本篇博客tensorflow1.7,整个项目源码:[github](https://github.com/shawshany/Traffic_sign_Classify)
# 引言
本次博客将分享Udacity无人驾驶纳米学位的另一个项目,交通标志的识别。
本次项目实现主要采用CNN卷积神经网络,具体的网络结构参考Lecun提出的LeNet结构。参考文献:[Lecun Paper](https://download.csdn.net/download/u010665216/10412418)
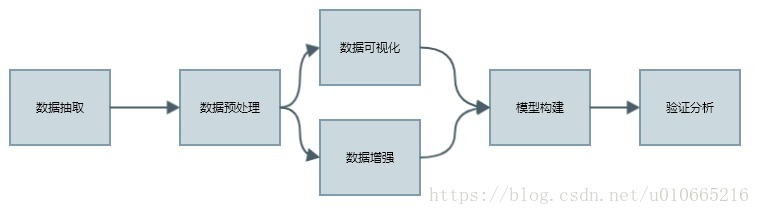
# 项目流程图
本项目的实现流程如下所示:
# 代码实现及解释
接下来我们就按照项目流程图来逐块实现,本项目数据集:[German data](https://d17h27t6h515a5.cloudfront.net/topher/2016/November/581faac4_traffic-signs-data/traffic-signs-data.zip)
如果打不开,则有备用链接:[备用](http://benchmark.ini.rub.de/?section=gtsrb&subsection=dataset)
```python
#import important packages/libraries
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import pickle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import csv
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from tensorflow.contrib.layers import flatten
from skimage import transform as transf
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import cv2
from prettytable import PrettyTable
%matplotlib inline
SEED = 2018
```
/home/ora/anaconda3/envs/tensorflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/h5py/__init__.py:36: FutureWarning: Conversion of the second argument of issubdtype from `float` to `np.floating` is deprecated. In future, it will be treated as `np.float64 == np.dtype(float).type`.
from ._conv import register_converters as _register_converters
WARNING:tensorflow:From /home/ora/anaconda3/envs/tensorflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/datasets/base.py:198: retry (from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.base) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Use the retry module or similar alternatives.
```python
# 导入数据并可视化
training_file = 'data/train.p'
testing_file = 'data/test.p'
with open(training_file,mode='rb') as f:
train = pickle.load(f)
with open(testing_file,mode='rb') as f:
test = pickle.load(f)
X_train,y_train = train['features'],train['labels']
X_test,y_test = test['features'],test['labels']
```
# Dataset Summary and Expoloration
下面我们对德国交通指示牌数据集进行可视化处理
```python
n_train = len(X_train)
n_test = len(X_test)
_,IMG_HEIGHT,IMG_WIDTH,IMG_DEPTH = X_train.shape
image_shape = (IMG_HEIGHT,IMG_WIDTH,IMG_DEPTH)
with open('data/signnames.csv','r') as sign_name:
reader = csv.reader(sign_name)
sign_names = list(reader)
sign_names = sign_names[1::]
NUM_CLASSES = len(sign_names)
print('Total number of classes:{}'.format(NUM_CLASSES))
n_classes = len(np.unique(y_train))
assert (NUM_CLASSES== n_classes) ,'1 or more class(es) not represented in training set'
n_test = len(y_test)
print('Number of training examples =',n_train)
print('Number of testing examples =',n_test)
print('Image data shape=',image_shape)
print('Number of classes =',n_classes)
```
Total number of classes:43
Number of training examples = 34799
Number of testing examples = 12630
Image data shape= (32, 32, 3)
Number of classes = 43
```python
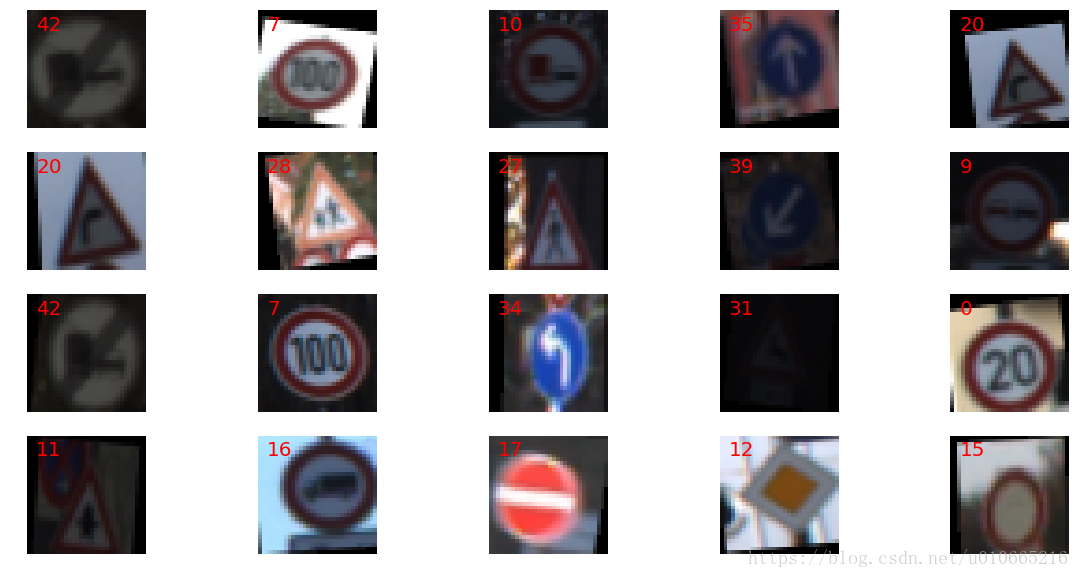
#data visualization,show 20 images
def visualize_random_images(list_imgs,X_dataset,y_dataset):
#list_imgs:20 index
_,ax = plt.subplots(len(list_imgs)//5,5,figsize=(20,10))
row,col = 0,0
for idx in list_imgs:
img = X_dataset[idx]
ax[row,col].imshow(img)
ax[row,col].annotate(int(y_dataset[idx]),xy=(2,5),color='red',fontsize='20')
ax[row,col].axis('off')
col+=1
if col==5:
row,col = row+1,0
plt.show()
ls = [random.randint(0,len(y_train)) for i in range(20)]
visualize_random_images(ls,X_train,y_train)
```

```python
def get_count_imgs_per_class(y, verbose=False):
num_classes = len(np.unique(y))
count_imgs_per_class = np.zeros( num_classes )
for this_class in range( num_classes ):
if verbose:
print('class {} | count {}'.format(this_class, np.sum( y == this_class )) )
count_imgs_per_class[this_class] = np.sum(y == this_class )
#sanity check
return count_imgs_per_class
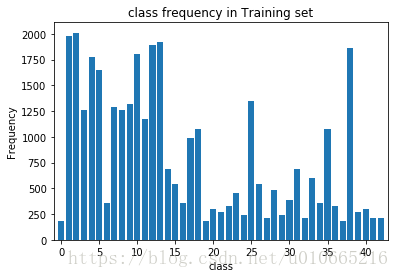
class_freq = get_count_imgs_per_class(y_train)
print('------- ')
print('Highest count: {} (class {})'.format(np.max(class_freq), np.argmax(class_freq)))
print('Lowest count: {} (class {})'.format(np.min(class_freq), np.argmin(class_freq)))
print('------- ')
plt.bar(np.arange(NUM_CLASSES), class_freq , align='center')
plt.xlabel('class')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.xlim([-1, 43])
plt.title("class frequency in Training set")
plt.show()
sign_name_table = PrettyTable()
sign_name_table.field_names = ['class value', 'Name of Traffic sign']
for i in range(len(sign_names)):
sign_name_table.add_row([sign_names[i][0], sign_names[i][1]] )
print(sign_name_table)
```
-------
Highest count: 2010.0 (class 2)
Lowest count: 180.0 (class 0)
-------
+-------------+----------------------------------------------------+
| class value | Name of Traffic sign |
+-------------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 0 | Speed limit (20km/h) |
| 1 | Speed limit (30km/h) |
| 2 | Speed limit (50km/h) |
| 3 | Speed limit (60km/h) |
| 4 | Speed limit (70km/h) |
| 5 | Speed limit (80km/h) |
| 6 | End of speed limit (80km/h) |
| 7 | Speed limit (100km/h) |
| 8 | Speed limit (120km/h) |
| 9 | No passing |
| 10 | No passing for vechiles over 3.5 metric tons |
| 11 | Right-of-way at the next intersection |
| 12 | Priority road |
| 13 | Yield |
| 14 | Stop |
| 15 | No vechiles |
| 16 | Vechiles over 3.5 metric tons prohibited |
| 17 | No entry |
| 18 | General caution |
| 19 | Dangerous curve to the left |
| 20 | Dangerous curve to the right |
| 21 | Double curve |
| 22 | Bumpy road |
| 23 | Slippery road |
| 24 | Road narrows on the right |
| 25 | Road work |
| 26 | Traffic signals |
| 27 | Pedestrians |
| 28 | Children crossing |
| 29 | Bicycles crossing |
| 30 |


















