没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

www.kolmb.com
www.kolmb.com

www.kolmb.com
KOLMB is a professional enterprise
specializing in making Linear
Motion Ball Bearing and related
linear-motion series.
To pursue the higher goal, the
company strictly carry out the
ISO9002:2000 quality system and
has passed the ISO9002 quality
system certification. The company
possess advanced state-of-art
manufacturing equipments, testing
instruments.
。 。 。 。 。 。
。。。。。。。。。。
Moreover, numerous senior
engineers and technicians have
been introduced to develop and
research new products. The
products have been selling to
Japan, U.K., Germany, Italy, Mid-
east area and other countries and
regions.。。。。。。。。。。。。。
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
www.kolmb.com
Basic Dynamic Load Rating (C)
This term is arrived at based on an evaluation of a
number of identical linear systems individually run
in the same conditions, if 90% of them can run with
the load (with a constant value in a constant
direction) for adistance of 50 km without damage
caused by rolling fatigue. This is the basis of the
rating.
Allowable Static Moment (M)
This term defines the allowable limit value of static
moment load,with reference to the amount of
permanent deformation similar to that used for
evaluation of basic rated load (Co).
Static Safety Factor (fs)
This factor is used based on the application
condition as shown in Table 1.
Rating Life of the Linear System
As long as the linear system reciprocates while
being loaded,continuous stress acts on the linear
system to cause flaking on the rolling bobies and
planes because of material fatigue. The travelling
distance of linear system until the fist flaking
occurs is called the life of the systems of the same
dimensions, structure,material,heat treatment and
processing method, when used in the same condi-
tions,This variation is brought about from the essential
variations in the material fatigue itself. The rating life
defined bellow is used as an index for the life expec-
tancy of the linear system.
Rating Life (L)
Rating life is the total travelling distance that 90%
of a group of systems of the same size can reach
without causing any flaking when they operate under
the same conditions.
The rating life can be obtained from the following
equation with the basic dynamic load rating and the
load on the linear system:
L:rating life (km) C:Basic dynamic load rating (N)
P:Load (N)
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Load Rating
Rating Life
Basic Static Load Rating (Co)
This term defines a static load such that, at the
contacting position where the maximurn stress is
exercised, the sum of the permanent deformation
of the rolling elements and that of the rolling plane is
0.0001 time of the diameter of the rolling elements.
Table 1.Stactic Safety Factors
Condition of use Low limit of fs
When the shaft has less deflection
and shock
1to2
When elastic deformation should
be considered with respect to
pinch load
2to4
When the equipment is subject to
vibration and impacts 3to5
Consideration and influence of vibration impact loads
and distribution of load should be taken into account
when designing a linear motion system . it is difficult
to calculate the actual load . The rating life is also
affected by the operating temperature. In these
conditions, the expression (1) is arranged as follows:
L:Rating life (km) fh:Hardness factor (See Fig.1)
C:Basic dynamic load rating (N)
fT:Temperatuer coefficient (See Fig.2) P:Load (N)
fC:Contact coefficient (See Table 2)
fw:Load coefficient (See Table 3)
The rating life in hours can be calculated by obtaining
the travelling distance per unit time. The rating life in
hours can be obtained from the following expression
when the stroke length and the number of strokes
are constant:
Lh:Rating life in hours (hr)
es:Stroke length (m)
L:Rating life (km)
n1:No.of strofes per minute (cpm)
Lh=
.
For ball type:L=( ) 50
.
For ball type:L=( ) 50
C
p
(1)
3
ff
HH
rr
c
pp
ff
cc
ff
33
ww
ff
.. ..
L
.
10
3
2 s
.
.
n1
60
1
CONTENTS
HRJ
62
PK
60
66
BALL BUSHING COMPARISON LIST
59
COUPLING
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
1
LINEAR BUSH SERIES
9
LM
10
LME
12
LMB
14
LM L
16
LME L
17
LMB L
18
KH
19
LMF/K/H
20
LMEF/K
22
LMBF/K
24
LMF/K/H L
26
LMEF/K L
28
LMBF/K L
30
SC L
42
KBA
47
KBA L
48
KBE
49
56
EK/EF
58
FK/FF
SME L
45
SHAFT SUPPORT SERIES
50
SLIDE UNIT SERIES
39
SC
41
32
LMF/KP
34
LMF/KP L
SME
44
LMHP
33
LMF/KC
36
LMHP L
35
LMEF/KC
37
LMBF/KC
38
40
SC S
43
TBR
46
KBA S
51
S K
52
SA
53
TA
54
SHF
55
BALLSCREW SUPPORT UNIT
57
BK/BFF
61
PKC
64
HOT
63
HRJ-C
65
HOT-C
www.kolmb.com
Hardness Factor (fH)
Temperature Coefficient (fT)
Contact Coeffcient (fc)
Load Coefficient (fw)
The shaft must be sufficiently hardened when a linear
bushing is used. lf not properly hardened, permissible
load is lowered and the life of the bushing will be
shortened.
If the temperature of the linear system exceeds 100℃,
hardness of the linear system and the shaft lowers to
decrease the permissible load compared to that of the
linear system used at room temperature. As a result,
the abnormal temperature rise shortens the rating life.
Generally two or more linear bushings are used on
one shaft. Thus, the load on each linear sysem differs
depending on each processing accuracy. Because the
linear bushings are not loaded equally, the number
of linear bushings per shaft changes the permissible
load of the system.
When calculating the load on the linear system, it is
necessary to accurately obtain object weight, inertial
force based on motion speed, moment load, and each
transition as time passes. However, it is difficult to
calculate those valuse accurately because reciprocating
motion involves the repetition of start and stop as well
as vibration and impact. A more practical approach is
to obtain the load coefficient by taking the actual
operatingconditions into account.
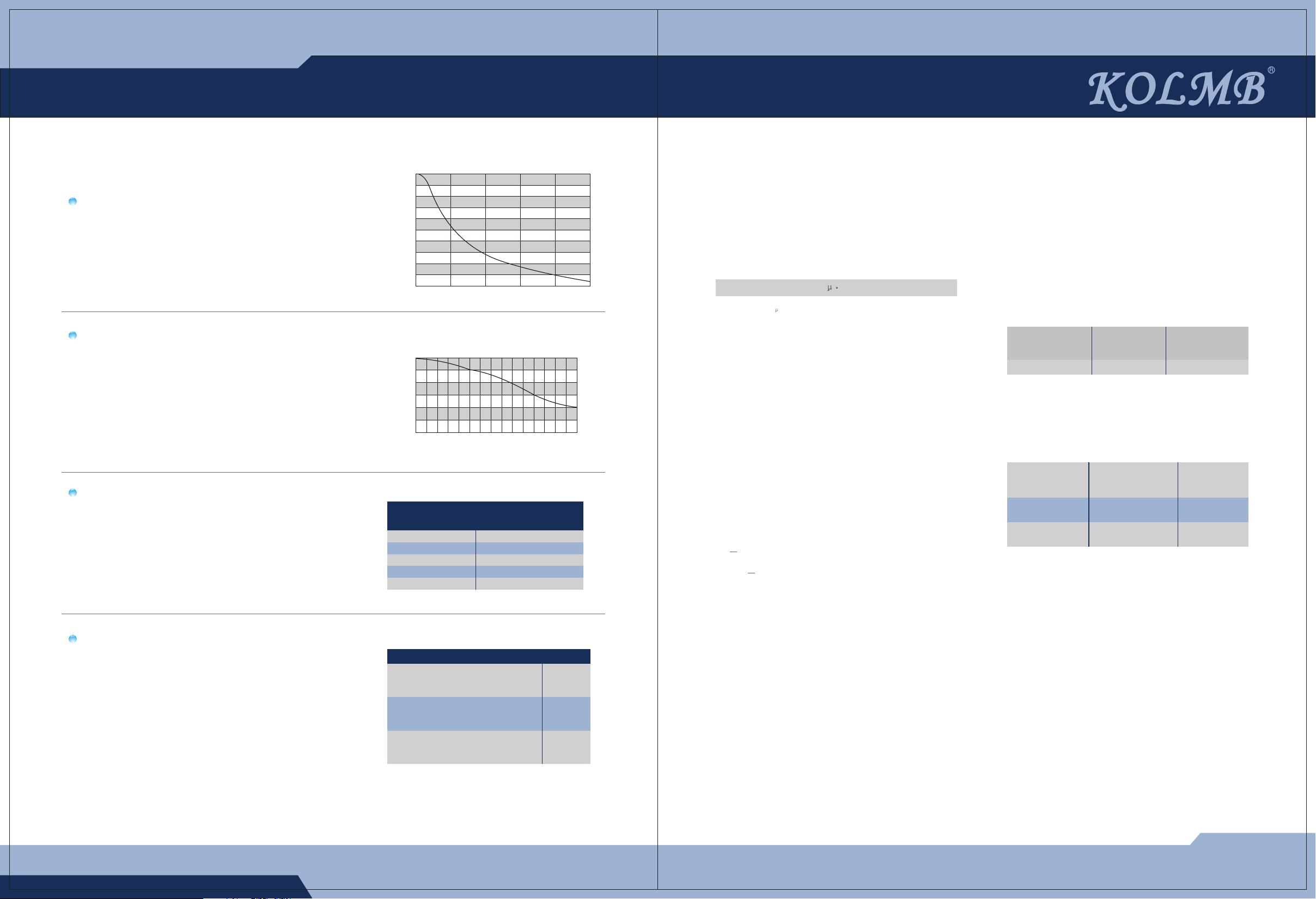
Fig.1 Hardness Factor
Fig.1 Hardness Factor
102030405060
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Raceway Hardness HRC
Hardness Factor f
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
250100 150 200
Temperature of Linear System
Temperature Coefficient f
Table 2 Contact Coefficient
Number of linear
systems per shaft
Contact coefficient fc
1
2
3
4
5
Table 3 Load Coefficient
1.00
0.81
0.72
0.66
0.61
Opearating Conditions
fw
Operation at low speed(15 m/min.
Or less) without impulsive shock
from outside
Operation at intermediate speed
(60 m/min. Or less) without
impulsive shock
Operation at high speed
(over 60 m/min.) With
impulsive shock from outside
1.0 to 1.5
1.5 to 2.0
2.0 to 3.5
The static frictional resistance of the KOLMB
linear system is so low as to be only slightly
different from the kinetic frictional resistance,
enabling smooth linear movement from low to
high speeds. in general, the frictional resistance
is expressed by the following equation.
The frictional resistance of each KOLMB linear
system depends on the model, load weight,
speed, and lubricant. The sealing resistance
depends on the lip interference and lubricant,
regardless of the load.
The ambient working temperature range for each
KOLMB linear system depends on the model.
Consult KOLMB on use outide the recommended
temperature range.
Temperature conversion equation
C=
F=
Using KOLMB linear systems without lubrication increases
the abrasion of the rolling elements, shortening the life
span, The KOLMB linear systems therefore require appro-
priate lubrication. For lubrication KOLMB recommends
turbine oil conforming to ISO Standards G32 to G68 or
lithium base soap grease NO.2. Some KOLMB linear
systems are sealed to biock dust out and seal lubricant in.
If used in a harsh or corrosive environment, however,
apply a protective cover to the part involving linear motion.
Frictional Resistance
F:Frictional resistance :Coefficient of friction
W:Load weight f:Sealing resistance
Ambient
Working Temperature
Lubrication and
Dust Prevention
weight. The sealing resistance of one linear system
is about 2000 to 500 gf. The coefficient of friction
depends on the load weight. Moment load. And pre-
load.Table 6 shows the coefficient of kinetic friction
of each type of linear system which has been installed
and lubricated properly and applied with normalload
(P/C=0.2)
Table 5 Coefficient of Linear System Friction (u)
Table 6 Ambient Working Temperature
Linear Bushing
LMLME LMB -20to80℃
Linear Bushing
LM-ALME-ALMB-A -20to110℃
Linear System
Type
Models
Coefficient of
Friction (u)
Linear Bushing
LMLME LMB 0.002 to 0.003
Linear System
Type
Models
Ambient
Working
Temperature
5
9
5
9
F= W+f
(F-32)
32+ C
3
2

5
4
www.kolmb.com
The KOLMB linear bushing consists of an outer cylinder,
ball retainer, balls and two end rings. The ball retainer
which holds the balls in the recirculating tuucks in held
inside the outer cylinder by end rings.
Those parts are assembled to optimize their required
functions.
The outer cylinder is maintained sufficient hardness
by heat treatment, therefore if ensures the bushings
projected travel life and satisfactory duravbility.
The ball retainer is made from steel or synthetics resin.
The steel retainer has high rigidity, obtained by heat
treat meant.
The synthetics resin retainer can reduce running noise.
The user can select the optimum type for meeting the
user's service conditions.
Structure and Features
The KOLMB linear bushing is produced from a solid
steelouter cylinder and incorporates an industrial stre-
ngth resin retainer.
The standard type of KOLMB linear bushing can be
loaded from any direction. Precision control is Possible
using only the shaft supporter, and the mounting
surface can be machined easily.
KOLMB linear bushings of each type are completely
interchangeable because of their standardized
dimensions and strict precision control. Replacement
because of wear or damage is therefore easy and
accurate.
KOLMB offers a full line of linear bushing: the stan-
dard, integral single-retainer closed types. The user
can choose from among these according to the
application requirements to be met.
1.High Precision and Rigidity
2.Ease of Assembly
3.Ease of Replacement
4.Veriety of Types
LINEAR BUSHING
Note that precision of inscribed circle diameters and outside diameters for the clearance adjustable type (…-AJ)
and the open type (…-OP) indicates the value obtained before the corresponding type is subjected to cutting
process.
Tolerance
Load Rating and
Life Expectancy
The life (L) of a linear bushing can be obtained
from the following equation with the basic dynamic
load rating and the load applied to the busha:
L:Rated life (km) fH:Hardness factor (See page5)
C:Basic dynamic load rating (N) fT:Temperature coefficient (See page5)
P:Working load (N) fc:Contact coefficient (See page5)
fw:Load coefficient
The lifespan (Ln) of a linear bushing in hours can be
obtained by calculating the travelling distance per
unit time.
The lifespan can be obtained from the following
equation if the stroke length and the number of
strokes are constant:
Lh:Lifespan s:Stroke length (m)
L:Rated life (km) n:Number of strokes per minute (cpm)
.
:L=( ) 50
f
H
r
c
p
f
c
f
w
f
. .
L=( ) 50
f
H
T
c
p
f
C
f
3
W
f
. .
(1)
(2)
Lh=
L 10
3
2 s n1 60
(
(
SLIDE UNIT
SC 20 L UU
KBA - LME SERIES SLIDE BLOCK
SME - LM SERIES OPEN SLIDE BLOCK
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
SHAFT DIAMETER
NO ENTRY - NO SEAL
U - SEAL ON ONE SIDE
UU - SEAL ON BOTH SIDES
LM F 20
UU
OP
N L
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
N - NICKEL PLATED TYPE
LM - ASIA SERIES
LME - EUROPE SERIES
LMB - ENGLISH SYSTEM SERIES
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
H - TWO SIDE CUT FLANGE TYPE
F - FOUND FLANGE TYPE
FP - PILOT PATTERN ROUND FLANGE TYPE
FC - CENTERED ROUND FLANGE TYPE
K - SQUARE FLANGE TYPE
KC - CENTERED SQUARE LANGE
KP - PILOT PATTERN SQUARE FLANGE TYPE
HP - PILOT PATTERN TWO SIDE CUT FLANGE TYPE
HC - CENTERED TWO SIDE CUT FLANGE
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
AJ - CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT
TYPE
OP - OPEN TYPE
NO ENTRY - NO SEAL
U - SEAL ON ONE SIDE
UU - SEAL ON BOTH SIDES
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
S - SHORTEN TYPE
L - LENGTHEN TYPE
A
NO ENTRY - STANDARD TYPE
A - STEEL RETAINER
S - SHORTEN TYPE
L - LENGTHEN TYPE
SHAFT DIAMETER
SC - LM SERIES SLIDE BLOCK
KBE - LME SERIES OPEN SLIDE BLOCK
TBR - LM SERIES OPEN SLIDE BLOCK
Type number format
剩余35页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

制冷技术咨询与服务
- 粉丝: 4068
- 资源: 2万+

下载权益

C知道特权

VIP文章

课程特权
开通VIP
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 【岗位说明】生物科技有限公司员工岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】省中医院药材挑选岗位操作规程.doc
- 【岗位说明】外科护士长岗位说明书.doc
- 【岗位说明】药房药店最新岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】药剂师中药师岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】医美机构市场部人员岗位职责说明书.doc
- 【岗位说明】医疗投资集团组织结构及各岗位说明.doc
- 【岗位说明】医疗器械经营企业各岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】医药行业制度制药公司市场部岗位职责范本.doc
- 【岗位说明】医院信息科岗位职责说明.doc
- 【岗位说明】责任护士岗位说明书.doc
- 【岗位说明】执业药师及药师岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】制药企业岗位职责制.doc
- 【岗位说明】用药咨询药师职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】中草药煎药人员岗位职责.doc
- 【岗位说明】中药处理岗位操作规程.doc
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功