没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
温馨提示
8051开发手册(英文版): Chapter 1 Types of Memory Chapter 3 Basic Registers Chapter 4 Addressing Modes Chapter 5 Program Flow Chapter 6 Low Level Information Chapter 7 Timers Chapter 8 Serial Port Operations Chapter 9 Interrupts Chapter 10 Additional Features in 8052
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

8051 Tutorial
1
8051 Tutorial
http://www.hobbyprojects.com/8051_tutorial/
Introduction
Chapter 1 Types of Memory
o Types of Memory
o Code Memory
o Internal RAM
o External RAM
o Special Function Registers (SFRs)
o Bit Memory
o Register Banks
Chapter 2 Special Function Registers
o What are SFRs?
o Types of SFRs
o Standard SFR Descriptions
o Non-Standard SFRs
Chapter 3 Basic Registers
o "R" Registers
o Accumulator
o Data Pointer (DPTR)
o B Register
o Stack Pointer (SP)
o Program Counter (PC)
Chapter 4 Addressing Modes
o Addressing Modes
o Immediate Addressing
o Direct Addressing
o Indirect Addressing
o External Direct Addressing
o External Indirect Addressing
Chapter 5 Program Flow
o Program Flow
o Conditional Branching
o Direct Jumps
o Direct Calls
o Return from Subroutines
o Interrupts
Chapter 6 Low Level Information
o Instruction Set, Timing and Low Level Information
Chapter 7 Timers
o Timers
o How Timers Count
o Measuring Time
o Timer SFRs
TMOD SFR
Mode 0 - 13-bit Timer
Mode 1 - 16-bit Timer

8051 Tutorial
2
Mode 2 - Auto-reload Timer
Mode 3 - Split Timer
TCON SFR
o How Long do Timers Take to Count?
o Initializing a Timer
o Reading a Timer
o Reading a Timer Value
o Timing the Length of an Event
o Detecting a Timer Overflow
o Timers as Event Counters
Chapter 8 Serial Port Operations
o Serial Port Operations
o Setting the Serial Baud Rate
o Setting the Serial Port Mode
o Reading from the Serial Port
o Writing to the Serial Port
Chapter 9 Interrupts
o Interrupts
o Events that trigger Interrupts
o Setting Up Interrupts
o Polling Sequence
o Interrupt Priorities
o What Happens When an Interrupt Occurs?
o Serial Interrupts
o What Happens When an Interrupt Ends?
o Register Protection
o Common Bugs in Interrupts
Chapter 10 Additional Features in 8052
o Introduction to 8052
o 256 bytes of additional Internal RAM
o New SFRs for 8052's Third Timer
o Timer 2 as a Baud-Rate Generator
o T2CON SFR
o Timer 2 in Auto-Reload Mode
o Timer 2 in Capture Mode
o Timer 2 Interrupt
Reference 8051 / 8052 Instruction Set
o ACALL: Absolute Call
o ADD, ADDC: Add Accumulator (With Carry)
o AJMP: Absolute Jump
o ANL: Bitwise AND
o CJNE: Compare and Jump if Not Equal
o CLR: Clear Register
o CPL: Complement Register
o DA: Decimal Adjust
o DEC: Decrement Register
o DIV: Divide Accumulator by B
o DJNZ: Decrement Register and Jump if Not Zero
o INC: Increment Register

8051 Tutorial
3
o JB: Jump if Bit Set
o JBC: Jump if Bit Set and Clear Bit
o JC: Jump if Carry Set
o JMP: Jump to Address
o JNB: Jump if Bit Not Set
o JNC: Jump if Carry Not Set
o JNZ: Jump if Accumulator Not Zero
o JZ: Jump if Accumulator Zero
o LCALL: Long Call
o LJMP: Long Jump
o MOV: Move Memory
o MOVC: Move Code Memory
o MOVX: Move Extended Memory
o MUL: Multiply Accumulator by B
o NOP: No Operation
o ORL: Bitwise OR
o POP: Pop Value From Stack
o PUSH: Push Value Onto Stack
o RET: Return From Subroutine
o RETI: Return From Interrupt
o RL: Rotate Accumulator Left
o RLC: Rotate Accumulator Left Through Carry
o RR: Rotate Accumulator Right
o RRC: Rotate Accumulator Right Through Carry
o SETB: Set Bit
o SJMP: Short Jump
o SUBB: Subtract From Accumulator With Borrow
o SWAP: Swap Accumulator Nibbles
o XCH: Exchange Bytes
o XCHD: Exchange Digits
o XRL: Bitwise Exclusive OR
o Undefined: Undefined Instruction
Appendix Numbering Systems

8051 Tutorial
4
Introduction
Despite it’s relatively old age, the 8051 is one of the most popular microcontrollers in
use today. Many derivative microcontrollers have since been developed that are
based on--and compatible with--the 8051. Thus, the ability to program an 8051 is an
important skill for anyone who plans to develop products that will take advantage of
microcontrollers.
Many web pages, books, and tools are available for the 8051 developer.
I hope the information contained in this document/web page will assist you in
mastering 8051 programming. While it is not my intention that this document
replaces a hardcopy book purchased at your local book store, it is entirely possible
that this may be the case. It is likely that this document contains everything you will
need to learn 8051 assembly language programming. Of course, this document is
free and you get what you pay for so if, after reading this document, you still are lost
you may find it necessary to buy a book.
This document is both a tutorial and a reference tool. The various chapters of the
document will explain the 8051 step by step. The chapters are targeted at people
who are attempting to learn 8051 assembly language programming. The appendices
are a useful reference tool that will assist both the novice programmer as well as the
experienced professional developer.
This document assumes the following:
A general knowledge of programming.
An understanding of decimal, hexadecimal, and binary number systems. For some
background information on these number systems, try appendix.
A general knowledge of hardware.
That is to say, no knowledge of the 8051 is assumed--however, it is assumed you’ve
done some amount of programming before, have a basic understanding of hardware,
and a firm grasp on the three numbering systems mentioned above. The concept of
converting a number from decimal to hexadecimal and/or to binary is not within the
scope of this document--and if you can’t do those types of conversions there are
probably some concepts that will not be completely understandable.
This document attempts to address the need of the typical programmer. For
example, there are certain features that are nifty and in some cases very useful--but
95% of the programmers will never use these features. To make this document more
applicable to the general programming public some details may be skimmed over
very briefly--or not at all.
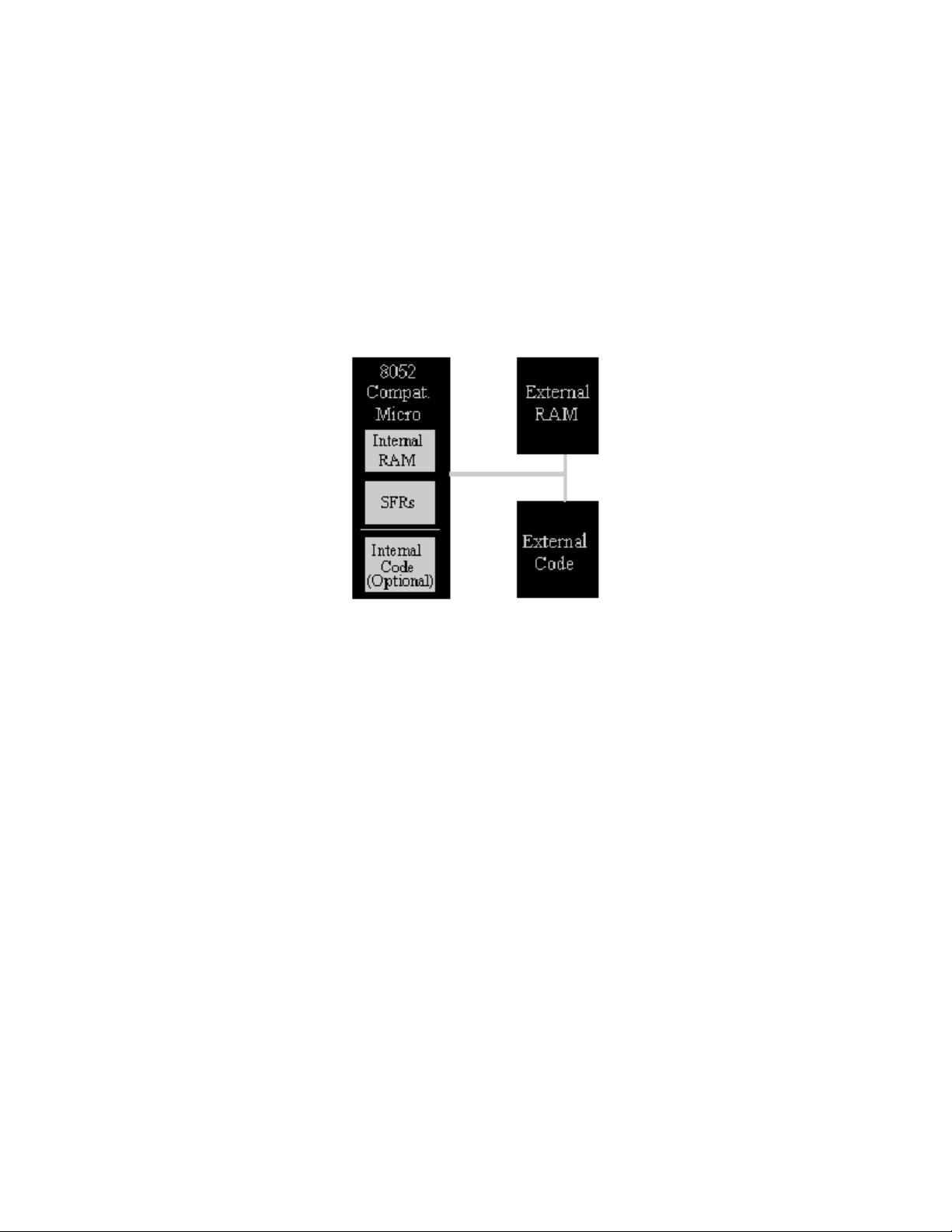
8051 Tutorial
5
Chapter 1 Types of Memory
Types Of Memory
The 8051 has three very general types of memory. To effectively program the 8051
it is necessary to have a basic understanding of these memory types.
The memory types are illustrated in the following graphic. They are: On-Chip
Memory, External Code Memory, and External RAM.
On-Chip Memory refers to any memory (Code, RAM, or other) that physically exists
on the microcontroller itself. On-chip memory can be of several types, but we'll get
into that shortly.
External Code Memory is code (or program) memory that resides off-chip. This is
often in the form of an external EPROM.
External RAM is RAM memory that resides off-chip. This is often in the form of
standard static RAM or flash RAM.
Code Memory
Code memory is the memory that holds the actual 8051 program that is to be run.
This memory is limited to 64K and comes in many shapes and sizes: Code memory
may be found on-chip, either burned into the microcontroller as ROM or EPROM.
Code may also be stored completely off-chip in an external ROM or, more commonly,
an external EPROM. Flash RAM is also another popular method of storing a program.
Various combinations of these memory types may also be used--that is to say, it is
possible to have 4K of code memory on-chip and 64k of code memory off-chip in an
EPROM.
When the program is stored on-chip the 64K maximum is often reduced to 4k, 8k, or
16k. This varies depending on the version of the chip that is being used. Each
剩余91页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

0x07c00
- 粉丝: 28
- 资源: 10
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- MD5加密算法(C语言实现,已编译,亲试可用~) 完整示例工程 - 基于STM32F103的运行环境,但代码移植性很高
- 基于K近邻分类算法的语音情感识别MATLAB代码
- Matlab Simulink仿真模型 三相异步电机弱磁控制 附赠模型指导
- 申瓯通信 HJK120集团电话说明书
- 永磁同步电机+SMO滑膜观测算法+simulink仿真
- 该程序复现《计及调度经济性的光热电站储热容量配置方法》模型,综合考虑火电机组发电成本、光热发电并网消纳的环境效益和运行维护成本、系统旋转备用成本等调度经济性因素,求解光热电站最佳储热容量,并在此基础上
- java的jdk8下载windows64位
- 一种基于改进的鲸鱼优化算法,通过MATLAB实现,通过模拟改进鲸鱼捕猎方式进行优化,具有多种优势,并且对比了多种优化算法,其优势明显 如有需要动动小手联系,保证程序正常运行
- rip宣告网段选择版本
- 永磁同步电机双矢量占空比模型预测转矩控制mptc,考虑全局最优占空比选择,使得全局占空比基本都小于1,仿真波形效果不错,有word文档解析
- 永磁同步电机改进型三矢量模型预测电流控制,参考张晓光老师的lunwenModel Predictive Switching Control for PMSM Drives,基于q轴电流的斜率,采用切控
- 毕业设计部署yolov9模型ncnn模型到树莓派4或5嵌入式源码.zip
- 2种方法SCL编写和CFC编写5个电机逆启顺停的顺控程序 方法一:使用西门子的电机功能块和联锁块编写5个电机逆启顺停的顺控程序 方法二、使用SCL编写逆启顺停的功能块,然后在CFC调用,采用SFC方式
- Akebi-GC-master.zip
- 【光学】基于matlab高斯光束F-P干涉仪传输模拟【含Matlab源码 10951期】.zip
- 【电磁】基于matlab微带线中的电势和场分布【含Matlab源码 10949期】.zip
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功