
Riddle of Wordle: Mining the Secret of Number Scores & Solution Words
Summary
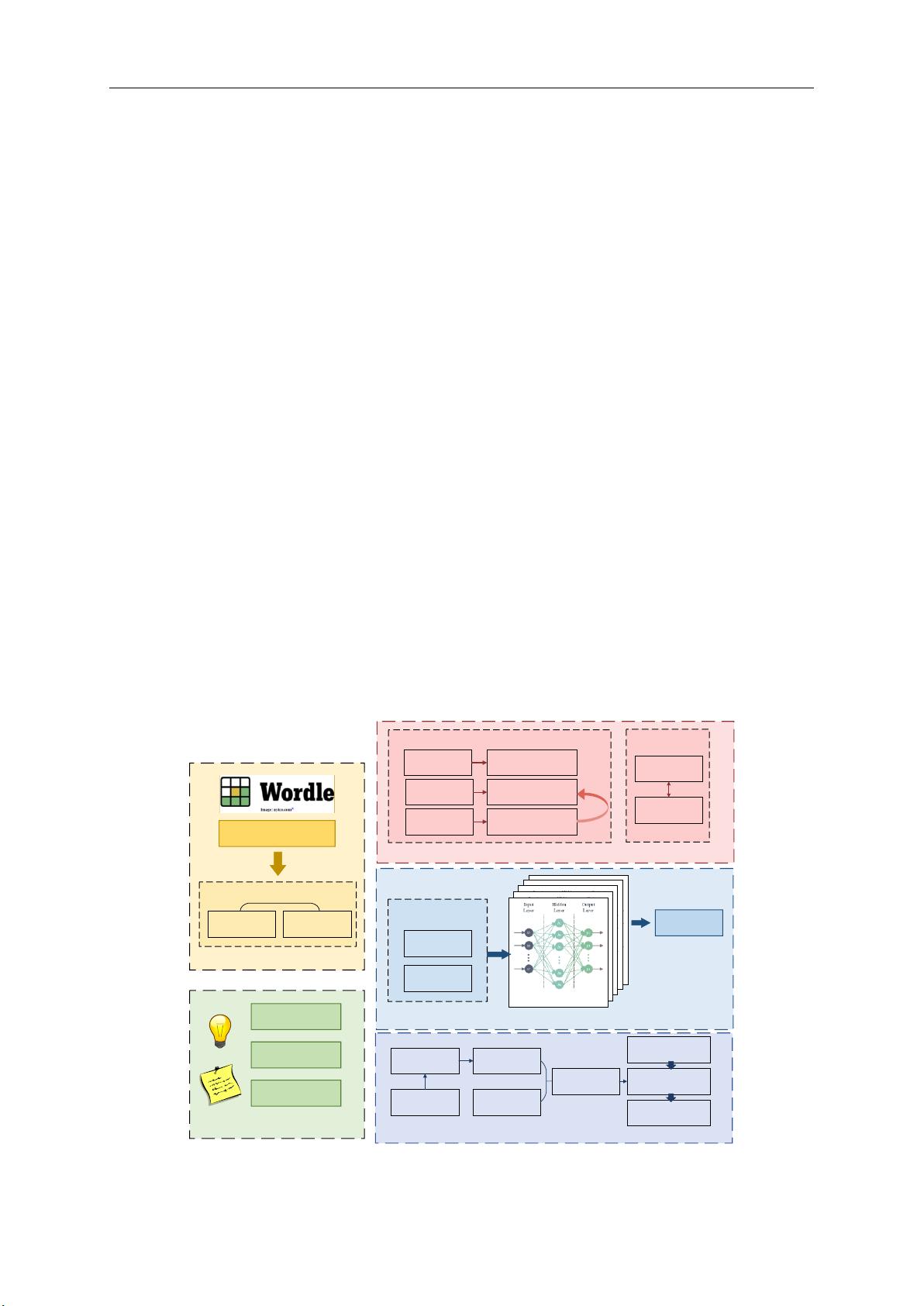
Wordle is a popular puzzle currently offered daily by the New York Times. The simple
rules and clever propagation properties have contributed to its popularity. In this article, we
build two prediction models for the prediction of the Twitter report number intervals and result
distributions, respectively, and develop a model for classifying the difficulty of solution words.
In TASK 1: After data preprocessing, we build a Wordle report number prediction model
based on 3rd-order gaussian regression and a non-homogeneous Poisson process from a statis-
tical perspective. Among them, the Gaussian regression is used to predict the trend signs of
report numbers, while the non-homogeneous Poisson process predicts the stochastic fluctua-
tions of report numbers on this basis. Moreover, we use the popularity relaxation function to
correct the stochastic process, which better approximates the popularity change. At a confi-
dence level of 75%, we predict the interval of the number of reports on March 1, 2023 to be
[7654, 20154]. In addition, we extract 8 attributes of words in terms of the number of letters,
letter location and so on, finding that these attributes did not have an effect on the percentage
of players' Hard Mode choices. Players' confidence in their performance ability and their play
mentality may be the main reasons for whether they choose the Hard Mode or not.
In TASK 2: We first extract the data features that affect the distribution of reported results,
including word attributes, and the percentage of difficulty patterns. Then, we build a BP neural
network to make preliminary predictions on the distribution of guessing results for a certain
solution word in the future. To improve the generalization performance of the prediction results,
we build an integrated BP neural network based on Bagging. Then, we predict the distribu-
tion of the reported results of EERIE on March 1, 2023 as (0, 1, 6, 25, 31, 25, 13) (in %). We
have more than 80% confidence that the absolute error of the predicted outcome for the per-
centage of each possible result does not exceed 5%.
In TASK 3: First, we build a word difficulty induction model based on the K-Means from
the distribution of user's reported data, and divide the difficulty into 4 classes. Then, we explore
the association between word attributes and difficulty based on Pearson’s coefficients, and
take the attributes with correlation coefficients greater than 0.6 as difficulty classification at-
tributes to build a word difficulty classification model. Moreover, we find that the frequency
of the first and second letters of the solution words, the number of vowels contained in the
pronunciation and the number of word properties have a high correlation with the difficulty
classification. Finally, the difficulty classification result of EERIR is the most difficult.
In TASK 4: While exploring the statistical properties of the number of reports, we find
that the distribution of the number of reports showed a similar pattern to its trend over time. In
addition, we also notice that the percentage fluctuation of 3 tries to complete the game was the
largest in the 359 days of reported outcome distribution data.
Finally, we perform a sensitivity analysis of the model and investigate the effect of
changes in the variable parameters of the model on the results.
Keywords: Gaussian regression; Poisson process; BP neural network; K-Means
Problem Chosen
C
2023
MCM/ICM
Summary Sheet
Team Control Number
2311717
更多数模资讯和学习资料,请关注b站/公众号:数学建模BOOM
b站主页:https://space.bilibili.com/350975620








 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功