IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.10 No.10, October 2010
185
Manuscript received October 5, 2010
Manuscript revised October 20, 2010
A Robust Digital Image Watermarking Scheme Using
Hybrid DWT-DCT-SVD Technique
Satyanarayana Murty. P
†
,Dr.P. Rajesh Kumar
††
†
Research Scholar, AITAM College of Engineering, Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA
††
Associate Professor, A.U College of Engineering, Vishakapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, INDIA
Abstract
Protection of digital multimedia content has become an
increasingly important issue for content owners and service
providers. As watermarking is identified as a major technology
to achieve copyright protection, the relevant literature includes
several distinct approaches for embedding data into a
multimedia element (primarily images, audio, and video). In this
paper, we present a hybrid watermarking scheme based on
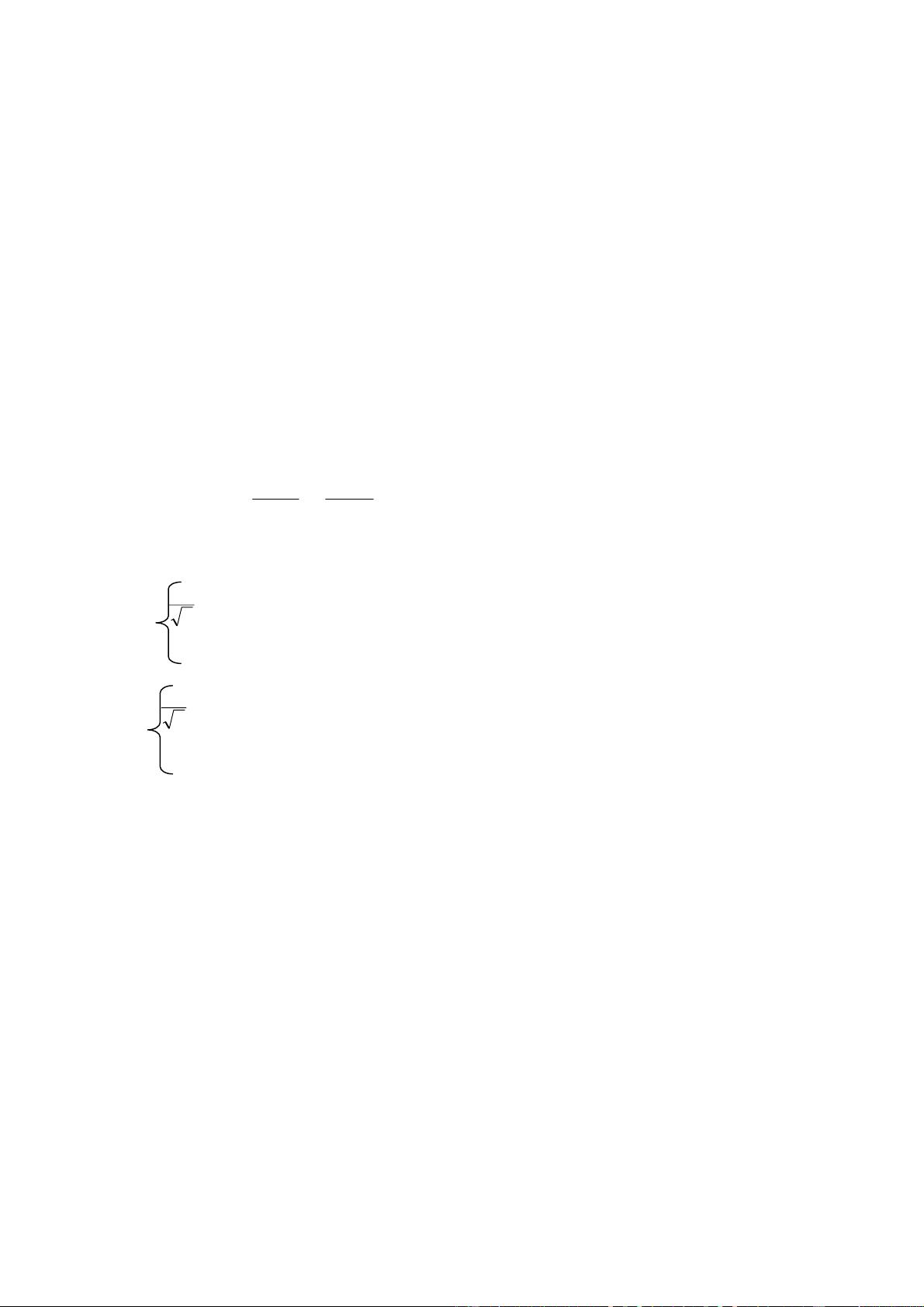
Discrete Wavelet Transform – Discrete Cosine Transform –
Singular Value Decomposition (DWT-DCT-SVD). Robustness
is achieved by taking DCT of the DWT coefficients of the HL
band of DWT. After applying DCT we map the DCT
coefficients in a zig – zag order into four quadrants and apply
the SVD to each quadrant. These four quadrants represent
frequency bands from the lowest to the highest. The singular
values in each quadrant are then modified by the singular values
of the DWT-DCT transformed visual watermark. We show that
embedding data in lowest frequencies is resistant to most of the
attacks and some attacks are resistant to other frequency bands.
Keywords
multimedia, DWT , DCT, zig – zag , SVD.
1. Introduction
There are several types of digital watermarking, with
different goals, and many schemes to accomplish those
types of watermarking. Digital watermarking is the
process of embedding information into an image that can
identify where the image came from or who has rights to
it. In some watermarking schemes, a Watermarked image
has a logo or some other information embedded into the
image so that it is readily visible. However, these
watermarks can be easily corrupted or removed using
simple image processing techniques. Other schemes use
invisible watermarking, in which the information is
virtually invisible after it is embedded. Watermark
embedding can be achieved in a number of different ways.
Some techniques embed a binary pattern into the spatial
domain of an image. Usually, the information can be
embedded while taking into account which areas of the
original image can hold more information while
remaining undetectable [1]-[6]. The watermark is
embedded by directly modifying pixel values in the
spatial domain. Correlation based approach [7,8] is
another spatial domain technique in which the
watermark is converted to a PN sequence which is then
weighted & added to the host image with a gain factor k.
For detection, the watermark image is correlated with
the watermark image. Watermarking in transform
domain is secure and robust to various attacks.
However, the size of the watermark that can be
embedded is generally 1/16 of the host image. Image
watermarking algorithms using Discrete Cosine
Transform (DCT) [9, 10], Discrete Wavelet Transform
(DWT) [11, 12, 13, 14], Singular Value Decomposition
(SVD) [15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24] are
available in the literature. The basic philosophy in
majority of the transform domain watermarking
schemes is to modify transform coefficients based on
the bits in watermark image. Domain transformation
watermarking schemes, in general, first use DCT and
DWT and then transform the image into the spatial
domain. Watermarking schemes usually focus on
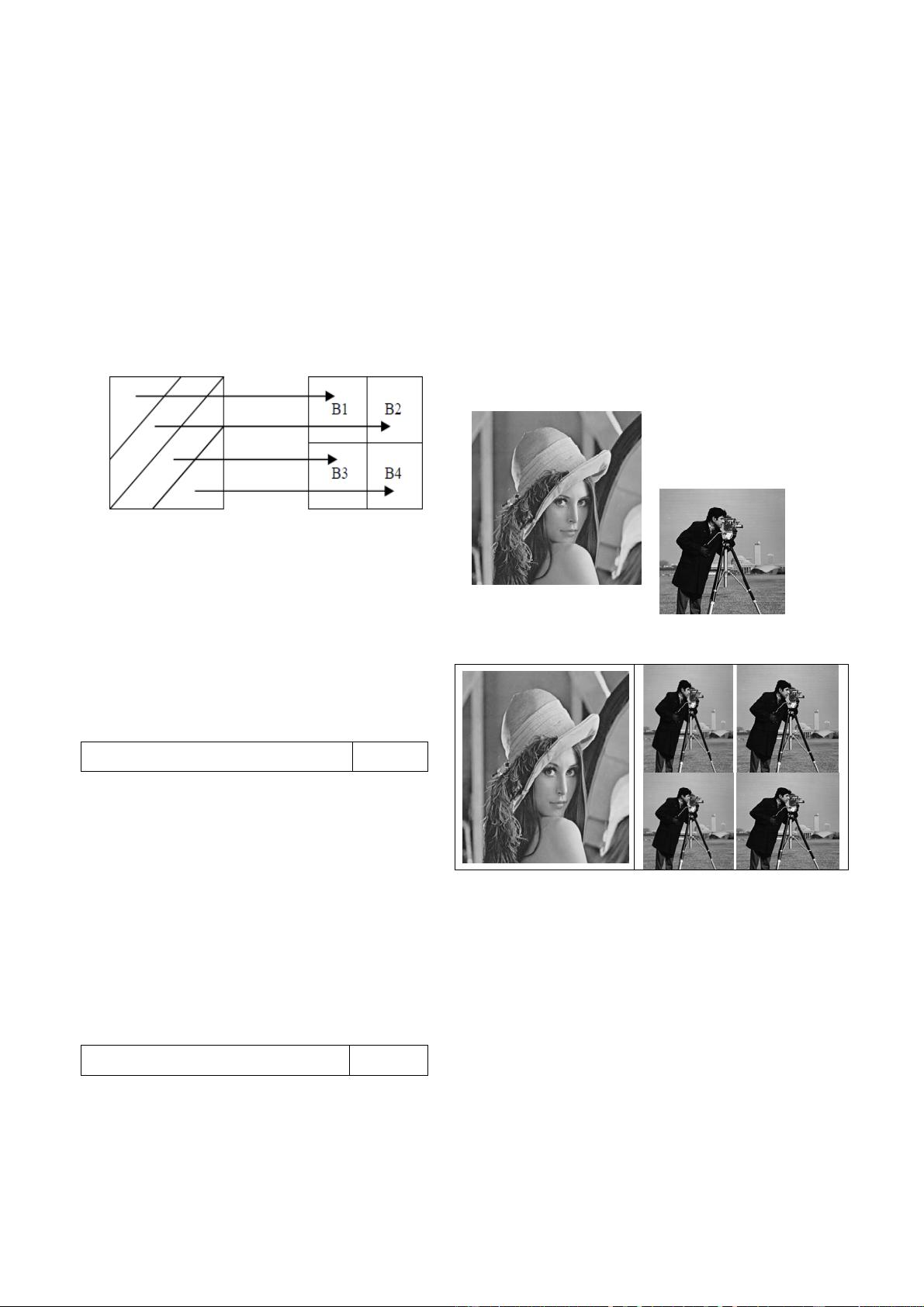
watermarking black and white or grayscale images. The
data hiding capacity is high in spatial domain and
frequency domain algorithms based on DCT, SVD.
However, these algorithms are hardly robust against
various attacks, prone to tamper and degrade the quality
of the watermarked image. The algorithms based on
DWT provide high image quality but are less robust to
various attacks. In this paper, we propose a hybrid
digital marking scheme based on DWT-DCT-SVD
which overcomes the above draw backs. The rest of the
paper is organized as follows: Section 2 briefly
describes various domain transforms while Section 3
proposes our hybrid DWT-DCT-SVD technique.
Section 4 contains our experimental results followed by
conclusions in Section 5.