
LDS-OFDM an Efficient Multiple Access Technique
Reza Hoshyar, Razieh Razavi and Mohammed AL-Imari
Centre for Communication Systems Research
University of Surrey
Guildford GU2 7XH, Surrey, U.K.
Email:{R.Hoshyar, R.Razavi, M.Al-imari}@surrey.ac.uk
Abstract—In this paper LDS-OFDM is introduced as an
uplink multicarrier multiple access scheme. LDS-OFDM uses
Low Density Signature (LDS) structure for spreading the symbols
in frequency domain. This technique benefits from frequency
diversity besides its ability of supporting parallel data streams
up to 400% more than the number of subcarriers (overloaded
condition). The performance of LDS-OFDM is evaluated and
compared with conventional OFDMA systems over multipath
fading channel. Monte Carlo based simulations for various
loading conditions indicate significant performance improvement
over OFDMA system.
Index Terms—Low density signature, OFDMA, frequency
diversity, overloading.
I. INTRODUCTION
In recent years, there has been considerable interest on
improving the efficiency of modulation and coding techniques
to be used for broadband wireless services. Future wireless
communication systems are expected to provide a range of
high data rate services with different Quality of Service (QoS)
requirements. In this regard, Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing (OFDM) as a multicarrier system is deemed to
be a useful approach to cope with wideband service demands
due to its capability of exploiting both time and frequency
resources as well as its interference shaping property [1].
By dividing a wideband fading channel into flat narrowband
channels, OFDM is able to mitigate the harmful effects of
multipath fading using a simple one-tap equalizer. This allows
performing a high data rate transmission while avoiding inter-
symbol interference due to channel frequency-selectivity [2].
OFDM based multi-carrier transmission is the main technol-
ogy for many existing and upcoming wireless communication
systems, such as IEEE 802.16 (WiMAX), IEEE 802.11a/g
(Wireless LANs), and LTE for 3GPP.
OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)
is an efficient extension of the OFDM transmission to a
multiuser communication scenario. In an OFDMA system, the
set of subcarriers is divided into several mutually exclusive
subsets and then each subset is allocated to transmission of
a user signal. This approach when the transmitters/receivers
are properly synchronized avoids Multiple Access Interference
(MAI) thanks to created frequency-domain orthogonality of
users’ signals. Furthermore, under low mobility conditions
where acquiring Channel State Information (CSI) of all users
is affordable, performance of OFDMA can be improved by
dynamic subcarrier and power allocation techniques included
in the Radio Resource Management (RRM) functionality of
the system [3].
As in OFDMA user-data symbols are assigned directly
to sub-channels, the frequency domain diversity will not be
achievable at modulation symbols level. Thus it will be crucial
to incorporate properly designed error correction coding and
interleaving schemes to obtain this diversity at a later stage
[4].
Considering that based on information theoretic treatment
orthogonal transmission is not an optimal approach, here we
propose an approach that combines benefits of OFDM based
multi-carrier transmission in avoiding Inter-Symbol Interfer-
ence (ISI) with a recent idea on Low Density Signature (LDS)
based spreading proposed for CDMA (Code Division Multiple
Access) systems. LDS that was proposed in [5] is effectively
a CDMA system with some desirable properties that allows
operating at overloaded conditions with performance still
close to single user case and with affordable complexity. By
overloaded we mean number of users being larger than the
system spreading factor. We propose to apply LDS based
spreading over OFDM subcarriers.
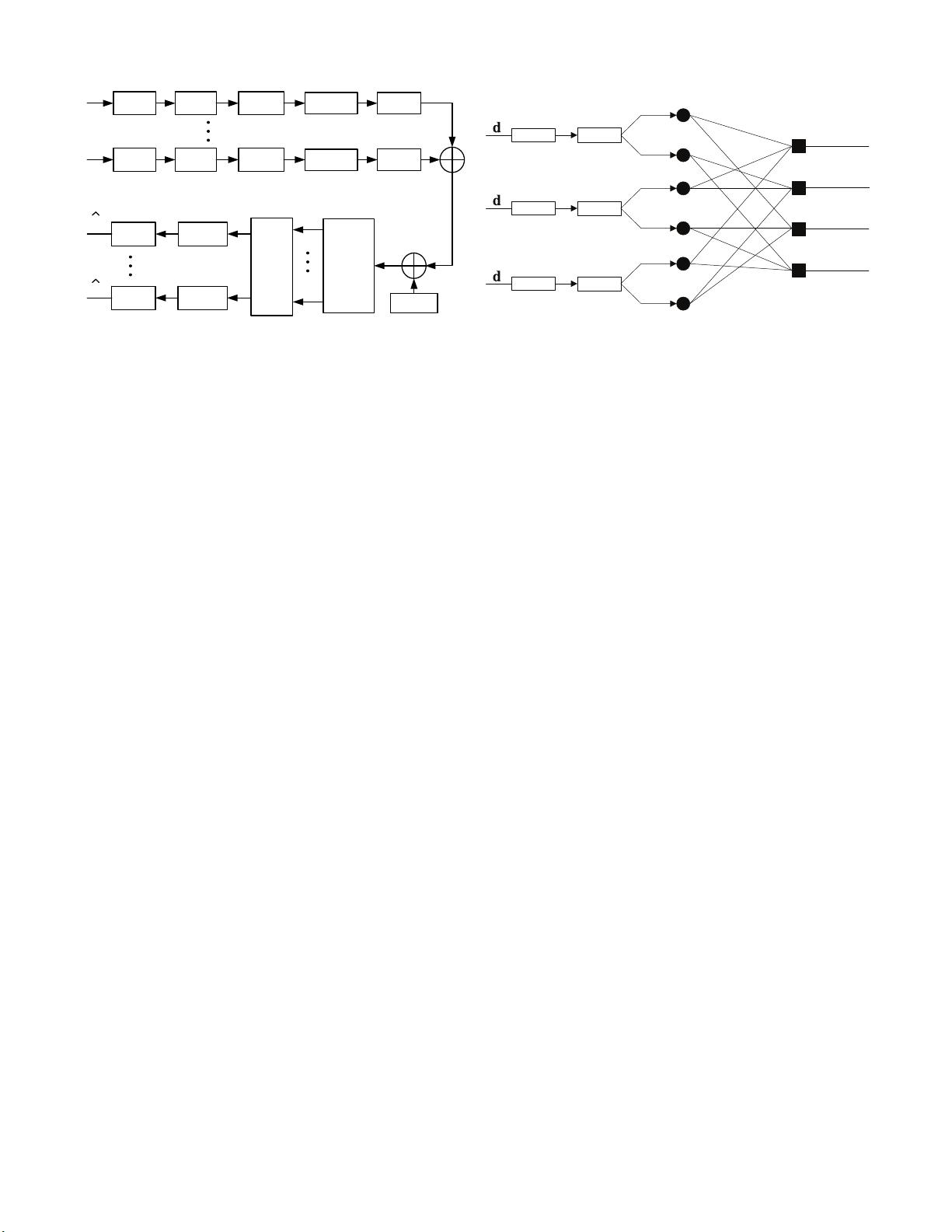
In LDS-OFDM due to low density signature structure every
data symbol will only be spread over a small subset of sub-
carriers (effective processing gain) and also every subcarrier
will only be used by a small subset of data symbols that could
belong to different users. Therefore each user transmission on
a given subcarrier will only be interfered by a small number
of other data symbols’ transmission. The LDS structure can
be captured by a low density graph thus similar to application
of LDS for CDMA system the detection of LDS-OFDM could
be based on the Message Passing Algorithm (MPA) presented
in [5]. The LDS-OFDM system can be understood as a system
which applies LDS as multiple access technique and OFDM
for multicarrier modulation. A primarily evaluation of LDS-
OFDM was carried out in [6].
Our simulation results show that the uplink LDS-OFDM
outperforms an equivalent OFDMA system in terms of bit
error rate when supporting equal-rate users with same overall
throughput. LDS-OFDM detector has larger complexity than
OFDM receiver which is due to using of MPA. The increased
computational complexity of the system compared to a con-
ventional receiver used for OFDMA is practically affordable
and is completely justified with respect to achieved gain in
performance.
This paper is organized as follows: Section II presents
978-1-4244-2519-8/10/$26.00 ©2010 IEEE

 LDS-OFDM.rar (1个子文件)
LDS-OFDM.rar (1个子文件)  LDS-OFDM.pdf 192KB
LDS-OFDM.pdf 192KB
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功
评论2