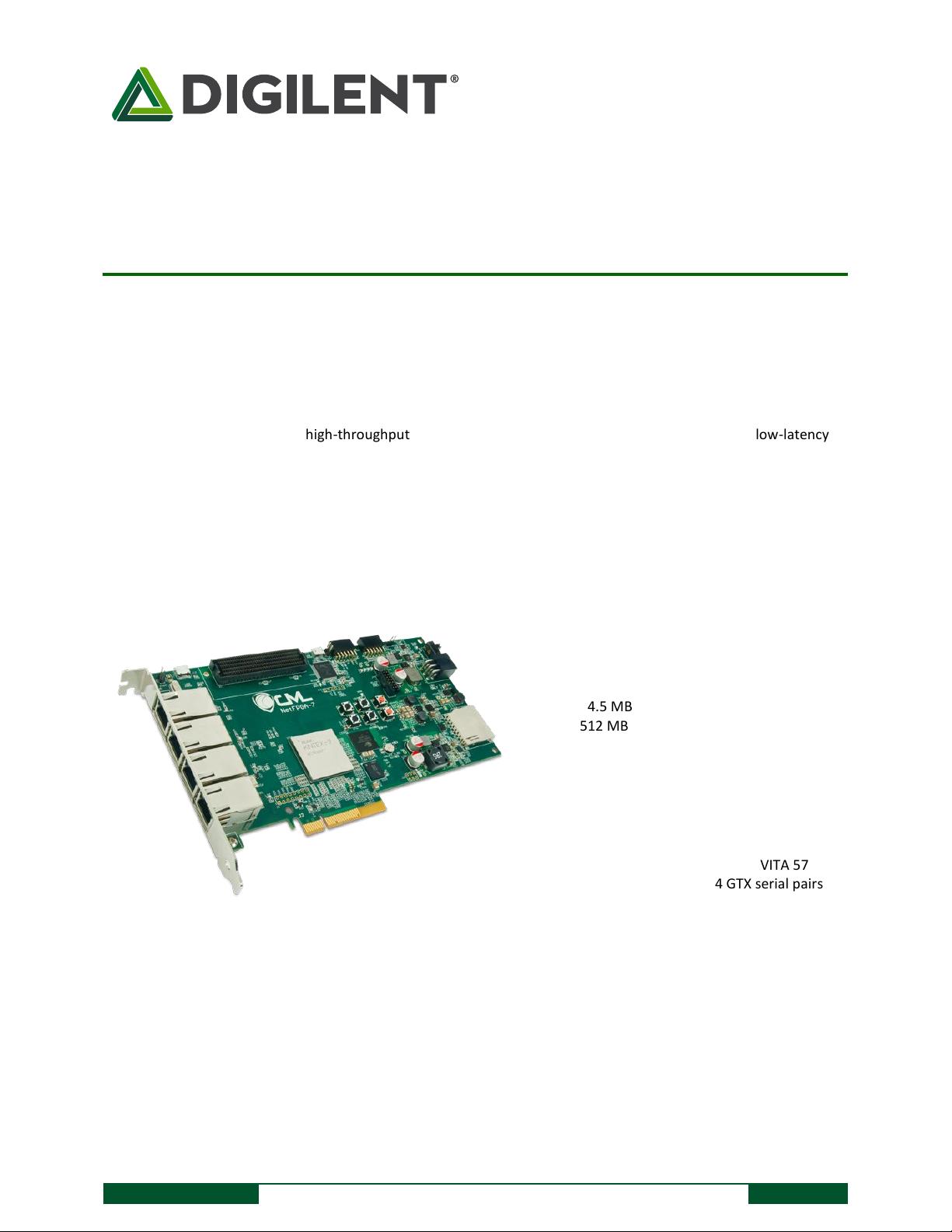
NetFPGA-1G-CML Kintex-7 FPGA 开发板用户手册 概述: NetFPGA-1G-CML 是一款功能强大且低成本的网络硬件开发平台,基于 Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K325T FPGA。该板卡具有四个以太网接口,可以negotiate 最高 1 GB/s 连接速度。512 MB 的 800 MHz DDR3 可以支持高吞吐量的数据缓存,而 4.5 MB 的 QDRII+ 可以实现低延迟的数据访问,如路由表。快速启动配置由 128 MB 的 BPI Flash 支持,该 Flash 也可以用于非易失性存储应用。标准 PCIe 形式 factor 支持高速 x4 Gen 2 接口。FMC 载体连接器提供了一个便捷的扩展接口,用于扩展卡功能通过 Select I/O 和 GTX 串行接口。FMC 连接器也可以支持 SATA-II 数据速率,用于网络存储应用。FMC 连接器还可以用于扩展卡功能,通过通信、测量和控制卡等。 关键特性: * Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K325T FPGA * 低抖动 200 MHz 振荡器 * 四个 10/100/1000 以太网 PHYs,具有 RGMII * X4 Gen 2 PCI Express 接口 * X16 4.5 MB QDRII+ 静态 RAM(450 MHz) * X8 512 MB DDR3 动态 RAM(800 MHz) * 1-Gbit BPI Flash * SD 卡槽 * 32 位 PIC 微控制器 * USB 微控制器 * 实时时钟 * 加密认证芯片 NetFPGA-1G-CML 板卡支持 Stanford NetFPGA 架构,提供了参考设计通过 NetFPGA GitHub 组织(www.github.com/organizations/NetFPGA)。该板卡还完全兼容 Xilinx Vivado 和 ISE 设计套件,以及 Xilinx SDK 用于嵌入式软件设计。 NetFPGA-1G-CML 板卡的主要应用领域包括: * 网络处理和存储 * 数据中心和云计算 * 网络安全和加密 * 通信和测量 * 嵌入式系统和物联网 NetFPGA-1G-CML 板卡是一款功能强大且灵活的网络硬件开发平台,适合各种网络应用和嵌入式系统的开发。


剩余20页未读,继续阅读

- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 6
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 基于ssm的公务员招考信息发布平台源码(java毕业设计完整源码+LW).zip
- Quartz 在项目中的使用实例,可以动态增删改查定时任务,包括 Quartz 的优秀配置
- (176958828)Java+springboot超市会员积分管理系统的设计与实现
- (178477228)超市会员积分管理系统主要用于实现了企业管理数据统计等
- (7674260)操作系统试卷
- 基于ssm的风顺农场供销一体系统的设计与实现源码(java毕业设计完整源码+LW).zip
- (177673816)以下是一个简单的Python代码,可以模拟春节烟花的效果:
- 高度灵活小机械手sw18可编辑全套设计资料100%好用.zip
- 数据库基本操作.sql
- 基于ssm的健达企业项目管理系统的设计与实现源码(java毕业设计完整源码+LW).zip
- 纵维立方 Anycubic Kobra 2 Neo 高温(285)固件
- (29868230)网上订餐系统的设计与实现
- 聚丙烯膜全球市场调研报告:2023年中国聚丙烯市场规模已达3424.86亿元
- (175403238)蚁狮优化算法(ALO)源代码+23个经典测试函数
- 图书管理设计【陈表达原创】.accdb
- (177354392)多目标蚁狮优化算法(MOALO)【含Matlab源码 1598期】.zip


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功