基于主从博弈的社区综合能源系统分布式协同优化运行策略.pdf
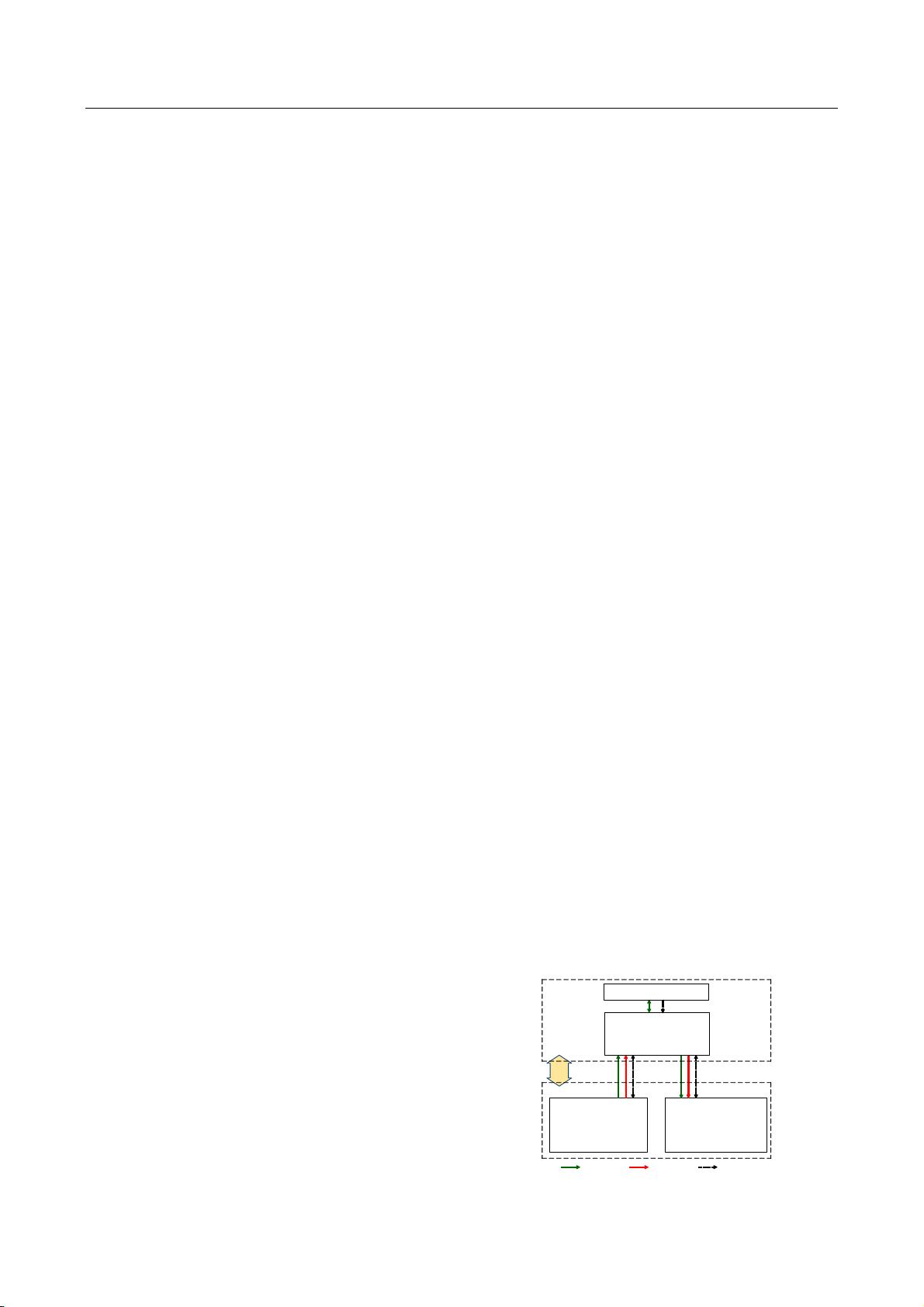
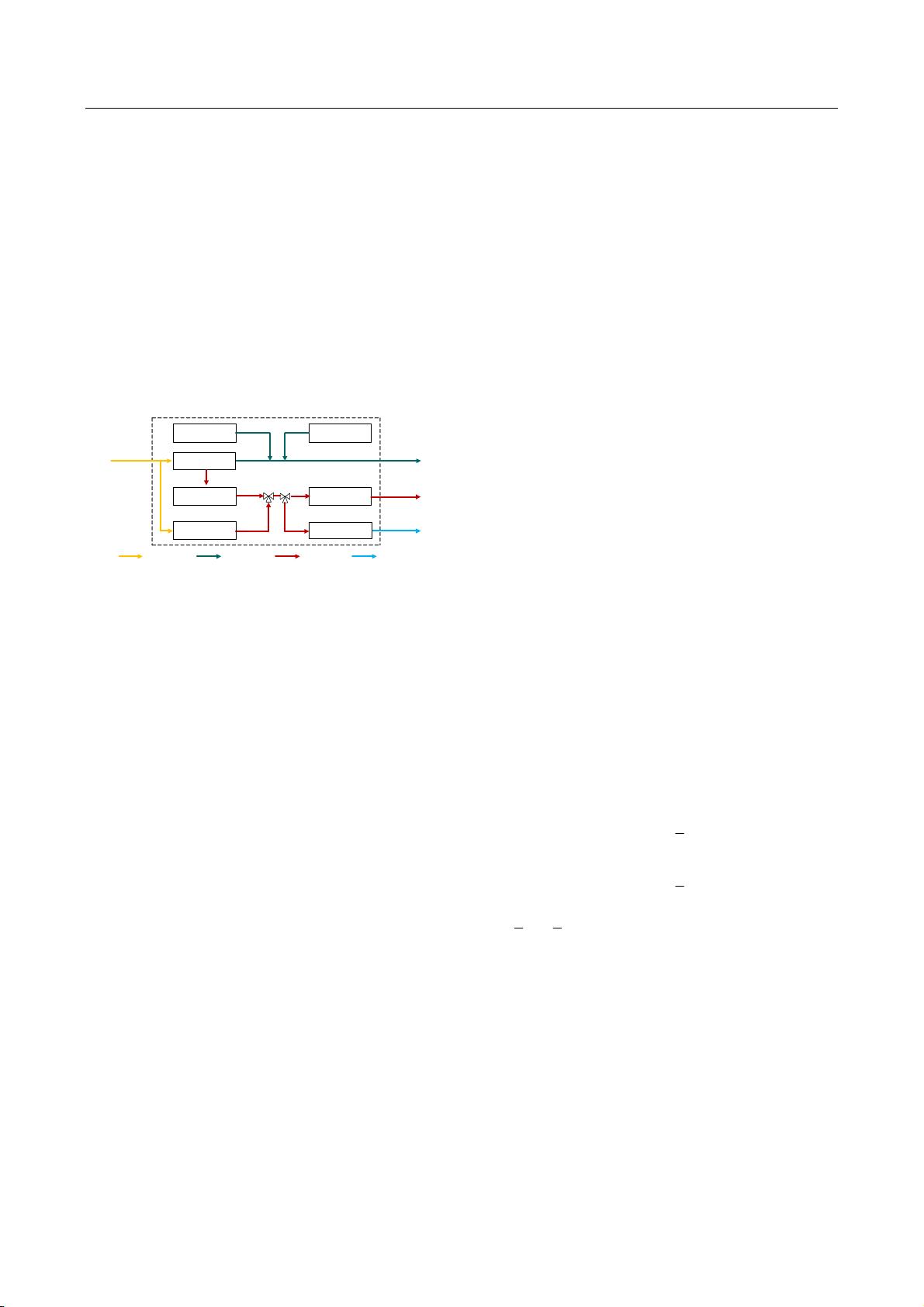
"基于主从博弈的社区综合能源系统分布式协同优化运行策略" 本文主要介绍了基于Stackelberg博弈的社区综合能源系统分布式协同优化运行策略。随着能源市场的转变,社区综合能源系统(CIES)的分布式特征日益突出,传统的集中优化方法难以揭示多个代理之间的交互关系。 本文提出了一种基于Stackelberg博弈的分布式协同优化策略,将综合能源零售商作为领导者,新能源联合冷热电厂(CCHP)操作员和负载聚合器作为追随者,解决了所有方在追求最优目标时的平衡策略。引入了CIES的交易模式和数学模型,并将其嵌入Stackelberg博弈框架中,建立了一种一领导多追随者的分布式协同优化模型。 然后,证明了所提出的模型的Stackelberg均衡是唯一的,并使用基于遗传算法和二次规划的分布式解决方案来解决该模型。通过实践示例验证了所提出的方法的有效性,提高了新能源CCHP操作员的利益和负载聚合器的消费者剩余价值。 本文的主要贡献在于: 1. 提出了基于Stackelberg博弈的分布式协同优化策略,解决了CIES中的多代理交互问题。 2. 证明了所提出的模型的Stackelberg均衡是唯一的,并提供了一种基于遗传算法和二次规划的分布式解决方案。 3. 通过实践示例验证了所提出的方法的有效性,提高了新能源CCHP操作员的利益和负载聚合器的消费者剩余价值。 关键词:综合能源系统、优化运行、需求响应、Stackelberg博弈、定价策略。 此外,本文还涉及到一些重要的概念和技术,包括: 1. 综合能源系统(CIES):一个集成了多种能源形式的系统,旨在提高能源效率和可持续发展。 2. Stackelberg博弈:一种静态非合作博弈模型,描述了领导者和追随者之间的交互关系。 3. 分布式协同优化:一种优化方法,旨在解决多代理之间的交互问题。 4. 遗传算法:一种搜索优化算法,用于解决复杂的优化问题。 5. 二次规划:一种优化方法,用于解决二次规划问题。 本文提出的基于Stackelberg博弈的分布式协同优化策略为CIES提供了一种有效的解决方案,提高了能源效率和可持续发展。

剩余10页未读,继续阅读

- 粉丝: 3w+
- 资源: 5971
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 全球干旱数据集【自校准帕尔默干旱程度指数scPDSI】-190101-202312-0.5x0.5
- 基于Python实现的VAE(变分自编码器)训练算法源代码+使用说明
- 全球干旱数据集【标准化降水蒸发指数SPEI-12】-190101-202312-0.5x0.5
- C语言小游戏-五子棋-详细代码可运行
- 全球干旱数据集【标准化降水蒸发指数SPEI-03】-190101-202312-0.5x0.5
- spring boot aop记录修改前后的值demo
- 全球干旱数据集【标准化降水蒸发指数SPEI-01】-190101-202312-0.5x0.5
- ActiveReports
- vgbvdsbnjkbfnb
- effsefefeffsfwfse


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功