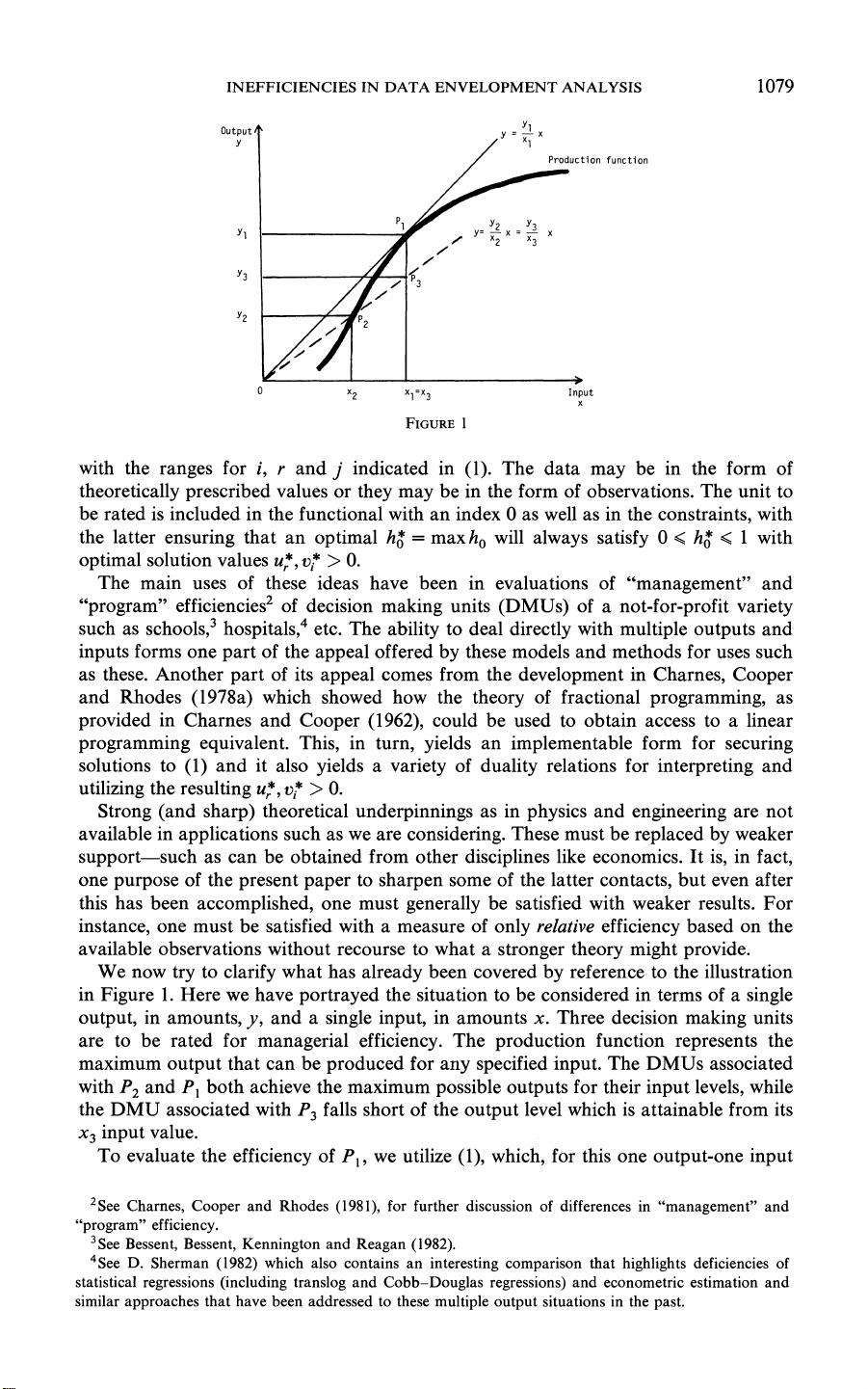
INEFFICIENCIES IN DATA
ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS 1079
Output
y
Y
y
Xi
Production function
y3
p
?
X2
x1=X3
Input
FIGURE
1
with the ranges for i, r and j
indicated in (1). The data may be in the form of
theoretically prescribed values or they
may be
in
the
form of
observations. The unit to
be
rated is included in the functional
with an index
0
as well as in the constraints, with
the latter
ensuring
that
an optimal ho
=
maxho
will always satisfy
0
<
ho
<
1
with
optimal
solution
values u,*, v* > 0.
The
main uses
of
these ideas have
been in evaluations of "management" and
"program"
efficiencies2 of
decision
making units (DMUs) of a not-for-profit variety
such as
schools,3 hospitals,4 etc. The
ability to deal directly with multiple outputs and
inputs
forms
one part
of
the appeal
offered by these models and methods for uses such
as these. Another
part
of its
appeal
comes
from
the
development
in
Charnes, Cooper
and Rhodes
(1978a)
which
showed
how
the
theory
of
fractional
programming,
as
provided
in
Charnes and Cooper
(1962), could be used to obtain access to a linear
programming equivalent. This,
in
turn,
yields an implementable form for securing
solutions to
(1) and
it
also yields a
variety
of
duality
relations for
interpreting and
utilizing
the
resulting u*, v*" >
0.
Strong (and sharp)
theoretical
underpinnings
as
in
physics
and
engineering
are not
available
in
applications
such
as we are
considering.
These
must be
replaced by
weaker
support-such
as can be
obtained
from
other
disciplines
like economics. It
is,
in
fact,
one
purpose
of the
present paper
to
sharpen
some of the latter
contacts,
but even after
this has
been
accomplished,
one must
generally
be satisfied with
weaker
results. For
instance,
one
must be satisfied with a
measure
of
only relative efficiency
based
on
the
available observations
without recourse to what a
stronger theory might provide.
We
now
try
to
clarify
what
has
already
been covered
by
reference
to
the illustration
in
Figure
1.
Here we have
portrayed
the situation to be
considered
in terms of
a single
output,
in
amounts, y, and
a
single
input,
in
amounts
x. Three decision
making
units
are to be rated for
managerial
efficiency.
The
production
function
represents
the
maximum output that can
be
produced for
any specified input.
The
DMUs associated
with
P2 and
PI
both achieve
the maximum
possible outputs for their input levels,
while
the DMU associated with
P3
falls
short of
the
output
level
which
is
attainable from
its
x3 input
value.
To
evaluate
the
efficiency
of
PI,
we
utilize
(1), which,
for
this one
output-one input
2See Charnes, Cooper and
Rhodes (1981),
for
further
discussion of differences in
"management" and
"program" efficiency.
3See Bessent,
Bessent, Kennington
and
Reagan (1982).
4See
D. Sherman
(1982)
which also
contains
an
interesting comparison
that
highlights
deficiencies of
statistical
regressions
(including translog and Cobb-Douglas
regressions)
and econometric estimation and
similar
approaches
that have been addressed to these multiple
output situations
in
the past.
剩余15页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

草原山峰
- 粉丝: 17
- 资源: 33
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 基于Html和Shell的“老罗投资/知行合一日拱一卒投资人生”主题设计源码
- 基于Java的OnlineMusic在线音乐播放器设计源码
- comsol多场耦合 水合物降压降压开采THMC,注气驱替甲烷THM,地质封存等多场耦合收敛技术,相关地质能源开采类多场耦合仿真案列分析,包括岩土类地质灾害防护,煤层气、页岩气开采,咸水封存co2,H
- 模糊逻辑控制(FLC)Matlab simulink仿真搭建模型: 提供以下帮助 波形纪录 参考文献 仿真文件 原理解释 电机参数说明 仿真原理结构和整体框图
- 基于ThinkPHP5+Vue3的RBAC权限控制前后端分离管理系统设计源码
- 基于.Net6架构的轻量级前后端分离微服务开发框架设计源码
- 主机厂基于Simulink MBD新能源电动汽车主驱电驱控制器算法模型及开发资料,量产模型,量产软件,量产代码,软件架构设计,输入输出定子,单元测试,MIL测试资料 Sumlink MCU电机控制策
- 基于微信小程序的JavaScript/TypeScript答题小程序设计源码
- 基于QT框架的语音图像识别与数据库操作综合练手小demo设计源码
- FDTD超材料吸收器吸收光谱
- 基于Vue框架的求职招聘系统移动端(Uniapp)设计源码
- 电压型同步发电机(VSG)离网仿真模型,包含电压电流双闭环,有功无功外环控制,阻抗 仅模型 MATLAB的2018以上版本都可以
- 基于MATLAB和Python的多种数据分析方法与图表生成设计源码
- 台式三轴自动螺丝机(sw16可编辑+工程图+bom)全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- 基于Vue框架的酒店管理小程序设计源码
- 基于TypeScript的鸿蒙移动应用程序个人日记本设计源码
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功