没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
ISO14229-2-2013
需积分: 38 35 下载量 91 浏览量
2018-12-14
17:22:57
上传
评论 1
收藏 1.63MB PDF 举报
温馨提示
该文档是Road vehicles— Unified diagnostic services (UDS) — Part 2: Session layer services 2013-02-15版本,可以编辑的PDF格式,非影印版。
资源推荐
资源详情
资源评论

Reference numbe
r
ISO 14229-2:2013(E)
©
ISO 2013
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
ISO
14229-2
First edition
2013-02-15
Road vehicles— Unified diagnostic
services (UDS) —
Part 2:
Session layer services
Véhicules routiers — Services de diagnostic unifiés (SDU) —
Partie 2: Séquence des couches de services
--`,,`,`,````,,``,,,,`,``,,`,,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---

ISO 14229-2:2013(E)
COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT
© ISO 2013
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from either ISO at the address below or
ISO's member body in the country of the requester.
ISO copyright office
Case postale 56 CH-1211 Geneva 20
Tel. + 41 22 749 01 11
Fax + 41 22 749 09 47
E-mail copyright@iso.org
Web www.iso.org
Published in Switzerland
ii
© ISO 2013 – All rights reserved
--`,,`,`,````,,``,,,,`,``,,`,,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---

ISO 14229-2:2013(E)
© ISO 2013 – All rights reserved
iii
Contents Page
1 Scope ...................................................................................................................................................... 1
2 Normative references ............................................................................................................................ 1
3 Terms, definitions and abbreviated terms .......................................................................................... 1
3.1 Terms and definitions ........................................................................................................................... 1
3.2 Abbreviated terms ................................................................................................................................. 2
4 Conventions ........................................................................................................................................... 2
5 Document overview ............................................................................................................................... 3
6 Session layer services .......................................................................................................................... 4
6.1 General ................................................................................................................................................... 4
6.2 Specification of session layer service primitives .............................................................................. 6
6.3 Session data unit specification ............................................................................................................ 7
7 Timing parameter definition ................................................................................................................. 9
7.1 General application timing considerations......................................................................................... 9
7.2 Application timing parameter definitions – defaultSession ............................................................ 10
7.3 Example for P4Server without enhanced response timing ............................................................. 15
7.4 Example for P4Server with enhanced response timing .................................................................. 16
7.5 Session timing parameter definitions for the non-default session ................................................ 17
7.6 Client and server timer resource requirements ............................................................................... 19
7.7 Error handling ...................................................................................................................................... 20
8 Timing handling during communication ........................................................................................... 21
8.1 Physical communication .................................................................................................................... 21
8.2 Functional communication ................................................................................................................. 29
8.3 Minimum time between client request messages ............................................................................ 36
Annex A (normative) T_PDU interface .......................................................................................................... 43
Annex B (informative) Vehicle diagnostic OSI layer architecture examples ............................................ 44
B.1 Vehicle diagnostic OSI layer gateway example ............................................................................... 44
B.2 Vehicle diagnostic OSI layer CAN router example .......................................................................... 45
B.3 Vehicle diagnostic OSI layer CAN switch example .......................................................................... 46
Bibliography ...................................................................................................................................................... 47
--`,,`,`,````,,``,,,,`,``,,`,,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---

ISO 14229-2:2013(E)
iv
© ISO 2013 – All rights reserved
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies
(ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been
established has the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and
non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
The main task of technical committees is to prepare International Standards. Draft International Standards
adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an
International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting a vote.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent
rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO 14229-2 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 22, Road vehicles, Subcommittee SC 3,
Electrical and electronic equipment.
ISO 14229 consists of the following parts, under the general title Road vehicles — Unified diagnostic services
(UDS):
Part 1: Specification and requirements
Part 2: Session layer services
Part 3: Unified diagnostic services on CAN implementation (UDSonCAN)
Part 4: Unified diagnostic services on FlexRay implementation (UDSonFR)
Part 5: Unified diagnostic services on Internet Protocol implementation (UDSonIP)
Part 6: Unified diagnostic services on K-Line implementation (UDSonK-Line)
The following part is under preparation:
Part 7: Unified diagnostic services on Local Interconnect Network implementation (UDSonLIN)
The titles of future parts will be drafted as follows:
Part n: Unified diagnostic services on … implementation (UDSon…)
--`,,`,`,````,,``,,,,`,``,,`,,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
ISO 14229-2:2013(E)
© ISO 2013 – All rights reserved
v
Introduction
ISO 14229 has been established in order to define common requirements for diagnostic systems that are
independent of the underlying serial data link.
To achieve this, ISO 14229 is based on the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Basic Reference Model in
accordance with ISO 7498-1 and ISO/IEC 10731, which structures communication systems into seven layers.
When mapped on this model, the services used by a diagnostic tester (client) and an Electronic Control Unit
(ECU, server) are broken into the following layers in accordance with Table 1:
Application layer (layer 7), unified diagnostic services specified in ISO 14229-1, ISO 14229-3 UDSonCAN,
ISO 14229-4 UDSonFR, ISO 14229-5 UDSonIP, ISO 14229-6 UDSonK-Line, ISO 14229-7 UDSonLIN,
further standards and ISO 27145-3 WWH-OBD.
Presentation layer (layer 6), vehicle manufacturer specific, ISO 27145-2 WWH-OBD.
Session layer services (layer 5) specified in this part of ISO 14229.
Transport layer services (layer 4), specified in ISO 15765-2 DoCAN, ISO 10681-2 Communication on
FlexRay, ISO 13400-2 DoIP, ISO 27145-4 WWH-OBD.
Network layer services (layer 3), specified in ISO 15765-2 DoCAN, ISO 10681-2 Communication on
FlexRay, ISO 13400-2 DoIP, ISO 27145-4 WWH-OBD.
Data link layer (layer 2), specified in ISO 11898-1, ISO 11898-2, ISO 17458-2, ISO 13400-3, IEEE 802.3,
ISO 14230-2 and further standards, ISO 27145-4 WWH-OBD.
Physical layer (layer 1), specified in ISO 11898-1, ISO 11898-2, ISO 17458-4, ISO 13400-3, IEEE 802.3,
ISO 14230-1, further standards, ISO 27145-4 WWH-OBD.
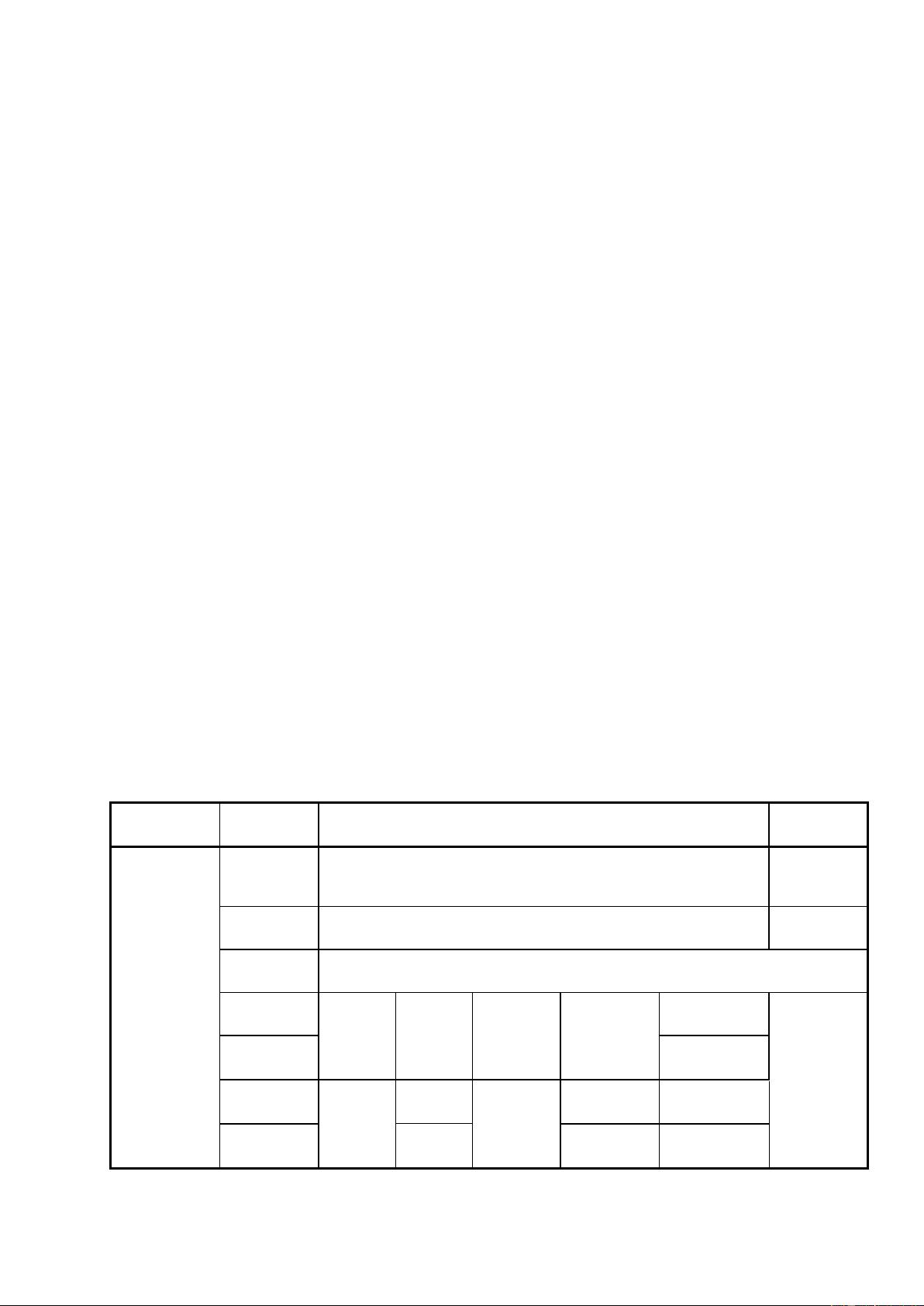
Table 1 — Example of diagnostic/programming specifications applicable to the OSI layers
Applicability
OSI seven
layer
Enhanced diagnostics services
WWH-OBD
Seven layer
according to
ISO/IEC
7498-1
and
ISO/IEC
10731
Application
(layer 7)
ISO 14229-1, ISO 14229-3 UDSonCAN, ISO 14229-4 UDSonFR,
ISO 14229-5 UDSonIP, ISO 14229-6 UDSonK-Line, ISO 14229-7
UDSonLIN, further standards
ISO
27145-3
Presentation
(layer 6)
vehicle manufacturer specific
ISO
27145-2
Session
(layer 5)
ISO 14229-2
Transport
(layer 4)
ISO
15765-2
ISO
10681-2
ISO
13400-2
Not
applicable
further
standards
ISO
27145-4
Network
(layer 3)
further
standards
Data link
(layer 2)
ISO
11898-1,
ISO
11898-2
ISO
17458-2
ISO
13400-3,
IEEE
802.3
ISO
14230-2
further
standards
Physical
(layer 1)
ISO
17458-4
ISO
14230-1
further
standards
--`,,`,`,````,,``,,,,`,``,,`,,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
剩余55页未读,继续阅读
资源评论

智驾
- 粉丝: 2561
- 资源: 60
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜最新资源
- 基于OPENMV的视觉智能小车(车可自己动,实现方块,颜色识别)
- C# usb hid 设备控制
- MYSQL window安装包,版本8.0
- 三菱PLC药片自动装瓶机控制系统设计自动药片装瓶机电气控制
- 图形用户界面(GUI)应用程序
- 企业商户自动发卡运营版带WAP手机端【多种主题+亲测可用】
- Unity程序开发:创建一个2D平台游戏
- 矩形三维随机裂隙网络 使用COMSOL with Matlab接口编程 可以直接导入COMSOL中,无需CAD,无需提取数据,方便快捷可以直接计算 裂隙由matlab编程生成,能够生成两组不同产
- python+celery+AWVS 实现的漏洞扫描器
- 1.3M宽干式拉丝机(双道砂带)sw16可编辑全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- C# USB HID 读卡器 (CPU卡和IC卡的读和写)上位机源码
- EWSA中文版使用教程.doc
- 罗技鼠标接收器与罗技鼠标相连的软件
- 履带车底盘sw16全套技术资料100%好用.zip
- h2database 2.2.224 版本 Jar包
- 基于Springboot的梦宇飞行培训管理系统
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功