person determine all possible defects. Therefore, certain methods
must be devised to solve the problem of subjectivity in quality evalu-
ation due to the limitations of human perception.
Previous researches have attempted overcome the limitations of
the subjective evaluation of visual quality inspection by human in-
spectors [8–18]. These research works developed an automatic proce-
dure replacement using computer vision and image-processing
technologies to detect damage positions and quantify defect level.
Moreover, the image-processing technique can be integrated with
tools for data collection and transformation such as digital camera,
wireless sensors, wireless scanner, PDA or mobile phone to automate
the process of damage inspection or monitoring. The previous re-
searches have studied to apply in both structural work and architec-
tural work. For example, the damage inspection in several concrete
structures by using digital image processing technique, Georgopoulos,
Loizos and Flouda [8], and Lee [9] conducted studies to quantify
defects and to classify crack types in road infrastructures. The results
of these studies helped to optimize infrastructure maintenance strate-
gies during the operation stage. Digital image processing (DIP) is a
popular information technology in this field. In the same, Yu, Jang
and Han [10] studied to propose a system by using digital image pro-
cessing technique for detecting and measuring cracks in a tunnel to
provide objective crack data to be used in evaluating safety. Furuta,
Namura, Nakatsu, Hattori, and Adachi [11] applied digital image pro-
cessing to assess damage level of bridge. Lee, Chang and Skibniewski
[12] studied the inspection of the deterioration of a steel bridge
coating. The study used digital image processing technique to quantify
the amount of rust on the steel surface. Moreover, the image proces-
sing can be applied to inspect the defect level in the architectural
work. For example, Zhu and Brilakis [13] studied to detect air pockets
in architectural concrete for quality assessment. Mostly, the previous
researches intended to apply image-processing technique to detect
defect positions on materials such as wood defect classification, de-
fects on tile (cracks, bumps, depressions, holes, dirt, drops, water
drop, ondulations, colour and texture) [14–18].
However, few researchers have focused on evaluating the inten-
sive defect level of the subjective attributes of aesthetic issues during
the construction stage. The subjectivity of human perception
can cause several problems. For example, some work items in archi-
tectural work cannot quantify the amount of a defect by a human vi-
sual inspection for supporting decision on quality, although there is a
standard specifying in the contract document. The decision making
depends on the individual experience and is unreliable. These can
lead to conflicts about what is an acceptable judgment of the defect
level. Therefore, this study aims to develop a system for evaluating
aesthetic defect levels by using within an organization to reduce
these problems.
This paper presents an innovative system of defect detection and
quantification. The system is able to specify the defect positions and
quantify the defect values to support the subjective visual quality in-
spection of the aesthetics of an architectural work. This method is
based on defect feature analysis and quantifies the defect value in dig-
ital images using a digital image processing technique. The proposed
system increases the reliability of aesthetic judgments by reducing
the input of human subjective judgment. We chose the inspection
of tiling work as the case study for developing the prototype of the
system. After giving a brief background of the problem and the previ-
ous works in this section, the content of this paper describes the con-
ceptual framework of the application of the proposed system and the
methodology of the system's development. In addition, it includes a
field verification of the potential and accuracy of the developed proto-
type system by comparing the results of human inspections and those
of the proposed system.
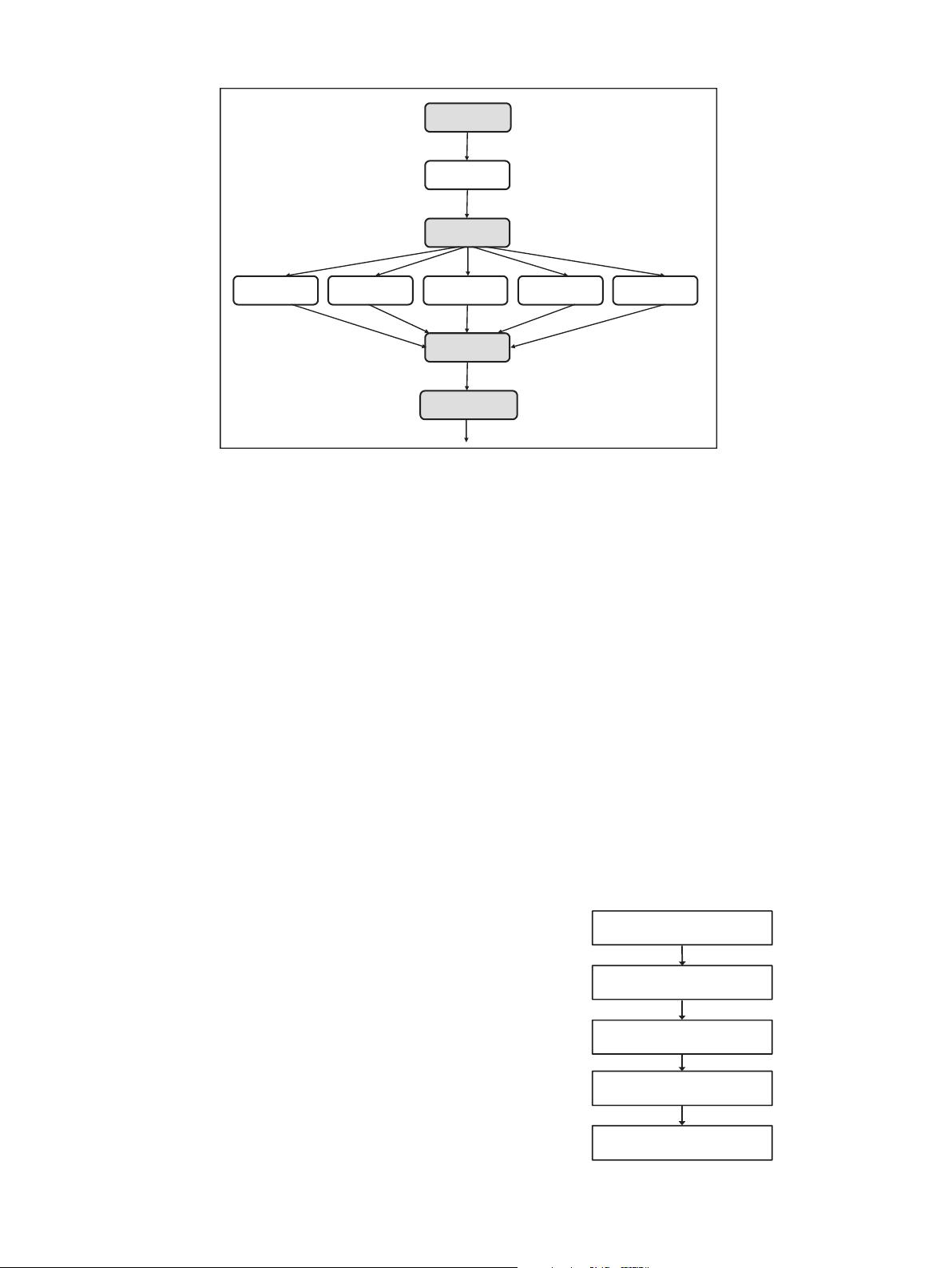
2. Principles of the digital image processing technique
Digital image processing in computer vision is a computerized
process that helps to enhance the properties of an image into a usable
form with an objective and easier feature analysis of images [19]. The
interest in digital image processing methods stems from two princi-
pal areas of application. These are the improvement of pictorial infor-
mation for human interpretation and the processing of scene data for
autonomous machine perception [20]. Digital image processing can
be roughly divided into four levels of the computerized process in a
continuum that is shown in Fig. 2 . Representations are depicted as
shaded rectangles. Two levels are often distinguished; these are
low-level image processing and high-level image understanding
[19,21,22].
(1) Low-level processing involves primitive operations that consist
of image acquisition, image compression and a pre-processing
method for noise filtering, edge extraction and image sharpen-
ing or the enhancement of certain object features that are
relevant to understanding the image.
(2) High-level processing attempts to imitate human cognition
(making sense of the image) and the human ability to make
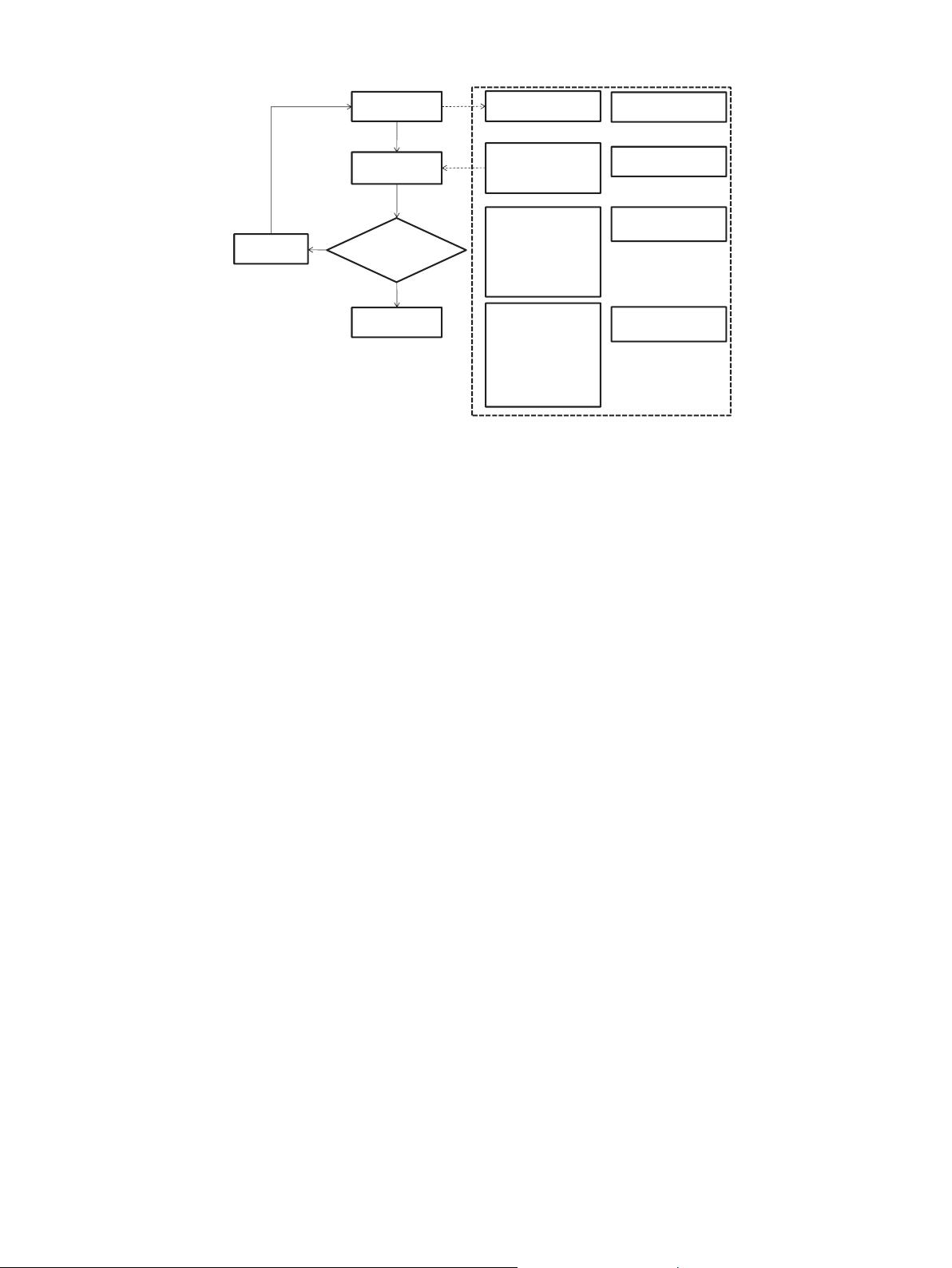
Inspection
Defect
quantification
(Measurable)
Acceptable
defect level
evaluation
Not pass
Correction
Continue next
process
Assessment tools
(Mechanical
instrument)
Contract document
- Standard
- Sampling
- Drawing
- Specification
pass
(Measurable)
(Subjective)
Visual
Individual experience
(Subjective)
Relate to
-Material
requirement
-Construction
requirement
-Functional
requirement
Aesthetic issue
in architectural work
Measurable attribute
Subjective attribute
Fig. 1. Quality evaluation in inspection processes.
161C. Laofor, V. Peansupap / Automation in Construction 24 (2012) 160–174



 maikel0maikel2014-06-18对视觉识别 有很大帮助,谢谢分享!
maikel0maikel2014-06-18对视觉识别 有很大帮助,谢谢分享! 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 
 前往需求广场,查看用户热搜
前往需求广场,查看用户热搜

 信息提交成功
信息提交成功